74--JT项目12(Redis缓存/spring boot整合redis)
1.还原系统配置
1.1 释放Linux资源
1.1.1 停止数据库主从服务
stop slave;
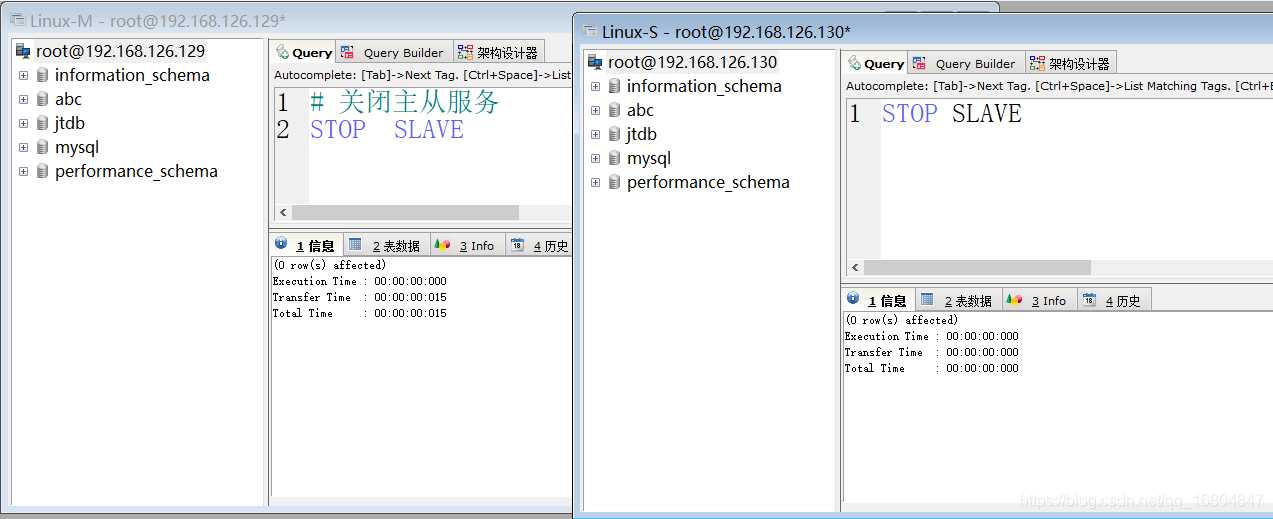
1.1.2 关闭数据库服务
说明:关闭主从数据库服务器.
命令: systemctl stop mariadb
1.1.3 关闭tomcat/mycat服务器
关闭tomcat : kill -9 pid
关闭mycat : kill -9 pid
1.1.4关闭nginx服务器
./nginx -s stop
1.2 修改代码中的配置
1.2.1 修改YML配置文件
说明:切换端口号和url地址.
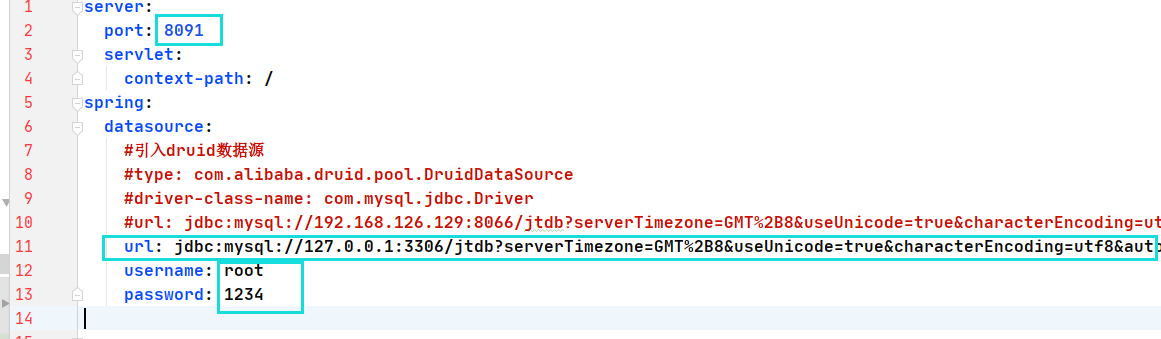
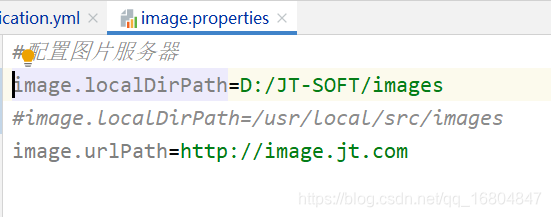
1.2.2 修改图片上传地址
1.3 修改环境配置
1.3.1 修改hosts文件
