十二、MySQL系列
一、MySQL版本选择
MySQL:推荐使用5.6与5.7 关于5.6:选择GA版本,GA 6个月-1年之间的版本,5.6.38尽量选择双数版本 关于5.7:选择GA版本,GA 6个月-1年之间的版本,5.717以上,推荐使用5.7.20
二、Mysql安装

#1.下载:MySQL Community Server 5.7.20 https://downloads.mysql.com/archives/community/ #2.解压 将下载好的压缩包,解压到指定目录,如C:\mysql-5.7.20-winx64 #3.添加环境变量 【右键计算机】--》【属性】--》【高级系统设置】--》【高级】--》【环境变量】--》【在第二个内容框汇总找到 变量名为Path 的一行,双击】--》【将M有SQL的bin目录路径追加到变值中,用;分割】 #4、初始化 mysqld --initialize-insecure --explicit_defaults_for_timestamp #5、启动MySQL服务 mysqld #启动MySQL服务 #6、启动MySQL客户端并连接MySQL服务 mysql -u root -p #连接MySQL服务器

#1.在初始化时mysql --initialize-insecure报错? 报错提示:TIMESTAMP with implicit DEFAULT value is deprecated. Please use --explicit_defaults_for_timestamp server option (see documentation for more details) 解决办法:使用:mysql --initialize-insecure --explicit_defaults_for_timestamp #2.在mysqld --initialize-insecure --explicit_defaults_for_timestamp报错 报错提示:[ERROR] –initialize specified but the data directory has files in it. Aborting. 解决办法:删除安装目录下的data文件夹

在命令行里执【mysqld】启动MySQL服务器时,当前终端窗口会被hang住,那么将mysql设置为系统服务即可解决此问题: ps:--install前,必须用mysql启动命令的绝对路径 #制作MySQL的Windows服务,在终端执行命令: mysql-5.7.20-winx64\bin\mysqld --install #移除MySQL的Windows服务,在终端执行此命令: mysql-5.7.20-winx64\bin\mysqld --remove 注册成服务之后,以后在启动和关闭MySQ服务时,仅需执行如下命令: #启动MySQL服务 net start mysql #关闭MySQL服务 net stop mysql

Centos7 #1.下载MySQL官方的Yum Repository wget -i -c http://dev.mysql.com/get/mysql57-community-release-el7-10.noarch.rpm #2.yum 安装MySQL官方的Yum Repository yum -y install mysql57-community-release-el7-10.noarch.rpm #3.安装M有SQL服务器 yum -y install mysql-community-server #4.启动MySQL systemctl start mysqld.service #5.查看MySQL状态 systemctl status mysqld.service #6.通过日志文件找出默认密码,称为p1 grep "password" /var/log/mysqld.log #7.进入数据库命令 mysql -uroot -p
三、账号权限
#1.授权远程用户登陆权限 ##授权远程主机192.168.60.96通过用户名zabbix,密码password访问数据库zabbix里所有表权限 grant all PRIVILEGES on zabbix.* to zabbix@'192.168.60.96' identified by 'password'; #2.修改密码 ##此命令前提,是通过mysql -uroot -p进入,而不是通过在配置文件/etc/my.cnf,里新增跳过密码命令skip-grant-tables ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'new password';
四、库操作
4.1创建数据库
#1.语法 CREATE DATABASE 数据库名 charset utf8; #2. 数据库命名规则 ##可以由字母、数字、下划线、@、#、$ ##区分大小写 ##唯一性 ##不能使用关键字如 create select ##不能单独使用数字 ##最长128位
4.2数据库增删改查
#1.查看数据库 show databases; show create database db1; select database(); #2.选择数据库 USE 数据库名 #3. 删除数据库 DROP DATABASE 数据库名; #4.修改数据库 ALTER DATABASE 数据库名 charset utf8; #5.创建数据库 CREATE DATABASE 数据库名 charset utf8;
五、表操作
5.1 创建表
#1 语法 create table 表名( 字段名1 类型[(宽度) 约束条件], 字段名2 类型[(宽度) 约束条件], 字段名3 类型[(宽度) 约束条件] ); #2 注意事项 2.1在同一张表中,字段名不能相同 2.2宽度和约束条件可选 2.3字段名和类型是必须的
5.2 创建表代码示例

mysql> create table user_info(); ERROR 1064 (42000): mysql> create table user_info( -> id int, -> name varchar(50), -> sex enum('male','female'), -> age int(3) -> ); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.09 sec) mysql> show tables; +---------------+ | Tables_in_db1 | +---------------+ | user_info | +---------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> desc user_info; +-------+-----------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------+-----------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | id | int(11) | YES | | NULL | | | name | varchar(50) | YES | | NULL | | | sex | enum('male','female') | YES | | NULL | | | age | int(3) | YES | | NULL | | +-------+-----------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ 4 rows in set (0.01 sec)
5.3 往表中插入数据代码示例

