创建tensor
Import from numpy
torch.from_numpy(data)
a=np.array([2,3.3])
a
#array([2. , 3.3])
torch.from_numpy(a)
#tensor([2.0000, 3.3000], dtype=torch.float64)
a=np.ones([2,3])
torch.from_numpy(a)
#tensor([[1., 1., 1.],
# [1., 1., 1.]], dtype=torch.float64)

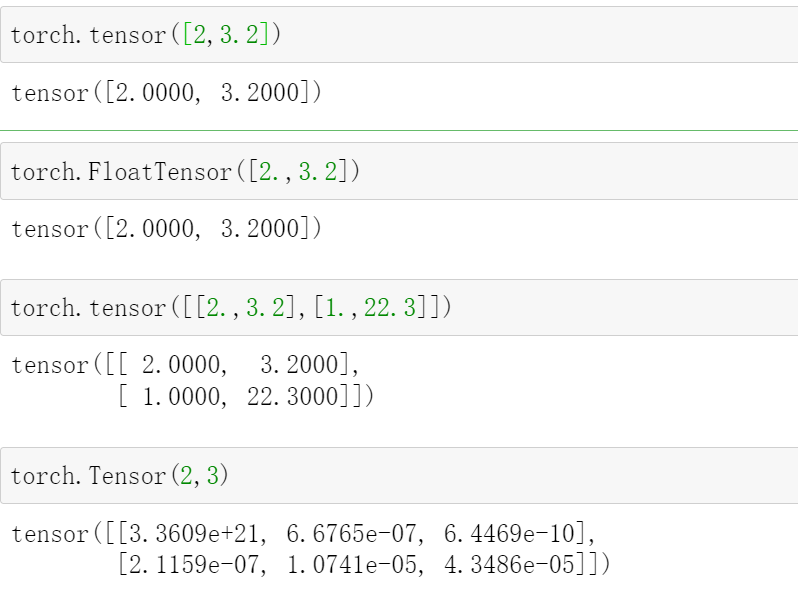
Import from list
这里会涉及到两个API:
torch.tensor([])
这个只能里面只能接收list
torch.Tensor()和torch.FloatTensor()
这个里面可以接收shape,也可以接收list,不过接收list的时候需要加上[]
例如torch.Tensor([2,3]),生成tensor([2, 3])
而torch.Tensor(2,3) 生成一个两行三列的tensor
torch.tensor([2,3.2])
# tensor([2.0000, 3.2000])
torch.FloatTensor([2.,3.2])
# tensor([2.0000, 3.2000])
torch.tensor([[2.,3.2],[1.,22.3]])
#tensor([[ 2.0000, 3.2000],
# [ 1.0000, 22.3000]])
torch.Tensor(2,3)
#tensor([[3.3609e+21, 6.6765e-07, 6.4469e-10],
