pytorch-LeNet
LeNet
总体来看,LeNet(LeNet-5)由两个部分组成:
• 卷积编码器:由两个卷积层组成;
• 全连接层密集块:由三个全连接层组成。
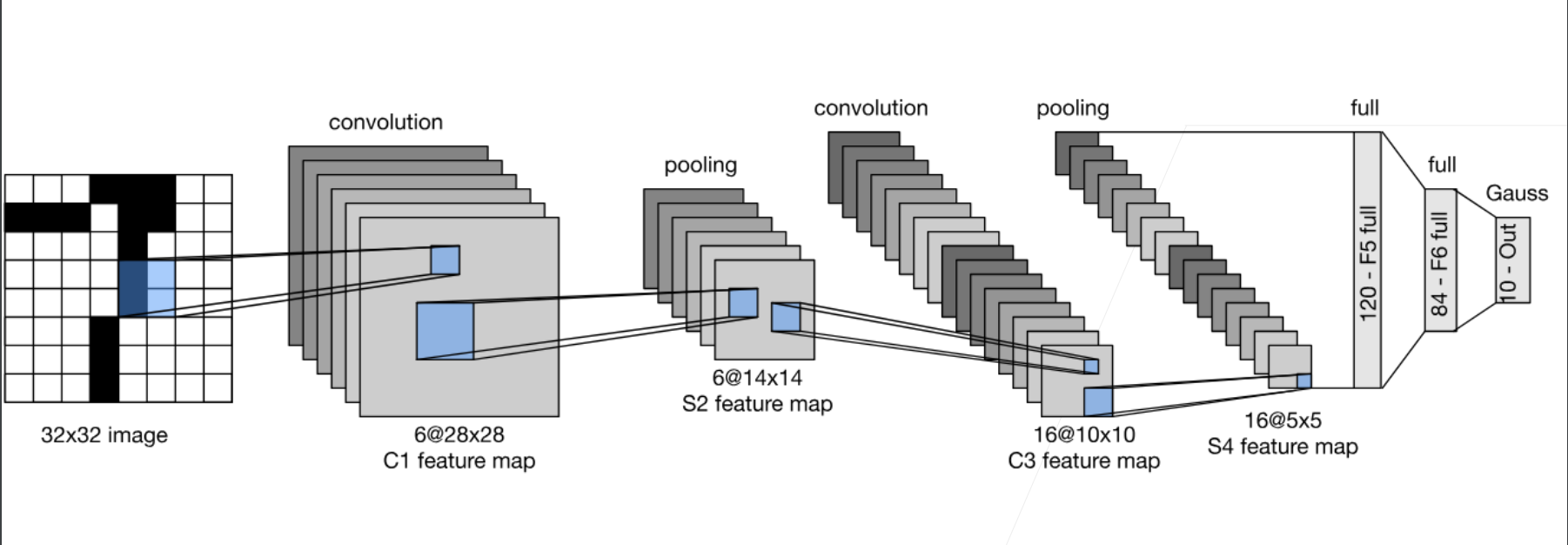
每个卷积块中的基本单元是一个卷积层、一个sigmoid激活函数和平均汇聚层。请注意,虽然ReLU和最大汇聚层更有效,但它们在20世纪90年代还没有出现。每个卷积层使用卷积核和⼀个激活函数。这些层将输入映射到多个⼆维特征输出,通常同时增加通道的数量。第⼀卷积层有6个输出通道,而第二个卷积层有16个输出通道。每个2 × 2池操作(步幅2)通过空间下采样将维数减少4倍。卷积的输出形状由批量大小、通道数、高度、宽度决定。
为了将卷积块的输出传递给稠密块,我们必须在小批量中展平每个样本。换言之,我们将这个四维输入转换成全连接层所期望的二维输入。这里的二维表示的第⼀个维度索引小批量中的样本,第二个维度给出每个样本的平面向量表示。LeNet的稠密块有三个全连接层,分别有120、84和10个输出。因为我们在执行分类任务,所以输出层的10维对应于最后输出结果的数量。
最早应用于手写的数字识别

总结:
- LeNet是早期成功的神经网络
- 先使用卷积层来学习图片的空间信息
- 然后使用全连接层来转换到类别空间
代码
import torch
from torch import nn
from d2l import torch as d2l
class Reshape(torch.nn.Module):
def forward(self, x):
return x.view(-1, 1, 28, 28)
net = torch.nn.Sequential(Reshape(),
nn.Conv2d(1, 6, kernel_size=5,padding=2),
nn.Sigmoid(),
nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),
nn.Conv2d(6, 16, kernel_size=5),
nn.Sigmoid(),
nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),
nn.Flatten(),
nn.Linear(16 * 5 * 5, 120),
nn.Sigmoid(),
nn.Linear(120, 84),
nn.Sigmoid(),
nn.Linear(84, 10))
检查一下模型:
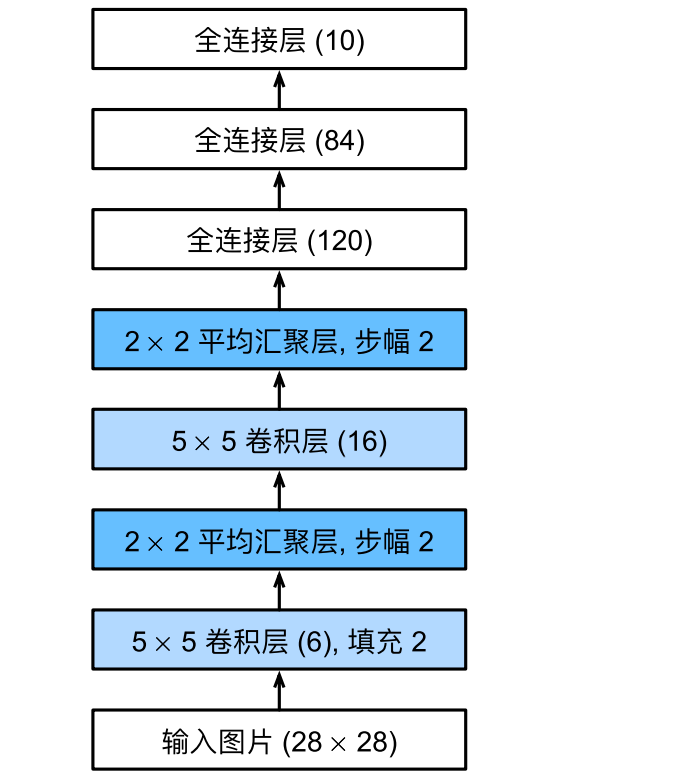
X = torch.rand(size=(1, 1, 28, 28), dtype=torch.float32)
for layer in net:
X = layer(X)
print(layer.__class__.__name__, 'output shape: \t', X.shape)
Reshape output shape: torch.Size([1, 1, 28, 28])
Conv2d output shape: torch.Size([1, 6, 28, 28])
Sigmoid output shape: torch.Size([1, 6, 28, 28])
AvgPool2d output shape: torch.Size([1, 6, 14, 14])