#插入表中数据 mysql> insert into user_info values -> (1,'lisl','male',18), -> (2,'lvxq','female',28); Query OK, 2 rows affected (0.02 sec) mysql> mysql> mysql> mysql> select * from user_info; #查看表中数据 +------+------+--------+------+ | id | name | sex | age | +------+------+--------+------+ | 1 | lisl | male | 18 | | 2 | lvxq | female | 28 | +------+------+--------+------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql>
5.4 查看表结构

mysql> describe user_info; +-------+-----------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------+-----------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | id | int(11) | YES | | NULL | | | name | varchar(50) | YES | | NULL | | | sex | enum('male','female') | YES | | NULL | | | age | int(3) | YES | | NULL | | +-------+-----------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql>
5.5 表的数据类型
#1.数字 1.1整型:tinyint int bigint tinyint [(m)] [unsigned] [zerofill] 默认m为4 小整数,数据类型用于保存一些范围的整数数值范围: 有符号:-128~127 无符号:0~255 ps:MySQL中无布尔值,使用tinyint(1)构造 int [(m)] [unsigned] [zerofill] 整数,数据类型用于保存一些范围的整数数值范围: 有符号:-2147483648~2147483647 无符号:0 ~ 4294967295 bigint [(m)] [unsigned] [zerofill] 大整数,数据类型用于保存一些范围的整数数值范围: 有符号:-9223372036854775808 ~9223372036854775807 无符号:0 ~ 18446744073709551615 1.2 小数: float:在位数比较短的情况下不不精准 float[(M,D)] [UNSIGNED] [ZEROFILL] m是数字总个数,最大值为255;d是小数点后个数,d最大值为30 有符号:-3.402823466E+38 to -1.175494351E-38, 无符号:1.175494351E-38 to 3.402823466E+38 double:在位数比较长的情况下不精准 double[(M,D)] [UNSIGNED] [ZEROFILL] m是数字总个数,最大值为255;d是小数点后个数,d最大值为30 eg:0.000001230123123123,存成:0.000001230000 有符号:-1.7976931348623157E+308 to -2.2250738585072014E-308 无符号:2.2250738585072014E-308 to 1.79769313486231 decimal:(如果用小数,则用推荐使用decimal decimal [(m[,d])] [unsigned] [zerofill] m是数字总个数,最大值为65;d是小数点个数,d最大值为30 精准 内部原理是以字符串形式去存 #2. 字符串 char(10):10个字符长度,简单粗暴,浪费空间,存取速度快 存root 写入硬盘的时候是root000000 字符串长度范围:0 ~ 255 (一个中文是一个字符,是utf8编码的3个字节) 存储:存储char类型的值时,会往右填充空格来满足长度 例如:指定长度为10,存>10个字符则报错,存<10个字符则用空格填充直到凑够10个字符存储 检索:在检索或者说查询时,查出的结果会自动删除尾部的空格,除非我们打开pad_char_to_full_length SQL模式 (SET sql_mode = 'PAD_CHAR_TO_FULL_LENGTH';) varchar(10):精准,节省空间,存取速度慢 字符长度范围:0 ~ 65535(如果大于21845会提示用其他类型,mysql行最大限制65535字节,字符编码为utf-8) 存储:varchar类型存储数据的真实内容,不会用空格填充,如果'ab ',尾部的空格也会被存起来 强调:varchar类型会在真实数据前加1-2Bytes的前缀,该前缀用来表示真实数据的bytes字节数(1-2Bytes最 大表示65535个数字,正好符号mysql对row的最大字节限制,即已经足够使用) 如果真实的数据<255bytes则需要1Bytes的前缀(1Bytes=8bit 2**8最大表示的数字为255) 如果真实的数据>255bytes则需要2Bytes的前缀(2Bytes=16bit 2**16最大表示的数字为65535) 检索:尾部有空格会保存下来,在检索或者说查询时,也会正常显示包含空格在内的内容 sql优化:创建表时,定长的类型往前放,比如性别,变长的往后放,比如地址或描述信息 >255个字符,超了就把文件路径存放到数据库中,比如图片,视频等找一个文件服务器存放,数据库中只保存路径或url #3.时间类型 作用:存储用户注册时间,文章发布时间,员工入职时间,出生时间,过期时间等 最常用:datetime 在实际应用的很多场景中,MySQL的这俩种日期类型都能够满足我们的需要,存储精度都为秒,但在某些情况下,会展现出他们 各自的优劣。下面总结一下俩种日期类型的区别 1.DATATIME的日期范围1001-9999年,TIMESTAMP的时间范围是1970-2038年 2.DATATIME存储时间与时区无关,TIMESTAMP存储时间与时区有关,显示的值也依赖于时区。在mysql服务器,操作系统以及 客户端连接都有时区的设置。 3.DATATIME使用8字节的存储空间,TIMESTAMP的存储空间为4字节。因此,TIMESTAMP比DATATIME的空间利用率更高。 4.DATATIME的默认值为null;TIMESTAMP的字段默认不为空(not null),默认值为当前时间(CURRENT_TIMESTAMP), 如果不做特殊处理,并且update语句中没有指定该列的更新值,则默认更新为当前时间 #4.枚举类型与集合类型 字段的值只能在给定范围中选择,如单选框,多选框 enum单选只能在给定的范围内选一个值,如性别sex 男male/女female set 多选 在给定的范围内可以选择一个或一个以上的值(爱好1,爱好2,爱好3...) 以下在进行具体代码举例
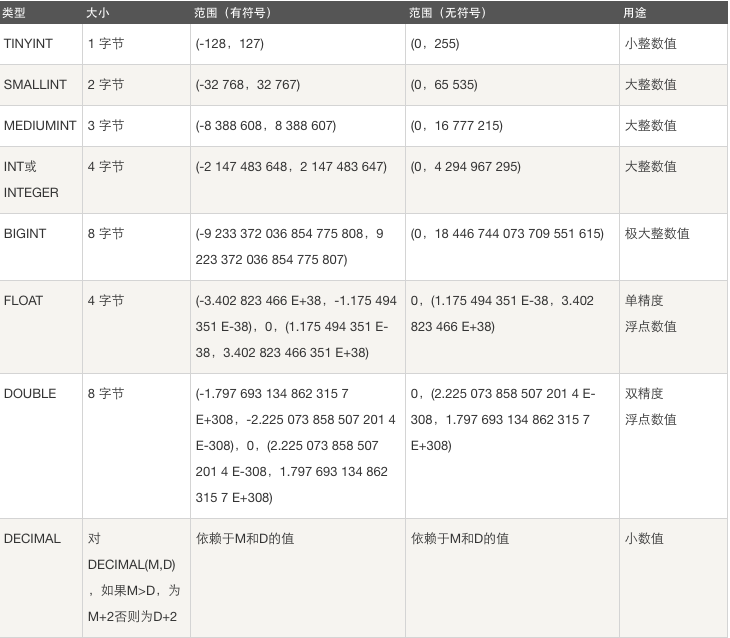
5.7 数据类型之整型代码示例