# [2.1159e-07, 1.0741e-05, 4.3486e-05]])
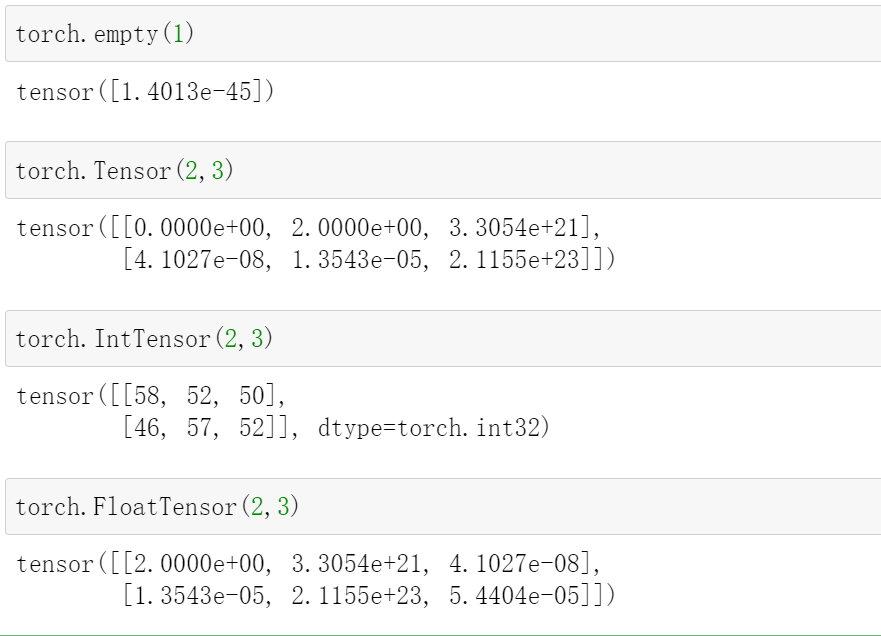
创建未初始化的tensor
-
Torch.empty()
-
Torch.FloatTensor(d1, d2, d3)
-
Torch.IntTensr(d1, d2, d3)
我们可以用这个创建,然后再后续赋值
rand/rand_like,randint(均匀分布)
torch.rand(shape)
里面的参数是一个shape,比如2,3是两行三列
这个是生成一个shape形状的[0,1]中均匀分布的tensor
注意这个范围是[0,1]
torch.rand_like(a)
里面的参数是一个tensor,这个就是生成一个和a一样shape的tensor,也是[0,1]中均匀分布的tensor
torch.randint(min,max,(shape))
这个可以指定范围,就是再[min,max)中均匀生成一个shape形状的tensor
torch.rand(3,3)
#tensor([[0.2096, 0.0753, 0.5869],
# [0.5584, 0.6180, 0.5574],
# [0.7021, 0.7409, 0.0298]])
a=torch.rand(3,4)
torch.rand_like(a)
#tensor([[0.4384, 0.2923, 0.8715, 0.6444],
# [0.5359, 0.9403, 0.6141, 0.1589],
# [0.2039, 0.7156, 0.0187, 0.6348]])
torch.randint(1,10,(3,3))