Conv2d output shape: torch.Size([1, 16, 10, 10])
Sigmoid output shape: torch.Size([1, 16, 10, 10])
AvgPool2d output shape: torch.Size([1, 16, 5, 5])
Flatten output shape: torch.Size([1, 400])
Linear output shape: torch.Size([1, 120])
Sigmoid output shape: torch.Size([1, 120])
Linear output shape: torch.Size([1, 84])
Sigmoid output shape: torch.Size([1, 84])
Linear output shape: torch.Size([1, 10])
在整个卷积块中,与上一层相比,每⼀层特征的高度和宽度都减小了。第⼀个卷积层使用2个像素的填充,来补偿5 × 5卷积核导致的特征减少。相反,第⼆个卷积层没有填充,因此高度和宽度都减少了4个像素。随着层叠的上升,通道的数量从输入时的1个,增加到第⼀个卷积层之后的6个,再到第二个卷积层之后的16个。同时,每个汇聚层的高度和宽度都减半。最后,每个全连接层减少维数,最终输出⼀个维数与结果
分类数相匹配的输出。
- 模型训练
现在我们已经实现了LeNet,让我们看看LeNet在Fashion-MNIST数据集上的表现。
batch_size = 256
train_iter, test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size=batch_size)
虽然卷积神经网络的参数较少,但与深度的多层感知机相比,它们的计算成本仍然很高,因为每个参数都参与更多的乘法。通过使用GPU,可以用它加快训练。
为了进行评估,我们需要对 之前描述的evaluate_accuracy函数进行轻微的修改。由于完整的数据集位于内存中,因此在模型使用GPU计算数据集之前,我们需要将其复制到显存中。
def evaluate_accuracy_gpu(net, data_iter, device=None):
"""使用GPU计算模型在数据集上的精度。"""
if isinstance(net, torch.nn.Module):
net.eval()
if not device:
device = next(iter(net.parameters())).device
metric = d2l.Accumulator(2)
for X, y in data_iter:
if isinstance(X, list):
X = [x.to(device) for x in X]
else:
X = X.to(device)
y = y.to(device)
metric.add(d2l.accuracy(net(X), y), y.numel())
return metric[0] / metric[1]
然后这里的train_ch6也是和前面的train_ch3不一样,这里使用GPU。
def train_ch6(net, train_iter, test_iter, num_epochs, lr, device):
"""用GPU训练模型(在第六章定义)。"""
def init_weights(m):
if type(m) == nn.Linear or type(m) == nn.Conv2d:
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(m.weight)
net.apply(init_weights)
print('training on', device)
net.to(device)
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=lr)
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
animator = d2l.Animator(xlabel='epoch', xlim=[1, num_epochs],
legend=['train loss', 'train acc', 'test acc'])
timer, num_batches = d2l.Timer(), len(train_iter)
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
metric = d2l.Accumulator(3)
net.train()
for i, (X, y) in enumerate(train_iter):
timer.start()
optimizer.zero_grad()
X, y = X.to(device), y.to(device)
y_hat = net(X)
l = loss(y_hat, y)
l.backward()
optimizer.step()
with torch.no_grad():
metric.add(l * X.shape[0], d2l.accuracy(y_hat, y), X.shape[0])
timer.stop()
train_l = metric[0] / metric[2]
train_acc = metric[1] / metric[2]
if (i + 1) % (num_batches // 5) == 0 or i == num_batches - 1:
animator.add(epoch + (i + 1) / num_batches,
(train_l, train_acc, None))
test_acc = evaluate_accuracy_gpu(net, test_iter)
animator.add(epoch + 1, (None, None, test_acc))
print(f'loss {train_l:.3f}, train acc {train_acc:.3f}, '
f'test acc {test_acc:.3f}')
print(f'{metric[2] * num_epochs / timer.sum():.1f} examples/sec '
f'on {str(device)}')
lr, num_epochs = 0.9, 10
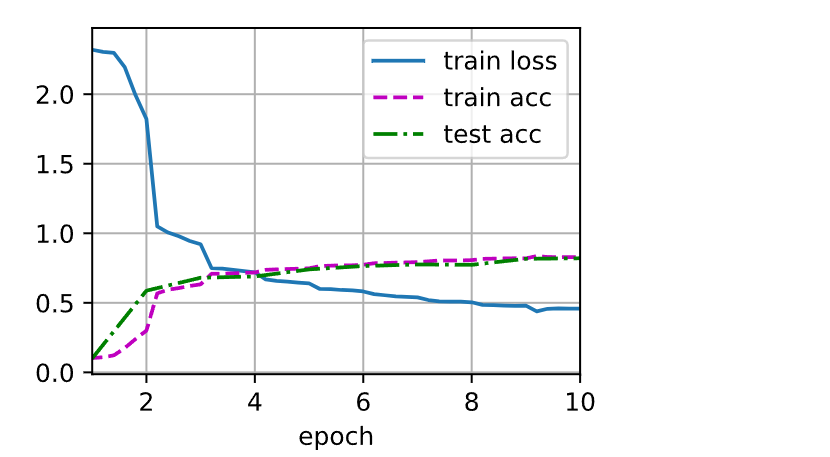
train_ch6(net, train_iter, test_iter, num_epochs, lr, d2l.try_gpu())
loss 0.458, train acc 0.829, test acc 0.820
29023.6 examples/sec on cuda:0



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)