##########################tinyint类型########################## mysql> create table t1 (x tinyint); #创建表t1字段x为tinyint类型 Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.07 sec) mysql> desc t1; #查看表t1结构,默认为4 +-------+------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------+------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | x | tinyint(4) | YES | | NULL | | +-------+------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ 1 row in set (0.01 sec) #插入数据,数据-129报错,说明默认有符号,范围-128 ~ 127 mysql> insert into t1 values -> (128); ERROR 1264 (22003): mysql> insert into t1 values -> (-128), -> (-127), -> (127); Query OK, 3 row affected (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from t1; #查询数据 +------+ | x | +------+ | -128 | | -128 | | -127 | | 127 | +------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) #指定tinyint为无符号类型 mysql> create table t2 (x tinyint unsigned); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.07 sec) #值-1超出无符号范围,报错 mysql> insert into t2 values (-1); ERROR 1264 (22003): mysql> insert into t2 values -> (0), -> (255); Query OK, 2 rows affected (0.01 sec) #值256超出无符号范围,报错 mysql> insert into t2 values (256); ERROR 1264 (22003): mysql> mysql> mysql> desc t2; #查看表结构,默认是3,因为有1位是符号位 +-------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | x | tinyint(3) unsigned | YES | | NULL | | +-------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from t2; #查询数据 +------+ | x | +------+ | 0 | | 255 | +------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) ##########################int类型########################## mysql> create table t3 (x int); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.12 sec) mysql> desc t3; #默认长度为11 +-------+---------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------+---------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | x | int(11) | YES | | NULL | | +-------+---------+------+-----+---------+-------+ 1 row in set (0.01 sec) mysql> insert into t3 values (-2147483649); #超出有符号范围 ERROR 1264 (22003): mysql> insert into t3 values (-2147483648); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec) mysql> insert into t3 values (2147483647); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec) mysql> insert into t3 values (2147483648); #超出有符号范围 ERROR 1264 (22003): mysql> mysql> select * from t3; +-------------+ | x | +-------------+ | -2147483648 | | 2147483647 | +-------------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) #指定int为无符号类型 mysql> create table t4 (x int unsigned); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.10 sec) mysql> desc t4; +-------+------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------+------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | x | int(10) unsigned | YES | | NULL | | +-------+------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> mysql> mysql> mysql> insert into t4 values (-1); #超出有符号范围 ERROR 1264 (22003): mysql> insert into t4 values (0); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec) mysql> insert into t4 values (4294967295); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec) mysql> insert into t4 values (4294967296); #超出有符号范围 ERROR 1264 (22003): mysql> mysql> select * from t4; +------------+ | x | +------------+ | 0 | | 4294967295 | +------------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql>
5.8 数据类型之字符串代码示例

#对比char与varchar存储空间(存储大小不等同于显示大小) mysql> create table t2 (x char(5),y varchar(5)); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.11 sec) mysql> desc t2 -> ; +-------+------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------+------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | x | char(5) | YES | | NULL | | | y | varchar(5) | YES | | NULL | | +-------+------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ 2 rows in set (0.01 sec) mysql> insert into t2 values('yes ','yes '); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) mysql> select x,char_length(x),y,char_length(y) from t2; #char_length()表示字符个数,不管该字符是英文,中文,空格都算一个 +------+----------------+------+----------------+ | x | char_length(x) | y | char_length(y) | +------+----------------+------+----------------+ | yes | 3 | yes | 4 | +------+----------------+------+----------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> SET sql_mode = 'PAD_CHAR_TO_FULL_LENGTH'; #修改sql_mode,让char的显示的跟存储空间大小一致 Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.00 sec) mysql> select x,char_length(x),y,char_length(y) from t2; +-------+----------------+------+----------------+ | x | char_length(x) | y | char_length(y) | +-------+----------------+------+----------------+ | yes | 5 | yes | 4 | +-------+----------------+------+----------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select x,length(x),y,length(y) from t2; #length()表示显示bytes字节长度 +-------+-----------+------+-----------+ | x | length(x) | y | length(y) | +-------+-----------+------+-----------+ | yes | 5 | yes | 4 | +-------+-----------+------+-----------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql>