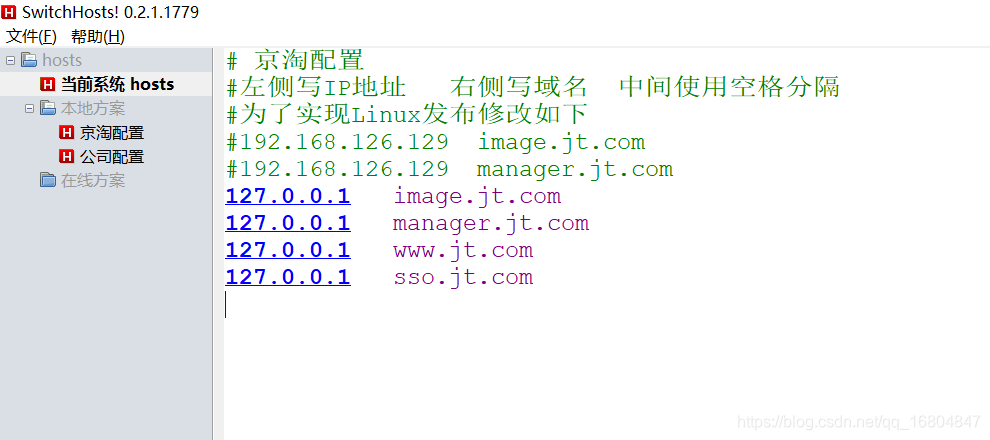
1.3.2 修改windows中的Nginx
修改完成之后,启动nginx服务器.
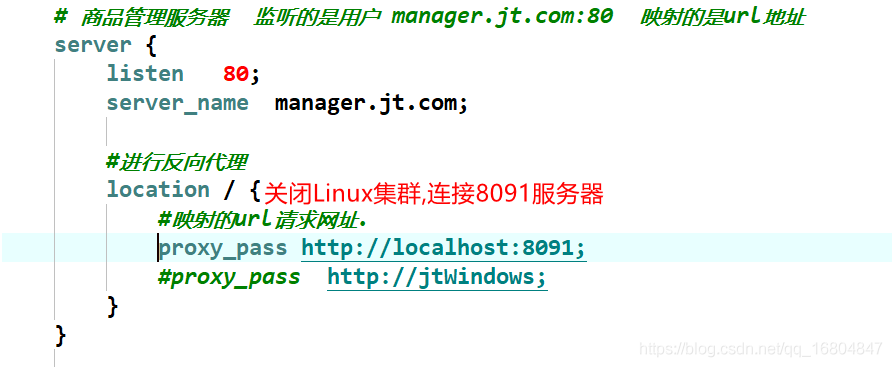
启动命令:进入到nginx的根目录下,执行以下命令
start nginx
nginx -s reload
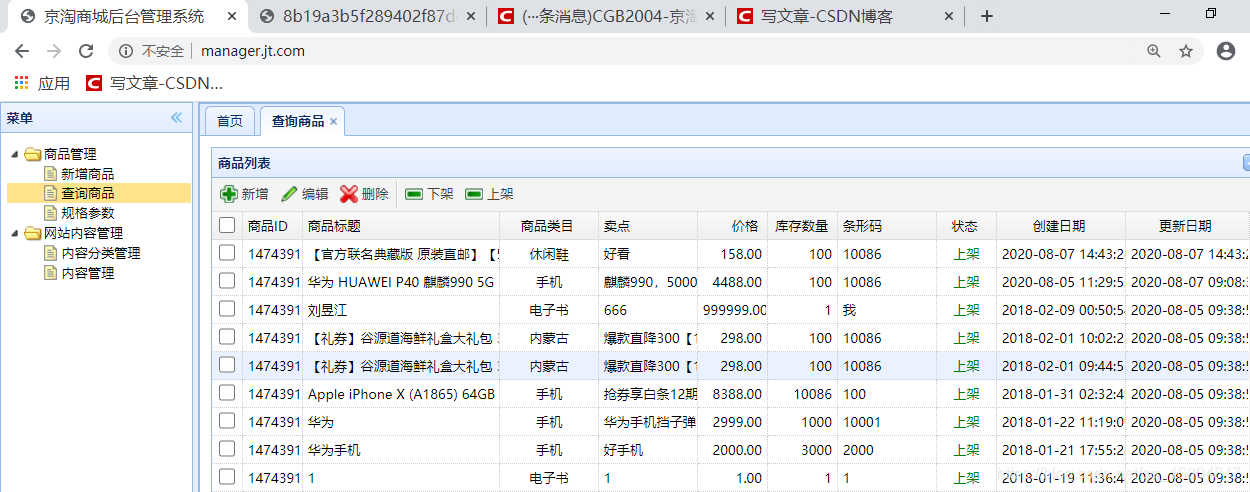
1.3.3 访问测试
检查修改的服务是否有效
2.Redis缓存
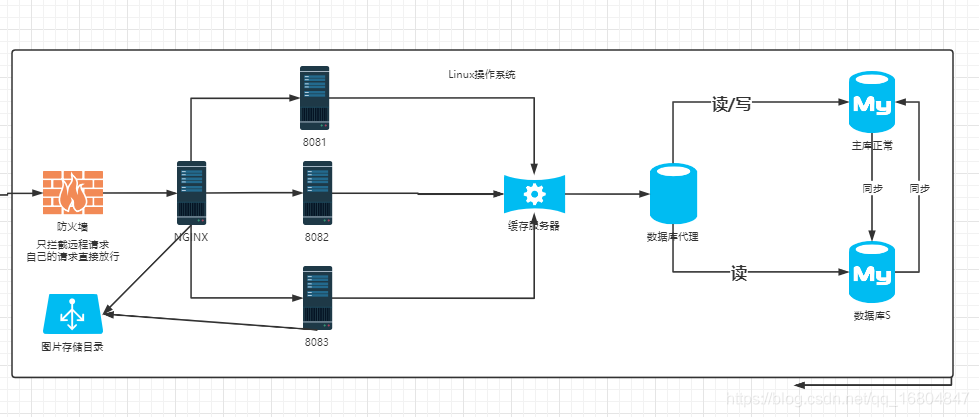
2.1 京淘项目架构优化
说明:为了提高数据库"查询"能力.引入缓存服务器.
2.2 缓存机制的介绍
说明:使用缓存机制主要的目的就是为了降低用户访问物理设备的频次.从缓存服务器中直接获取数据,快速的响应用户,提高整体的查询速度.用户体验更好.
如何实现:
1.缓存机制应该采用什么样的数据结构 进行构建? K-V结构 K必须唯一
2.应该使用什么语言进行开发? C语言
3.缓存的运行环境是哪? 内存
4.内存断电即擦除, 如何保证数据的安全性?? 实现持久化(写入磁盘)操作
5.内存中的数据如何进行优化 (不能一直存? ) 内存优化的算法 LRU算法(最近最少使用算法)
2.3 Redis介绍
Redis 是一个开源(BSD许可)的,内存中的数据结构存储系统,它可以用作数据库、缓存和消息中间件。 它支持多种类型的数据结构,如 字符串(strings), 散列(hashes), 列表(lists), 集合(sets), 有序集合(sorted sets)
与范围查询, bitmaps, hyperloglogs 和 地理空间(geospatial) 索引半径查询。 Redis 内置了 复制(replication),LUA脚本(Lua scripting), LRU驱动事件(LRU eviction),事务(transactions) 和不同级别的 磁盘持久化(persistence), 并通过 Redis哨兵(Sentinel)和自动 分区(Cluster)提供高可用性(high availability).
