Vue2入门之超详细教程九-监视属性
1、简介
监视属性watch:
1.当被监视的属性变化时,回调函数自动调用,进行相关操作
2.监视的属性必须存在,才能进行监视!!
3.监视的两种写法:
(1) new Vue时传入watch配置
(2) 通过vm.$watch监视
深度监测:
(1) Vue中的watch默认不监测对象内部值的改变(一层)
(2) 配置deep:true可以监测对象内部值改变(多层)
备注:
(1) Vue自身可以监测对象内部值的改变,但Vue提供的watch默认不可以
(2) 使用watch时根据数据的具体结构,决定是否采用深度监视
学习Vue之前最后会一些HTML和CSS的基础知识,HTML基础知识 传送门,CSS基础知识 传送门。
2、监视属性
1. 天气案例
在vscode中创一个新目录,叫“08_监视属性”,在下面创建一个“1_计算属性方式实现.html”文件,在里面输入以下代码:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Document</title> <script type="text/javascript" src="../js/development/vue.js"></script> </head> <body> <div id="root"> <h2>今天天气很{{info}}</h2> <button @click="changeWeather">切换天气</button> </div> <script type="text/javascript"> Vue.config.douctionTip = false new Vue({ el:'#root', data:{ isHot:true }, computed:{ info(){ return this.isHot ? '炎热':'凉爽' } }, methods:{ changeWeather(){ this.isHot = !this.isHot } } }) </script> </body> </html>
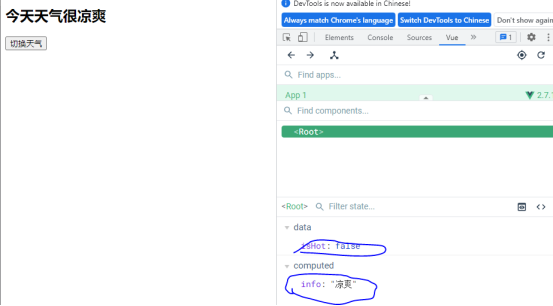
该案例,当点击按钮时,会调用changeWeather方法,赋值isHot为isHot的取反的值
2. 监视属性
第一种写法
可以监视Vue中的属性,当发生变化时会被调用
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Document</title> <script type="text/javascript" src="../js/development/vue.js"></script> </head> <body> <div id="root"> <h2>今天天气很{{info}}</h2> <button @click="changeWeather">切换天气</button> </div> <script type="text/javascript"> Vue.config.douctionTip = false new Vue({ el:'#root', data:{ isHot:true }, computed:{ info(){ return this.isHot ? '炎热':'凉爽' } }, methods:{ changeWeather(){ this.isHot = !this.isHot } }, watch:{ isHot:{ //初始化时立即调用一下 // immediate:true, //handler什么时候调用?当IsHot发生改变时被调用,可以接收两个值,第一个为修改后,第二个为修改前 handler(newValue,oldValue){ console.log('isHot被修改该了',newValue,oldValue) } } } }) </script> </body> </html>
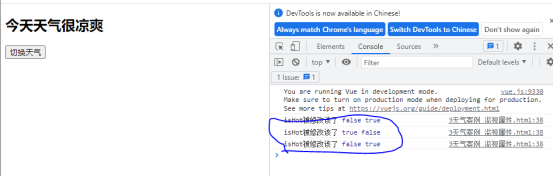
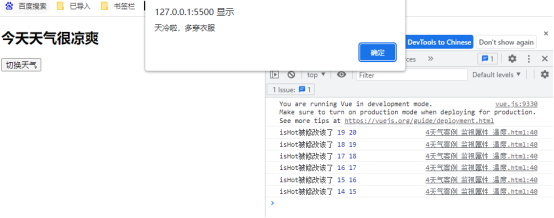
使用场景:比如当气温低于15度是时,提醒多穿衣服:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Document</title> <script type="text/javascript" src="../js/development/vue.js"></script> </head> <body> <div id="root"> <h2>今天天气很{{info}}</h2> <button @click="changeWeather">切换天气</button> </div> <script type="text/javascript"> Vue.config.douctionTip = false new Vue({ el:'#root', data:{ isHot:true, temperature:20 }, computed:{ info(){ return this.isHot ? '炎热':'凉爽' } }, methods:{ changeWeather(){ this.isHot = !this.isHot this.temperature-- } }, watch:{ temperature:{ //初始化时立即调用一下 // immediate:true, //handler什么时候调用?当IsHot发生改变时被调用,可以接收两个值,第一个为修改后,第二个为修改前 handler(newValue,oldValue){ console.log('isHot被修改该了',newValue,oldValue) if(newValue < 15){ alert('天冷啦,多穿衣服') } } } } }) </script> </body> </html>
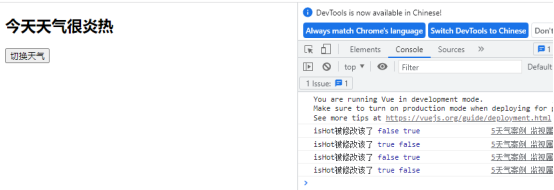