mysql> select concat('数据:',x,'长度:',char_length(x)),concat(y,char_length(y)) from t2; +------------------------------------------+--------------------------+ | concat('数据:',x,'长度:',char_length(x)) | concat(y,char_length(y)) | +------------------------------------------+--------------------------+ | 数据:yes 长度:5 | yes 4 | +------------------------------------------+--------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
5.8.1 CHAR与VARCAR相同点
虽然CHAR和VARCHAR的存储方式不太相同,但是对于两个字符串的比较,都只比较其值,忽略CAHR值存在的右填充,即使将SQL_MODE设置为PAD_CHAR_TO_FULL_LENGTH也一样,但不适用于like

#char在不同的sql_mode模式取值或者使用like的差别 mysql> create table t4 (name char(10)); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.04 sec) mysql> insert into t4 values ('Monty'); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec) mysql> select name = 'Monty',name = 'Monty ' from t4; #不管sql_mode模式,char被取值都可正常匹配到 +----------------+-------------------+ | name = 'Monty' | name = 'Monty ' | +----------------+-------------------+ | 1 | 1 | +----------------+-------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select name LIKE 'Monty' , name LIKE 'Monty' from t4; #当sql_mode = 'PAD_CHAR_TO_FULL_LENGTH',使用like,只有当"Monty "为10个字符,才可被匹配到 +--------------------+-------------------+ | name LIKE 'Monty' | name LIKE 'Monty' | +--------------------+-------------------+ | 0 | 0 | +--------------------+-------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> SET sql_mode ='' #修改sql_mode模式为空 -> ; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> select name LIKE 'Monty' , name LIKE 'Monty ' from t4; #当sql_mode='',空格会被自动去除,因此like可以匹配到Monty +--------------------+--------------------+ | name LIKE 'Monty' | name LIKE 'Monty ' | +--------------------+--------------------+ | 1 | 0 | +--------------------+--------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql>
5.8.2 关于字符串总结
#InnoDB存储引擎:建议使用VARCHAR类型 单从数据类型的实现机制去考虑,char数据类型的处理速度更快,有时甚至可以超出varchar处理速度的50% 但对于InnoDB数据表,内部的行存储格式没有区分固定长度和可变长度列(所有数据行都使用指向数据列值的头指针),因此在本质上,使用固定长度的CHAR列不一定比使用可变长度VARCHAR列性能要好。因而,主要的性能因素是数据行使用的存储总量。由于CHAR平均占用的空间多于VARCHAR,因此使用VARCHAR来最小化需要处理的数据行的存储总量和磁盘I/O是比较好的 #其他字符串系列(效率:char>varchar>text) TEXT系列 TINYTEXT TEXT MEDIUMTEXT LOGTEXT BLOB系列 TINYBLOB BLOB MEDIUMBLOB LONGBLOB BINARY系列 BINARY VARBINARY
5.9 时间类型代码示例

mysql> create table t5 (born_year year); #year的范围1901 ~ 2155 Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.04 sec) mysql> desc t5; +-----------+---------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-----------+---------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | born_year | year(4) | YES | | NULL | | +-----------+---------+------+-----+---------+-------+ 1 row in set (0.01 sec) mysql> insert into t5 values (1990),(1901),(2155),(2156); #2156超出范围,存储为000 Query OK, 4 rows affected, 1 warning (0.07 sec) Records: 4 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 1 mysql> select * from t5; +-----------+ | born_year | +-----------+ | 1990 | | 1901 | | 2155 | | 0000 | +-----------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> insert into t5 values (1900); #能插入,但是存储为000 Query OK, 1 row affected, 1 warning (0.01 sec) mysql> insert into t5 values (1901); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from t5 -> ; +-----------+ | born_year | +-----------+ | 1990 | | 1901 | | 2155 | | 0000 | | 0000 | | 1901 | +-----------+ 6 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql>
mysql> create table t6 (d date,t time, dt datetime); #date为日期 ;time为时间;datetime为日期+时间 Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.04 sec) mysql> desc t6; +-------+----------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------+----------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | d | date | YES | | NULL | | | t | time | YES | | NULL | | | dt | datetime | YES | | NULL | | +-------+----------+------+-----+---------+-------+ 3 rows in set (0.01 sec) mysql> insert into t6 values (now(),now(),now()); #显示当前日期,时间,日期+时间 Query OK, 1 row affected, 1 warning (0.01 sec) mysql> select * from t6; +------------+----------+---------------------+ | d | t | dt | +------------+----------+---------------------+ | 2018-07-15 | 10:04:42 | 2018-07-15 10:04:42 | +------------+----------+---------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> create table t7 (time timestamp); #时间戳 Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.04 sec) mysql> insert into t7 values(); #默认是当前时间,格式与datetime一样 Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec) mysql> insert into t7 values(null); #null也为当前时间 Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec) mysql> select * from t7; +---------------------+ | time | +---------------------+ | 2018-07-15 10:07:45 | | 2018-07-15 10:08:05 | +---------------------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
时间类型总结1
#1.单独插入时间时,需要以字符串的形式,按照对应的格式插入 #2.插入年份时,尽量使用4位值 #3.插入两位年份时,<=69,以20开头,比如50,结果2050 >=70,以19开头,比如71,结果1971 mysql> create table t8 (y year); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.04 sec) mysql> insert into t8 values (50),(71); Query OK, 2 rows affected (0.01 sec) Records: 2 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0 mysql> select * from t8; +------+ | y | +------+ | 2050 | | 1971 | +------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
时间类型总结2
在实际应用的很多场景中,MySQL的这两种日期类型都能够满足我们的需要,存储精度都为秒,但在某些情况下,会 展现出他们各自的优劣。下面就来总结一下两种日期类型的区别。 1.DATETIME的日期范围1001-9999年,TIMESTAMP的时间范围是1970-2038年 2.DATETIME存储时间与时区无关,TIMESTAMP存储时间与时区有关,显示的值也依赖于时区。在mysql服务器, 操作系统以及客户端连接都有时区的设置。 3.DATETIME使用8字节的存储空间,TIMESTAMP的存储空间为4字节。因此,TIMESTAMP比DATETIME空间利用 率更高 4.DATETIME的默认值为null;TIMESTAMP的字段默认不为空(not null),默认值为当前时间(CURRENT_TIMESTAMP), 如果不做特殊处理,并且update语句中没有指定该列的更新值,则默认更新为当前时间
mysql> create table t9 (update_time datetime not null default now()); #设置不为空,默认为当前时间
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.04 sec)
mysql> create table t10 (update_time timestamp); #不用设置,允许为空就是当前时间
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.03 sec)
mysql> insert into t9 values();
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> insert into t10 values();
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> select * from t9;
+---------------------+
| update_time |
+---------------------+
| 2018-07-15 10:27:52 |
+---------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from t10;
+---------------------+
| update_time |
+---------------------+
| 2018-07-15 10:27:58 |
+---------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
5.10 枚举类型代码举例