#tensor([[1, 7, 8],
# [2, 5, 2],
# [7, 9, 4]])

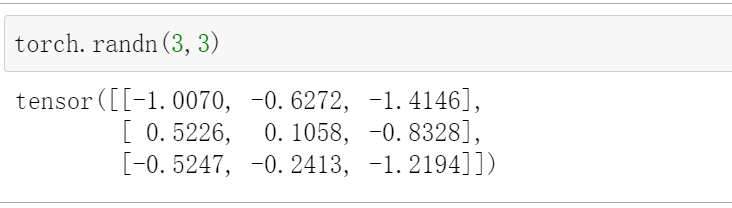
randn
torch.randn(shape)
这个是生成的tensor符合正态分布,均值为0,方差为1
torch.randn(3,3)
#tensor([[-1.0070, -0.6272, -1.4146],
# [ 0.5226, 0.1058, -0.8328],
# [-0.5247, -0.2413, -1.2194]])
如果想指定mean和std,需要用到
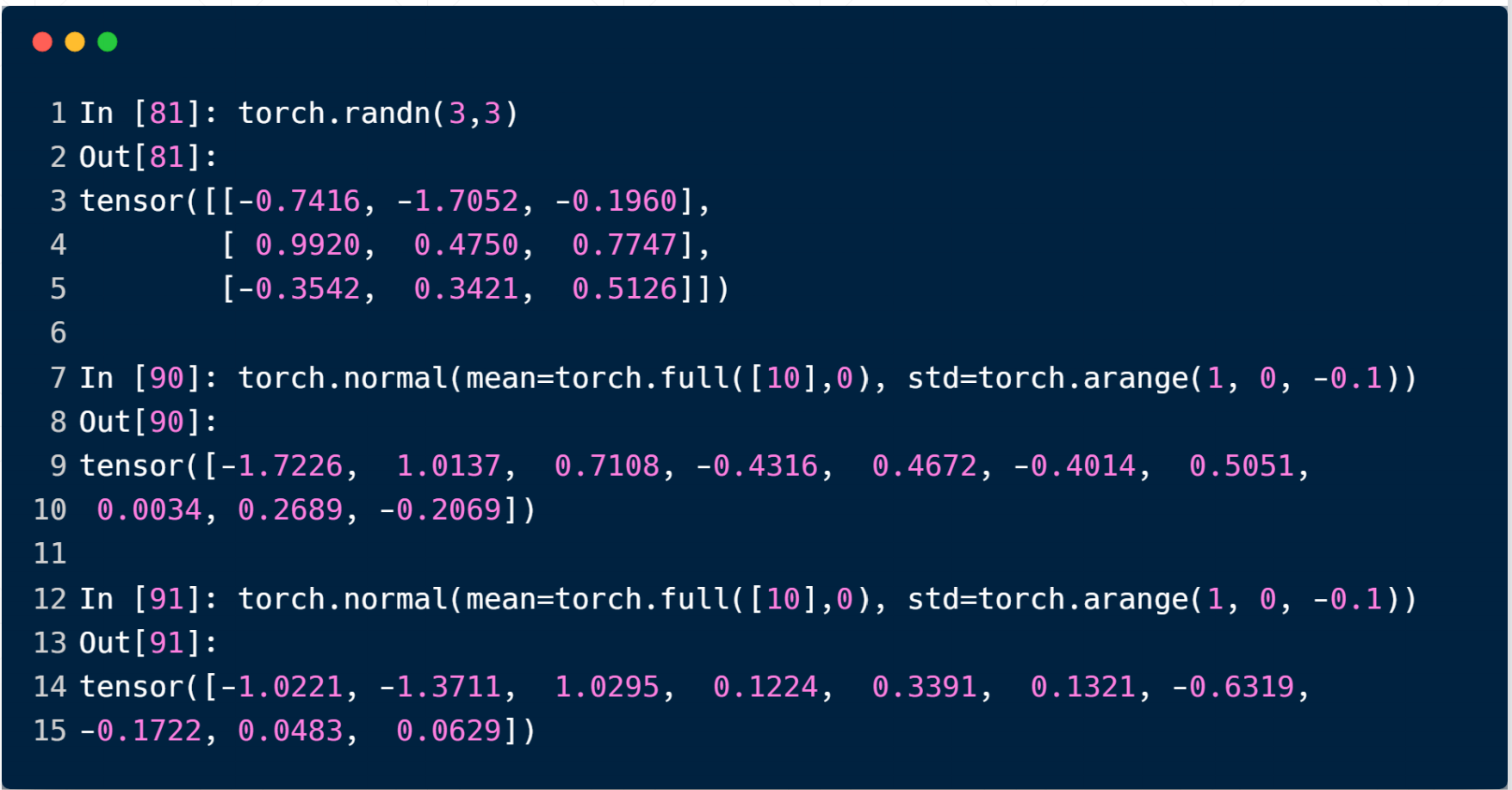
full(全部赋值为一个数值)
torch.full((shape),k)
这个是一个填充的函数
就是初始化一个形状为shape的tensor,里面的元素全部初始化为k
torch.full((2,3),5)
#tensor([[5, 5, 5],
# [5, 5, 5]])

arange/range(生成等差数列)
torch.arange(a,b,stop)
这个是生成一个[a,b),步长为stop的等差数列
torch.arange(0,10)
# tensor([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
torch.arange(0,10,2)
# tensor([0, 2, 4, 6, 8])
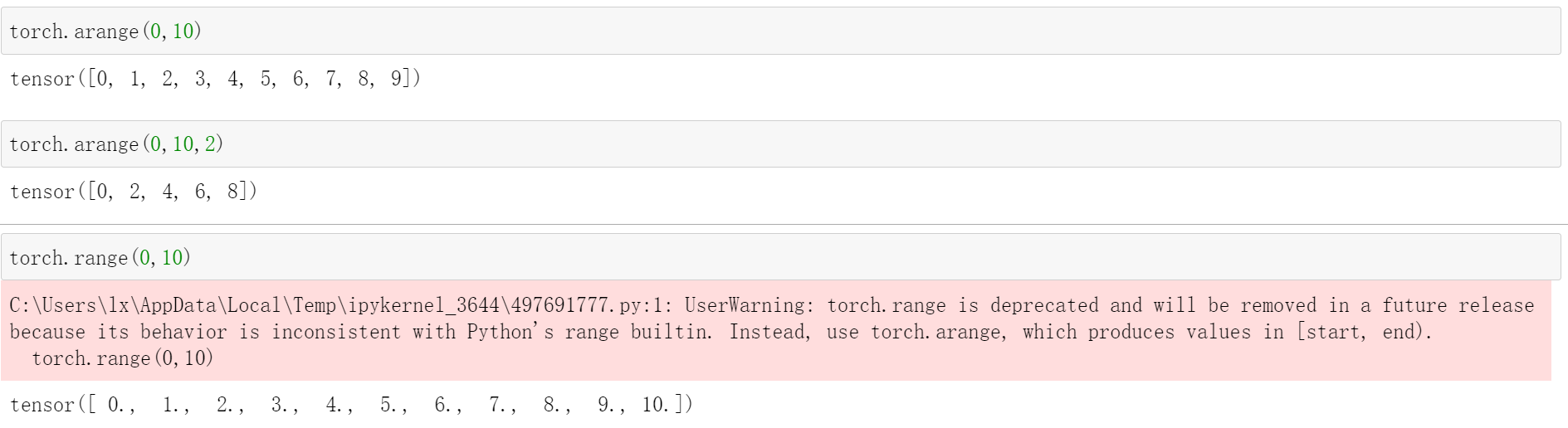
注意pytorch中不建议使用range