速度快:
tomcat: 150-220/秒
nginx: 3-5万/秒
redis: 写 8.6万/秒 读 11.2万/秒 ~ 平均10万次/秒
2.4 Redis安装
2.4.1 上传Redis
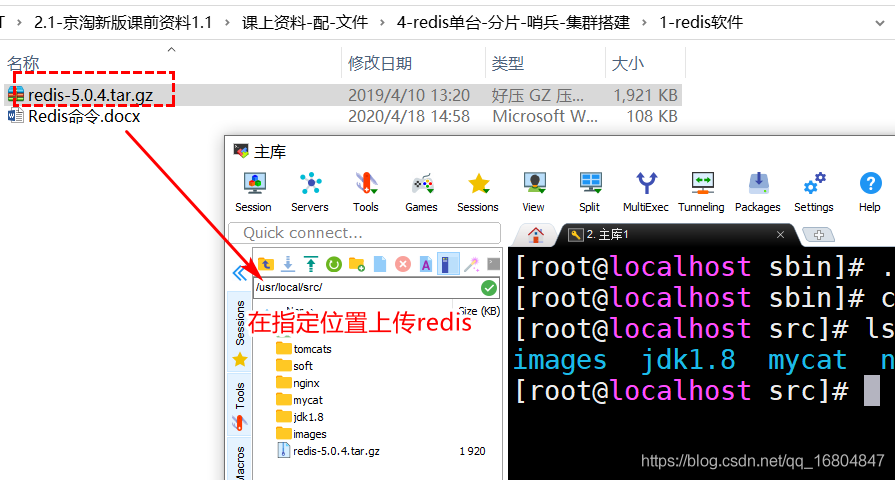
2.4.2 解压Redis
命令:
tar-xvf redis-5.0.4.tar.gz
mv redis redis-5.0.4
2.4.3 编译安装Redis
1.执行编译操作 make
2.安装redis make install
2.4.4 修改redis配置文件
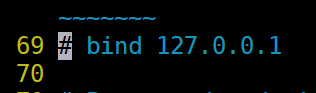
2).取消保护模式
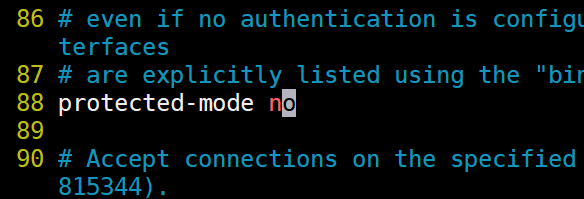
3).开启后台启动

2.4.5 Redis常规命令
要求:进入redis根目录中执行.
特点:redis每次启动时都会读取配置文件. 如果需要准备多台redis则需要准备多个配置文件
1.启动命令 redis-server redis.conf
没有开启后台运行的效果
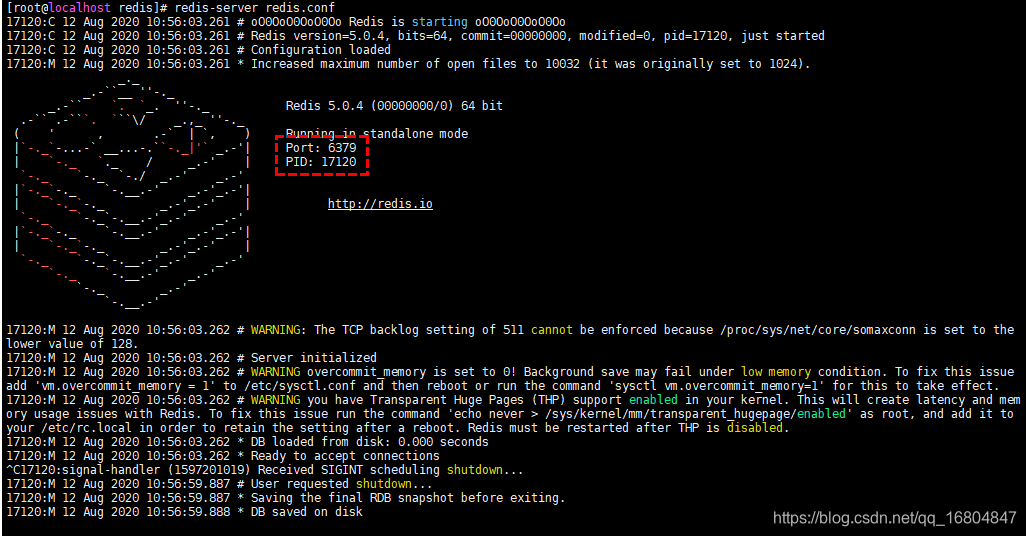
开启后台运行的效果
命令: redis-server redis.conf
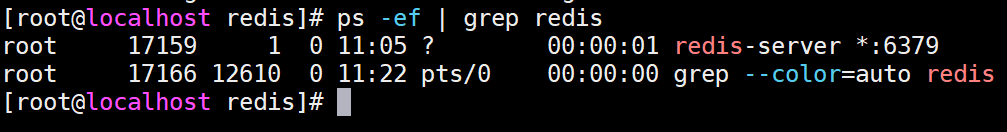
2.检索redis服务
命令: ps -ef | grep redis
- 进入redis客户端中
命令: redis-cli -p 6379
4.关闭redis
方式1: redis-cli -p 6379 shutdown
方式2:
先检索服务 ps -ef | grep redis
然后杀死进程 kill -9 pid
2.5 Redis入门案例
2.5.1 添加jar包
在父级工程中添加jar包
<!--spring整合redis -->
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.data</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
2.5.2 编辑测试API
package com.jt.test;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;
import redis.clients.jedis.Transaction;
import redis.clients.jedis.params.SetParams;
import java.util.Map;
@SpringBootTest //需要依赖spring容器进行操作,从容器中动态的获取对象
public class TestRedis {
@Autowired
private Jedis jedis;
/**
* 完成redis入门案例的测试
*/
@Test
public void test01(){
// Jedis jedis = new Jedis("192.168.126.129",6379);
//想redis中存储数
jedis.set("2004","今天没下雨,尴尬");
String value = jedis.get("2004");
System.out.println(value);
}
@Test
public void test02(){
Jedis jedis = new Jedis("192.168.126.129",6379);
//判断redis中是否存在key
if (jedis.exists("2004")){
//如果存在则设置超时时间
jedis.expire("2004",100);
//线程休眠
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
//获取剩余的存活时间
Long time = jedis.ttl("2004");
System.out.println("还能活"+time);
//撤销超时时间
jedis.persist("2004");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 需求说明:
* 1.redis.set操作,后面的操作会将之前的value覆盖
* 要求:如果key已经存在,则不允许赋值
* 环境问题: 检测redis中是否已经存在该数据
*/
@Test
public void test03() {
Jedis jedis = new Jedis("192.168.126.129", 6379);
jedis.flushAll();
jedis.setnx("boos","liq");
jedis.setnx("boss","zpk");
System.out.println(jedis.get("boss"));
}
/**
* 为数据添加超时时间,保证原子性操作
* 锁机制: 保证原子性
* 小结: setnx
* setex
*/
@Test
public void test04() {
Jedis jedis = new Jedis("192.168.126.129", 6379);
jedis.setex("aaa",20,"xxxxxx");//满足原子性需求
}
/**
* 需求:
* 1 要求赋值操作时,如果数据已经存在,则不允许赋值
* 2 同时要求添加超时时间,并且满足原子性需求
* private static final String XX = "xx";只 有key存在时,才能赋值