mysql> create table consumer( -> name varchar(50), -> sex enum('male','female'), -> level enum('vip1','vip2','vip3','黑卡'), #多选一 -> hobby set ('play','music','read','study') #多选多 -> ); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.04 sec) mysql> desc consumer; +-------+------------------------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------+------------------------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | name | varchar(50) | YES | | NULL | | | sex | enum('male','female') | YES | | NULL | | | level | enum('vip1','vip2','vip3','黑卡') | YES | | NULL | | | hobby | set('play','music','read','study') | YES | | NULL | | +-------+------------------------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ 4 rows in set (0.01 sec) mysql> insert into consumer values -> ('lisl','male','黑卡','play,read'), -> ('chenhong','female','vip1','gilr'); #'girl'不存在hobby里,警告,不报错,查询显示该字段为空 Query OK, 2 rows affected, 1 warning (0.01 sec) Records: 2 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 1 mysql> select * from consumer; +----------+--------+-------+-----------+ | name | sex | level | hobby | +----------+--------+-------+-----------+ | lisl | male | 黑卡 | play,read | | chenhong | female | vip1 | | +----------+--------+-------+-----------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql>
5.11 修改表ALTER TABLE
#语法 #1.修改表名 ALTER TABLE 表名 RENAME 新表名 #2.增加字段 ALTER TABLE 表名 ADD 字段名 数据类型 [完整性约束条件...], ADD 字段名 数据类型 [完整性约束条件...]; ALTER TABLE 表名 ADD 字段名 数据类型 [完整性约束条件...] FIRST; ALTER TABLE 表名 ADD 字段名 数据类型 [完整性约束条件...] AFTER 字段名; #3.删除字段 ALTER TABLE 表名 DROP 字段名; #4.修改字段 ALTER TABLE 表名 MODIFY 字段名 数据类型 [完整性约束条件...]; ALTER TABLE 表名 CHANGE 旧字段名 新字段名 旧数据类型 [完整性约束条件...]; ALTER TABLE 表名 CHANGE 旧字段名 新字段名 新数据类型[完整性约束条件...];