第二种写法
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Document</title> <script type="text/javascript" src="../js/development/vue.js"></script> </head> <body> <div id="root"> <h2>今天天气很{{info}}</h2> <button @click="changeWeather">切换天气</button> </div> <script type="text/javascript"> Vue.config.douctionTip = false const vm = new Vue({ el:'#root', data:{ isHot:true }, computed:{ info(){ return this.isHot ? '炎热':'凉爽' } }, methods:{ changeWeather(){ this.isHot = !this.isHot } }, }) vm.$watch('isHot',{ handler(newValue,oldValue){ console.log('isHot被修改该了',newValue,oldValue) } }) </script> </body> </html>
3. 深度监视
以上监测都是针对一级属性监测,当存在多级属性时如何进行检测呢?
多级监测
比如:numbers属性下存在两个属性a和b,我们只针对a变动做检测
再使用以上方式就不可以了,这会必须使用’numbers.a’这种方式,注意这里不能直接简写为numbers.a必须用引号引起来,完整代码如下:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Document</title> <script type="text/javascript" src="../js/development/vue.js"></script> </head> <body> <div id="root"> <h2>今天天气很{{info}}</h2> <button @click="changeWeather">切换天气</button> <hr> <h3>a的值是{{numbers.a}}</h3> <button @click="numbers.a++">点我让a+1</button> </div> <script type="text/javascript"> Vue.config.douctionTip = false new Vue({ el:'#root', data:{ isHot:true, numbers:{ a:1, b:1 } }, computed:{ info(){ return this.isHot ? '炎热':'凉爽' } }, methods:{ changeWeather(){ this.isHot = !this.isHot } }, watch:{ 'numbers.a':{ //handler什么时候调用?当IsHot发生改变时被调用,可以接收两个值,第一个为修改后,第二个为修改前 handler(newValue,oldValue){ console.log('a被改变了',newValue,oldValue) } } } }) </script> </body> </html>
深度监测
以上面代码为例,如果想a或者b任意一个发生变化时都可以监测到,你可能想可以这样写:
watch:{
'numbers':{
handler(newValue,oldValue){
console.log('numbers被改变了',newValue,oldValue)
}
}
}
明确告诉大家,这样是不可以的,如下图,这样写只会监测粉色线中的部分,并不会监测绿色内的部分
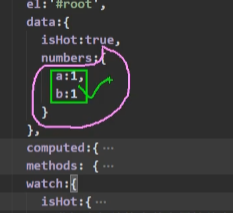
像这种方式我们只需要加一个配置即可:
deep:true,
完整代码如下:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Document</title> <script type="text/javascript" src="../js/development/vue.js"></script> </head> <body> <div id="root"> <h2>今天天气很{{info}}</h2> <button @click="changeWeather">切换天气</button> <hr> <h3>a的值是{{numbers.a}}</h3> <button @click="numbers.a++">点我让a+1</button> <hr> <h3>b的值是{{numbers.b}}</h3> <button @click="numbers.b++">点我让b+1</button> <button @click="numbers={a:111,b:222}">彻底替换掉numbers</button> </div> <script type="text/javascript"> Vue.config.douctionTip = false new Vue({ el:'#root', data:{ isHot:true, numbers:{ a:1, b:1 } }, computed:{ info(){ return this.isHot ? '炎热':'凉爽' } }, methods:{ changeWeather(){ this.isHot = !this.isHot } }, watch:{ 'numbers':{ deep:true, handler(newValue,oldValue){ console.log('numbers被改变了',this.numbers.a,this.numbers.b) } } } }) </script> </body> </html>
