记一次SpringBoot国际化原理分析
关键字:LocaleContextHolder、LocaleContext、LocaleResolver
第一步:Web服务器第一次接收请求时会初始化国际化策略
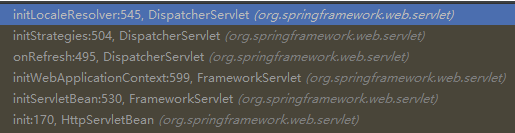
DispatcherServlet初始化
/**
* 初始化
*/
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
initMultipartResolver(context);
//重点初始化国际化
initLocaleResolver(context);
initThemeResolver(context);
initHandlerMappings(context);
initHandlerAdapters(context);
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
initViewResolvers(context);
initFlashMapManager(context);
}
/**
* 给DispatcherServlet属性localeResolver赋值
* 便于后续每次请求使用,可以自定义LocaleResolver的实现类
*/
private void initLocaleResolver(ApplicationContext context) {
try {
//从spring容器中获取LocaleResolver的实例(自定义的话要重写这个接口,并将其注册到Spring,注意bean的名字:localeResolver)
//LOCALE_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME为DispatcherServlet#LOCALE_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME = "localeResolver";
this.localeResolver = context.getBean(LOCALE_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME, LocaleResolver.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Detected " + this.localeResolver);
}
else if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Detected " + this.localeResolver.getClass().getSimpleName());
}
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// We need to use the default.
this.localeResolver = getDefaultStrategy(context, LocaleResolver.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No LocaleResolver '" + LOCALE_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME +
"': using default [" + this.localeResolver.getClass().getSimpleName() + "]");
}
}
}
this.localeResolver赋值是关键一步,下面我们自定义一个LocaleResolver实现类MessageLocaleResolver:
特别注意:请求头中传的值是zh-CN,不是下划线zh_CN
重要说三遍:
是zh-CN不是zh_CN
是zh-CN不是zh_CN
是zh-CN不是zh_CN
.......
/**
* 国际化解析器
* bean的名字必须为localeResolver
* @author 匿名者
* @since 2021-01-24
* @see DispatcherServlet#LOCALE_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME
* @see DispatcherServlet#initLocaleResolver(org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext)
* @see Request#getLocale()
*/
public class MessageLocaleResolver implements LocaleResolver {
private String localeHeader = "locale";
@Override
public Locale resolveLocale(HttpServletRequest request) {
//从请求头中获取语言标识,类似zh-CN,注意中间要用"-"
String language = request.getHeader(localeHeader);
//当为空时,采用默认的
if(StringUtils.isBlank(language)) {
return Locale.getDefault();
}
Locale locale = Locale.forLanguageTag(language);
return locale;
}
@Override
public void setLocale(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Locale locale) {
}
第二步:后续每次请求都会调用 buildLocaleContext(request);
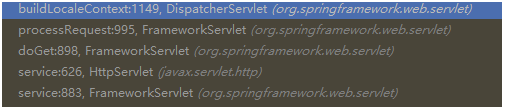
1、将“第一步”得到的this.localeResolver(自定义MessageLocaleResolver的实例),调用其resolveLocale方法返回LocaleContext(函数式接口)对象
注意:每次请求都会调用MessageLocaleResolver#resolveLocale,然后将LocaleContext放入LocaleContextHolder中
/**
* this.localeResolver已经被第一步赋值,即this.localeResolver等于spring中实现LocaleResolver接口的实例
*/
@Override
protected LocaleContext buildLocaleContext(final HttpServletRequest request) {
LocaleResolver lr = this.localeResolver;
if (lr instanceof LocaleContextResolver) {
return ((LocaleContextResolver) lr).resolveLocaleContext(request);
}
else {
//调用自定义LocaleResolver的实现类resolveLocale方法,从请求中获取国际化标识
return () -> (lr != null ? lr.resolveLocale(request) : request.getLocale());
}
}
2、将上一步方法返回的LocaleContext放入LocaleContextHolder中,LocaleContextHolder内部有两个ThreadLocal属性,所以同一个请求所在线程都可以通过LocaleContextHolder.getLocale()方法获取当前国际化标识
LocaleContextHolder类的两个属性
private static final ThreadLocal
//子类可以获取ThreadLocal中值
private static final ThreadLocal
上述方法调用流程如下(每次请求都会调用):
protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Throwable failureCause = null;
LocaleContext previousLocaleContext = LocaleContextHolder.getLocaleContext();
//********调用org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet#buildLocaleContext,返回LocaleContext(返回的是函数式接口的实现)
LocaleContext localeContext = buildLocaleContext(request);
RequestAttributes previousAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = buildRequestAttributes(request, response, previousAttributes);
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptor(FrameworkServlet.class.getName(), new RequestBindingInterceptor());
//**********将buildLocaleContext方法返回的localeContext,放入LocaleContextHolder上下文中
initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes);
try {
doService(request, response);
}
catch (ServletException | IOException ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw new NestedServletException("Request processing failed", ex);
}
finally {
resetContextHolders(request, previousLocaleContext, previousAttributes);
if (requestAttributes != null) {
requestAttributes.requestCompleted();
}
logResult(request, response, failureCause, asyncManager);
publishRequestHandledEvent(request, response, startTime, failureCause);
}
}
最后:国际化标识使用:
1、配置文件:指定国际化文件所在目录
spring:
messages:
basename: i18n/messages
2、编写根据编号获取具体国际化内容(一般在全局异常处理时根据异常code获取相应的国际化信息返回给前端)
/**
* 获取国际化信息
* @author 匿名者
* @since 2021-01-12
*/
public class MessageSourceHolder {
@Autowired
private MessageSource messageSource;
/**
* 根据编号获取
* @param code
* @return
*/
public String getMessage(String code) {
return messageSource.getMessage(code, null,LocaleContextHolder.getLocale());
}
/**
* 根据编号获取,并解析占位符
* @param code
* @param args
* @return
*/
public String getMessage(String code, Object[] args) {
return messageSource.getMessage(code, args,LocaleContextHolder.getLocale());
}
}
上述简单介绍了国际化的语言识别流程,大家可根据需要自己定制localeResolver,如果有发现问题,请及时告知