########################修改表名########################### mysql> alter table t1 rename t1111; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.03 sec) mysql> show tables; +---------------+ | Tables_in_db1 | +---------------+ | t1111 | | t2 | | t3 | | t4 | | t5 | | user_info | +---------------+ 6 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> mysql> desc t1111 -> ; +-------+------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------+------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | x | tinyint(4) | YES | | NULL | | +-------+------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) ########################增加字段########################### mysql> alter table t1111 add name varchar(15) not null; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.21 sec) mysql> alter table t1111 add id int FIRST; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.15 sec) mysql> alter table t1111 add host char(20) not null after id; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.20 sec) mysql> desc t1111 -> ; +-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | id | int(11) | YES | | NULL | | | host | char(20) | NO | | NULL | | | x | tinyint(4) | YES | | NULL | | | name | varchar(15) | NO | | NULL | | +-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) ########################修改字段########################### #修改id约束条件默认值0 mysql> alter table t1111 modify id int default 0; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec) mysql> desc t1111; +-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | id | int(11) | YES | | 0 | | | x | tinyint(4) | YES | | NULL | | | name | varchar(15) | NO | | NULL | | +-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) #修改id数据类型为char类型,没有默认值 mysql> alter table t1111 modify id char(10); Query OK, 4 rows affected (0.25 sec) mysql> desc t1111; +-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | id | char(10) | YES | | NULL | | | x | tinyint(4) | YES | | NULL | | | name | varchar(15) | NO | | NULL | | +-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) #修改字段x为computer_id mysql> alter table t1111 change x computer_id int default 0; Query OK, 4 rows affected (0.22 sec) mysql> desc t1111; +-------------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | id | char(10) | YES | | NULL | | | computer_id | int(11) | YES | | 0 | | | name | varchar(15) | NO | | NULL | | +-------------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from t1111; +------+-------------+------+ | id | computer_id | name | +------+-------------+------+ | NULL | -128 | | | NULL | -128 | | | NULL | -127 | | | NULL | 127 | | +------+-------------+------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
5.12 复制表
#复制表结构 + 记录 (key不会复制:主键、外键和索引) create table e2 select * from employees; #只复制表结构 #方法一:缺点(key不会复制:主键、外键和索引) mysql> create table e3 select * from employees where 1=2; //条件Wie假,查不到任何记录 #方法二 :优点(完整复制表结构) create table e4 like employees;

#复制表结构+记录 #查看原表 mysql> desc employees; +-------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment | | name | char(15) | NO | | NULL | | +-------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from employees; +----+----------+ | id | name | +----+----------+ | 1 | lisl | | 2 | zhangsan | +----+----------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) #复制原表的表结构和记录,无法复制表结构中的主键,外键,递增id,并设置默认值为0 mysql> create table e2 select * from employees; Query OK, 2 rows affected (0.10 sec) mysql> desc e2; +-------+----------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------+----------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | id | int(11) | NO | | 0 | | | name | char(15) | NO | | NULL | | +-------+----------+------+-----+---------+-------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from e2; +----+----------+ | id | name | +----+----------+ | 1 | lisl | | 2 | zhangsan | +----+----------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) #只复制表结构一 mysql> create table e3 select * from employees where 1=2; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.08 sec) mysql> desc e3; +-------+----------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------+----------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | id | int(11) | NO | | 0 | | | name | char(15) | NO | | NULL | | +-------+----------+------+-----+---------+-------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) #只复制表结构二 mysql> create table e4 like employees; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.08 sec) mysql> desc e4; +-------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment | | name | char(15) | NO | | NULL | | +-------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from e4; Empty set (0.00 sec)
5.13 删除表
DROP TABLE 表名 mysql> drop table e4;
六、完整性约束
6.1介绍
约束条件与数据类型的宽度一样,都是可选参数 作用:用于保证数据的完整性和一致性 主要分为: PRIMARY KEY (PK) 标识该字段为该表的主键,,可以唯一的标识记录 foreign key (FK) 标识该字段Wie该表的外键 not null 标识字段不能为空 unique key (uk) 标识该字段的值是唯一的 auto_increment 标识该字段的值自动增长(整数类型,而且为主键) default 为该字段设置默认值 unsigned 无符号 zerofill 使用0 填充
6.2 各个约束条件示例集锦