4. 监测属性的简写形式
Vue中简写形式
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Document</title> <script type="text/javascript" src="../js/development/vue.js"></script> </head> <body> <div id="root"> <h2>今天天气很{{info}}</h2> <button @click="changeWeather">切换天气</button> </div> <script type="text/javascript"> Vue.config.douctionTip = false new Vue({ el:'#root', data:{ isHot:true, numbers:{ a:1, b:1 } }, computed:{ info(){ return this.isHot ? '炎热':'凉爽' } }, methods:{ changeWeather(){ this.isHot = !this.isHot } }, watch:{ //正常写法 // 'isHot':{ // //immediate:true, //初始化时让handler调用一下 // //deep:true, //深度监视 // handler(newValue,oldValue){ // console.log('isHot被改变了',this.numbers.a,this.numbers.b) // } // } //简写形式 isHot(){ console.log('isHot被改变了',this.numbers.a,this.numbers.b) } } }) </script> </body> </html>
vm.$watch中简写形式
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Document</title> <script type="text/javascript" src="../js/development/vue.js"></script> </head> <body> <div id="root"> <h2>今天天气很{{info}}</h2> <button @click="changeWeather">切换天气</button> </div> <script type="text/javascript"> Vue.config.douctionTip = false const vm = new Vue({ el:'#root', data:{ isHot:true, numbers:{ a:1, b:1 } }, computed:{ info(){ return this.isHot ? '炎热':'凉爽' } }, methods:{ changeWeather(){ this.isHot = !this.isHot } }, }) //正常写法 // vm.$watch('isHot',{ // immediate:true, // deep:true, // handler(newValue,oldValue){ // console.log('isHot被修改了',newValue,oldValue) // } // }) //简写方式 vm.$watch('isHot',function(newValue,oldValue){ console.log('isHot被修改了',newValue,oldValue) }) </script> </body> </html>
3、测试
我们来检测一个不存在的属性’123’来看看效果
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Document</title> <script type="text/javascript" src="../js/development/vue.js"></script> </head> <body> <div id="root"> <h2>今天天气很{{info}}</h2> <button @click="changeWeather">切换天气</button> </div> <script type="text/javascript"> Vue.config.douctionTip = false const vm = new Vue({ el:'#root', data:{ isHot:true }, computed:{ info(){ return this.isHot ? '炎热':'凉爽' } }, methods:{ changeWeather(){ this.isHot = !this.isHot } }, }) vm.$watch('123',{ handler(newValue,oldValue){ console.log('isHot被修改该了',newValue,oldValue) } }) </script> </body> </html>
以上代码的效果为,正常执行,也不会报错,但不会监视到内容,所以也不会执行监视内部的代码
4、小结
如果只要要监视的属性,可以直接在new Vue中写
不确定要监视的属性,可以使用vm.$watch()方式
多级监测属性时,不能使用简写方式,必须用引号引起来
深度监测属性时,需要加一个配置:deep:true
当需要使用immediate或deep等配置是,不能使用监测属性的简写形式




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· C#/.NET/.NET Core技术前沿周刊 | 第 29 期(2025年3.1-3.9)
· 从HTTP原因短语缺失研究HTTP/2和HTTP/3的设计差异