* private static final String NX = "nx";只有key不存在时,赋值
*
* private static final String PX = "px"; 亳秒
private static final String EX = "ex";秒
*/
@Test
public void test05() {
Jedis jedis = new Jedis("192.168.126.129", 6379);
SetParams params = new SetParams();
params.nx().ex(10);
jedis.set("AAA","CCC",params);
System.out.println(jedis.get("AAA"));
}
/**
* 测试hash数据类型
*/
@Test
public void test06() {
Jedis jedis = new Jedis("192.168.126.129", 6379);
jedis.hset("person","name","tomcat");
jedis.hset("person","age","18");
Map<String, String> person = jedis.hgetAll("person");
System.out.println(person);
jedis.hsetnx("user","id","1");
jedis.hsetnx("user","name","tom");
Map<String, String> user = jedis.hgetAll("user");
System.out.println(user);
}
/**
* 测试list集合数据类型
*/
@Test
public void test07() {
Jedis jedis = new Jedis("192.168.126.129", 6379);
jedis.lpush("list","1","2","3","4","5");
String value = jedis.rpop("list");
System.out.println(value);
}
/**
* 实现redis的事务控制
*/
@Test
public void testMulti() {
Jedis jedis = new Jedis("192.168.126.129", 6379);
Transaction transaction = jedis.multi();//开启
try{
transaction.set("AAA","123");
transaction.set("BBB","123");
transaction.exec();//提交
}catch (Exception e){
transaction.discard();//回滚
}
String aaa = jedis.get("AAA");
System.out.println(aaa);
}
}
2.6 SpringBoot整合Redis
2.6.1 编辑配置文件
# 配置单台redis
redis.host=192.168.126.129
redis.port=6379
2.6.2 编辑配置类
package com.jt.config;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;
//表明该类是一个配置类
@Configuration
@PropertySource("classpath:properties/redis.properties")
public class RedisConfig {
@Value("${redis.host}")
private String host;
@Value("${redis.port}")
private Integer port;
@Bean
public Jedis jedis(){
return new Jedis(host,port);
}
}
2.6.3 编辑测试类
说明:校验springBoot整合是否正确
package com.jt.test;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;
import redis.clients.jedis.Transaction;
import redis.clients.jedis.params.SetParams;
import java.util.Map;
@SpringBootTest //需要依赖spring容器进行操作,从容器中动态的获取对象
public class TestRedis {
@Autowired
private Jedis jedis;
/**
* 完成redis入门案例的测试
*/
@Test
public void test01(){
// Jedis jedis = new Jedis("192.168.126.129",6379);
//想redis中存储数
jedis.set("2004","今天没下雨,尴尬");
String value = jedis.get("2004");
System.out.println(value);
}
}
2.7 数据如何保存到Redis中
2.7.1 业务说明
说明:由于redis中一般使用String数据类型保存业务数据.但是代码中java对象Redis没办法直接保存,所以需要中间的转化的过程.使用JSON方式进行数据中转.