##################not null############################# #在linux下操作:(windows下默认是0) mysql> create table t5 (id int not null); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.08 sec) mysql> desc t5; +-------+---------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------+---------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | id | int(11) | NO | | NULL | | +-------+---------+------+-----+---------+-------+ 1 row in set (0.01 sec) mysql> insert into t5 values (); #为空报错 ERROR 1364 (HY000): ##################default############################# #设置age字段有默认值后,无论age字段是null还是not null,都可以插入空 #插入空默认填入default指定值 mysql> create table t12 (age int default 18); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.04 sec) mysql> insert into t12 values(); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec) mysql> desc t12; +-------+---------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------+---------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | age | int(11) | YES | | 18 | | +-------+---------+------+-----+---------+-------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from t12; +------+ | age | +------+ | 18 | +------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) ##################unique############################# mysql> create table t13 (id int unique); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.05 sec) mysql> insert into t13 values(100); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec) mysql> insert into t13 values(100); #不能重复,否则报错 ERROR 1062 (23000): Duplicate entry '100' for key 'id' mysql> select * from t13 -> ; +------+ | id | +------+ | 100 | +------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) #联合唯一 mysql> create table t14 (ip char(20),port int,unique(ip,port)); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.05 sec) mysql> insert into t14 values('127.0.0.1',3306); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec) mysql> insert into t14 values('127.0.0.1',3307); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec) mysql> insert into t14 values('127.0.0.1',3306); ERROR 1062 (23000): Duplicate entry '127.0.0.1-3306' for key 'ip' mysql> select * from t14; +-----------+------+ | ip | port | +-----------+------+ | 127.0.0.1 | 3306 | | 127.0.0.1 | 3307 | +-----------+------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) ##################primary key############################# #定义主键的三种方法: #单列做主键方法 ##方法一:not null + unique mysql> create table t1 ( -> id int not null unique, #成为主键 -> name varchar(20) not null unique, #已经有主键了,因此依然是not null 和unique -> comment varchar(100) -> ); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.08 sec) mysql> show tables; +---------------+ | Tables_in_db2 | +---------------+ | t1 | +---------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> desc t1; +---------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +---------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | | | name | varchar(20) | NO | UNI | NULL | | | comment | varchar(100) | YES | | NULL | | +---------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) ##方法二:在某一个字段后用primary key mysql> create table t2 ( -> id int primary key, #设置为主键 -> name varchar(20), -> comment varchar(100) -> ); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.05 sec) mysql> desc t2; +---------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +---------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | | | name | varchar(20) | YES | | NULL | | | comment | varchar(100) | YES | | NULL | | +---------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) ##方法三:在所有字段后单独定义primary key mysql> create table t4 ( -> id int, -> name varchar(20), -> comment varchar(100), -> constraint pk_name primary key(id)); #创建id为主键,并命名为pk_name Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.06 sec) mysql> desc t4; +---------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +---------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | | | name | varchar(20) | YES | | NULL | | | comment | varchar(100) | YES | | NULL | | +---------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) #多列做主键 mysql> create table t5 ( -> ip varchar(15), -> port char(5), -> service_name varchar(10) not null, -> primary key(ip,port) #并列ip-port为主键 -> ); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.06 sec) mysql> desc t5; +--------------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +--------------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | ip | varchar(15) | NO | PRI | NULL | | | port | char(5) | NO | PRI | NULL | | | service_name | varchar(10) | NO | | NULL | | +--------------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> insert into t5 values -> ('127.0.0.1','3306','mysqld'), -> ('127.0.0.1','8080','http') -> ; Query OK, 2 rows affected (0.02 sec) mysql> insert into t5 values ('127.0.0.1','3306','nginx'); #ip_port已存在 ERROR 1062 (23000): Duplicate entry '127.0.0.1-3306' for key 'PRIMARY' ##################auto_increment############################# #自增id mysql> create table t6 ( -> id int primary key auto_increment, -> name varchar(20), -> sex enum('male','female') default 'male' -> ); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.07 sec) mysql> desc t6; +-------+-----------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------+-----------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment | | name | varchar(20) | YES | | NULL | | | sex | enum('male','female') | YES | | male | | +-------+-----------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> insert into t6(name) values -> ('lisl'), -> ('lvq') -> ; Query OK, 2 rows affected (0.02 sec) mysql> select * from t6; +----+------+------+ | id | name | sex | +----+------+------+ | 1 | lisl | male | | 2 | lvq | male | +----+------+------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) ##################foreign key############################# #外键:多对一,在多的这张表设置外键关联一的那张表 mysql> create table department( -> id int primary key, -> name varchar(20) not null -> )engine=innodb; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.07 sec) mysql> create table employee( -> id int primary key, -> name varchar(20) not null, -> dpt_id int, -> constraint fk_name foreign key(dpt_id) references department(id) on delete cascade on update cascade #设置外键,更新与删除原表操作会同步到外键表 -> )engine=innodb; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.07 sec) #插入部门表数据 mysql> insert into department values -> (1,'HR'), -> (2,'Sale'), -> (3,'IT'); Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.01 sec) #插入员工表数据 mysql> insert into employee values -> (1,'lisl',1), -> (2,'lvx',2), -> (3,'hsy',2), -> (4,'wcx',3) -> ; Query OK, 4 rows affected (0.02 sec) #查询员工表数据 mysql> select * from employee; +----+------+--------+ | id | name | dpt_id | +----+------+--------+ | 1 | lisl | 1 | | 2 | lvx | 2 | | 3 | hsy | 2 | | 4 | wcx | 3 | +----+------+--------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) #查询部门表数据 mysql> select * from department; +----+------+ | id | name | +----+------+ | 1 | HR | | 2 | Sale | | 3 | IT | +----+------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) #删除部门表id=3的部门,员工表与该部门相关的也随之被删除同步 mysql> delete from department where id=3; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec) mysql> select * from department; +----+------+ | id | name | +----+------+ | 1 | HR | | 2 | Sale | +----+------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from employee; +----+------+--------+ | id | name | dpt_id | +----+------+--------+ | 1 | lisl | 1 | | 2 | lvx | 2 | | 3 | hsy | 2 | +----+------+--------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) #更新部门表id=2为2222,员工表对应的部门id也随之更新同步 mysql> update department set id=2222 where id=2; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.02 sec) mysql> select *from employee; +----+------+--------+ | id | name | dpt_id | +----+------+--------+ | 1 | lisl | 1 | | 2 | lvx | 2222 | | 3 | hsy | 2222 | +----+------+--------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> ##################多对多############################# #作者表与书表属于多对多关系,即额外在构建一张author2book表,关联俩个字段外键(author_id,book_id) #创建作者表 mysql> create table author( -> id int primary key auto_increment, -> name varchar(20) -> ); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.07 sec) #创建书表 mysql> create table book( -> id int primary key auto_increment, -> name varchar(20) -> ); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.07 sec) #创建作者与书多对多关系的author2book表 mysql> create table author2book( -> id int not null unique auto_increment, -> author_id int not null, -> book_id int not null, -> constraint fk_author foreign key(author_id) references author(id) -> on delete cascade -> on update cascade, -> constraint fk_book foreign key(book_id) references book(id) -> on delete cascade -> on update cascade, -> primary key(author_id,book_id) -> ); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.06 sec) #添加作者表数据 mysql> insert into author(name) values('lisl'),('lxq'),('wcx'); Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.02 sec) #添加书表数据 mysql> insert into book(name) values('python'),('linux'),('network'); Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.01 sec) #关联作者与书的关系 mysql> insert into author2book(author_id,book_id) values -> (1,1), -> (1,2), -> (2,3), -> (2,2); Query OK, 4 rows affected (0.01 sec) mysql> select * from author2book -> ; +----+-----------+---------+ | id | author_id | book_id | +----+-----------+---------+ | 1 | 1 | 1 | | 2 | 1 | 2 | | 3 | 2 | 3 | | 4 | 2 | 2 | +----+-----------+---------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from author; +----+------+ | id | name | +----+------+ | 1 | lisl | | 2 | lxq | | 3 | wcx | +----+------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from book; +----+---------+ | id | name | +----+---------+ | 1 | python | | 2 | linux | | 3 | network | +----+---------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) ##################一对一############################# #客户表与学生表 #学生一定来自于客户,一对一,外键关联客户表 #客户不一定是学生 #创建客户表 mysql> create table customer( -> id int primary key auto_increment, -> name varchar(20) not null, -> qq varchar(10) not null, -> phone char(16) not null -> ); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.06 sec) #创建学生表 mysql> create table student( -> id int primary key auto_increment, -> class_name varchar(20) not null, -> customer_id int unique, #保证属于客户是唯一 -> foreign key(customer_id) references customer(id) #关联外键 -> on delete cascade -> on update cascade -> ); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.06 sec) #插入客户表哦数据 mysql> insert into customer(name,qq,phone) values -> ('lisl','6666',18233882288), -> ('lxq','8888',13611112222); Query OK, 2 rows affected (0.01 sec) #插入学生表数据 mysql> insert into student(class_name,customer_id) values -> ('python class',1); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec) mysql> select * from customer; +----+------+------+-------------+ | id | name | qq | phone | +----+------+------+-------------+ | 1 | lisl | 6666 | 18233882288 | | 2 | lxq | 8888 | 13611112222 | +----+------+------+-------------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from student; +----+--------------+-------------+ | id | class_name | customer_id | +----+--------------+-------------+ | 1 | python class | 1 | +----+--------------+-------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql>
七、数据操作
6.1 插入数据
#1.插入完整数据(顺序插入) 语法一: INSERT INTO 表名(字段1,字段2,字段3...字段n) VALUES(值1,值2,值3,...值n); 语法二: INSERT INTO 表名 VALUES (值1,值2,值3,...值n) #2.指定字段插入数据 语法: INSERT INTO 表名(字段1,字段3,字5,...) VALUES (值1,值3,值5,..) #3.插入多条记录 语法: INSERT INTO 表名 VALUES (值1,值2,值3,...值n), (值1,值2,值3,...值n), (值1,值2,值3,...值n); #4.插入查询结果 语法: INSERT INTO 表名(字段1,字段2,字段3,...字段n) SELECT (字段1,字段2,字段3,...字段n) FROM 表2 WHERE ...; eg: #将book表里的id=3的条目的name字段,插入到book表里 insert into book(name) select name from book where id=3;
6.2 删除数据
语法: DELETE FROM 表名 WHERE condition; #删出的数据,不会影响原本的自增id顺序 eg: #删除id=2的数据 delete from book where id =2;
6.3修改数据
语法: UPDATE 表名 SET 字段1=值1,字段2=值2,where condition; eg: #修改mysqlroot密码 update mysql.user set authentication_string=password('123456') where User='root'; flush privileges; #刷新权限
6.4查询数据
八、pymysql模块使用
8.1 安装
pip3 install pymysql
8.2 数据库数据信息
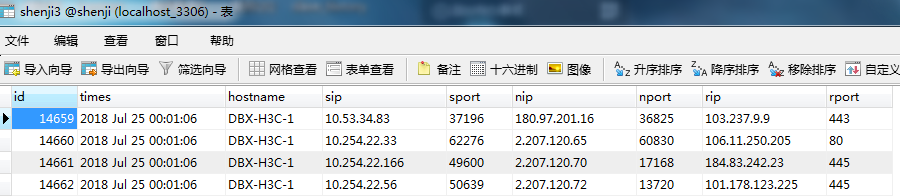
8.3 pymysql模块常规使用
import pymysql sip='10.53.34.83' sport='37196' #链接 conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1',user='root',password='123456',database='shenji',charset='utf8') #获取游标 cursor=conn.cursor() #执行完毕返回的结果集默认已元组显示 cursor=conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) #以字典形式返回 #执行sql语句,(此方法有安全隐患) sql='select * from shenji3 where sip="%s" and sport="%s"'%(sip,sport) print(sql) res=cursor.execute(sql) #执行sql语句,返回sql查询成功的记录 print(res) cursor.close() conn.close() if res: print('登录成功') else: print('登录失败')
8.4 execute()之sql注入
注意:注意--会注释掉它之后的sql,正确的语法:--后至少有一个任意字符 sql注入根本原理:根据程序的字符串拼接name='%s',我们输入一个xxx' --haha,用我们输入的xxx加‘在程序中拼接成一个判断条件name='xxx' --haha' 最后那一个空格,在一条sql语句中如果遇到select * from t1 where id > 3 -- and name='lisl';则--之后的条件被注释掉了