List java对象 --------- JSON ------------ Redis中 使用String数据类型保存.
2.7.2 ObjectMapper API介绍
package com.jt.test;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import com.jt.pojo.ItemDesc;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
public class TestObjectMapper {
private static final ObjectMapper MAPPER = new ObjectMapper();
@Test
public void test01(){
ItemDesc itemDesc = new ItemDesc();
itemDesc.setItemId(100L).setItemDesc("测试JSON转化").setCreated(new Date())
.setUpdated(itemDesc.getCreated());
try {
//1.将java对象转化为JSON
String json = MAPPER.writeValueAsString(itemDesc);
System.out.println(json);
//2.将JSON转化为对象 利用反射机制实例化对象 利用get/set方法为对象赋值
ItemDesc itemDesc2 = MAPPER.readValue(json, ItemDesc.class);
System.out.println(itemDesc2.toString()); //只输出当前对象的数据
//3.将集合信息转化为JSON List
List<ItemDesc> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(itemDesc);
String listJSON = MAPPER.writeValueAsString(list);
System.out.println(listJSON);
//将json转化为List集合
List<ItemDesc> list2 = MAPPER.readValue(listJSON,list.getClass());
System.out.println(list2);
} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
2.7.3 编辑工具API
说明:改工具API主要负责将用户参数转化为JSON,或者将JSON串转化为对象. 简化客户端调用
package com.jt.utils;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
public class ObjectMapperUtils {
//1. 创建工具API对象
private static final ObjectMapper MAPPER = new ObjectMapper();
//2.封装API 将对象转化为JSON
public static String toJSON(Object object){
if (object==null ){
throw new RuntimeException("对象不能为null");
}
try {
String json = MAPPER.writeValueAsString(object);
return json;
} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException(e.getMessage());
}
}
//3.封装API 将JSON转化为对象 用户传递什么类型,则返回什么对象 利用泛型
public static <T> T toObject(String json,Class<T> target){
//判断json串
if (json==null || "".equals(json) || target==null){
throw new RuntimeException("参数不能为null");
}
try {
T t = MAPPER.readValue(json,target);
return t;
} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException(e.getMessage());
}
}
}
2.7.4 编辑工具API测试
@Test
public void testObjectMapperUtils(){
ItemDesc itemDesc = new ItemDesc();
itemDesc.setItemId(100L).
setItemDesc("测试JSON对象转字符串").
setCreated(new Date()).
setUpdated(itemDesc.getCreated());
String json = ObjectMapperUtils.toJSON(itemDesc);
System.out.println(json);
ItemDesc itemDesc1 = ObjectMapperUtils.toObject(json, ItemDesc.class);
System.out.println(itemDesc1);
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号