linspace/logspace(等分)
torch.linspace(a,b,steps=)
这个是从[a,b]中等分的取steps个,注意这个两边都是闭区间
torch.logspace(a,b,steps=)是再[10a,10b]之间取steps个

注意这里100=1,10-1=0.1
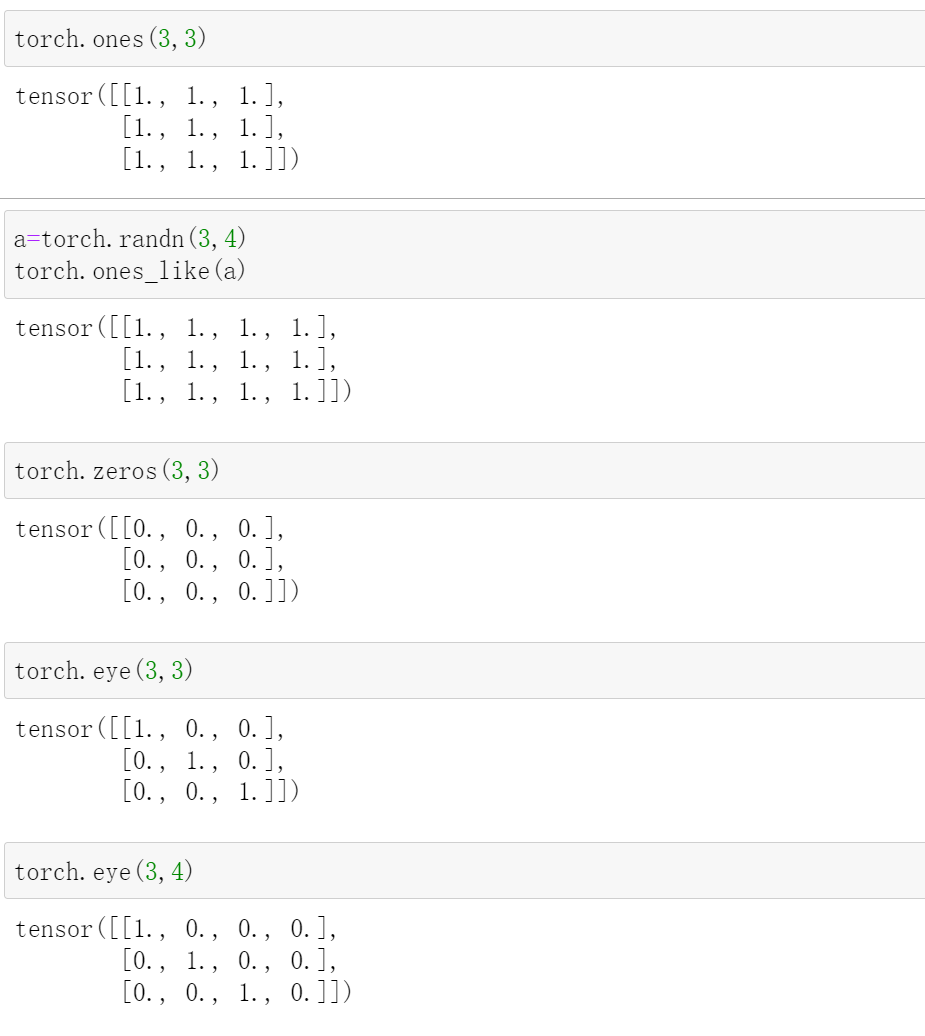
ones/zeros/eye
torch.ones(shape)/torch.ones_like(a)
生成全1矩阵
torch.zeros(shape)/torch.zeros_like(a)
生成全0矩阵
torch.eye(shape)
这里是生成一个对角矩阵,对角是1,剩下全是0
torch.ones(3,3)
#tensor([[1., 1., 1.],
# [1., 1., 1.],
# [1., 1., 1.]])
a=torch.randn(3,4)
torch.ones_like(a)
#tensor([[1., 1., 1., 1.],
# [1., 1., 1., 1.],
# [1., 1., 1., 1.]])
torch.zeros(3,3)
#tensor([[0., 0., 0.],
# [0., 0., 0.],
# [0., 0., 0.]])
torch.eye(3,3)
#tensor([[1., 0., 0.],
# [0., 1., 0.],
# [0., 0., 1.]])
torch.eye(3,4)
#tensor([[1., 0., 0., 0.],
# [0., 1., 0., 0.],
# [0., 0., 1., 0.]])
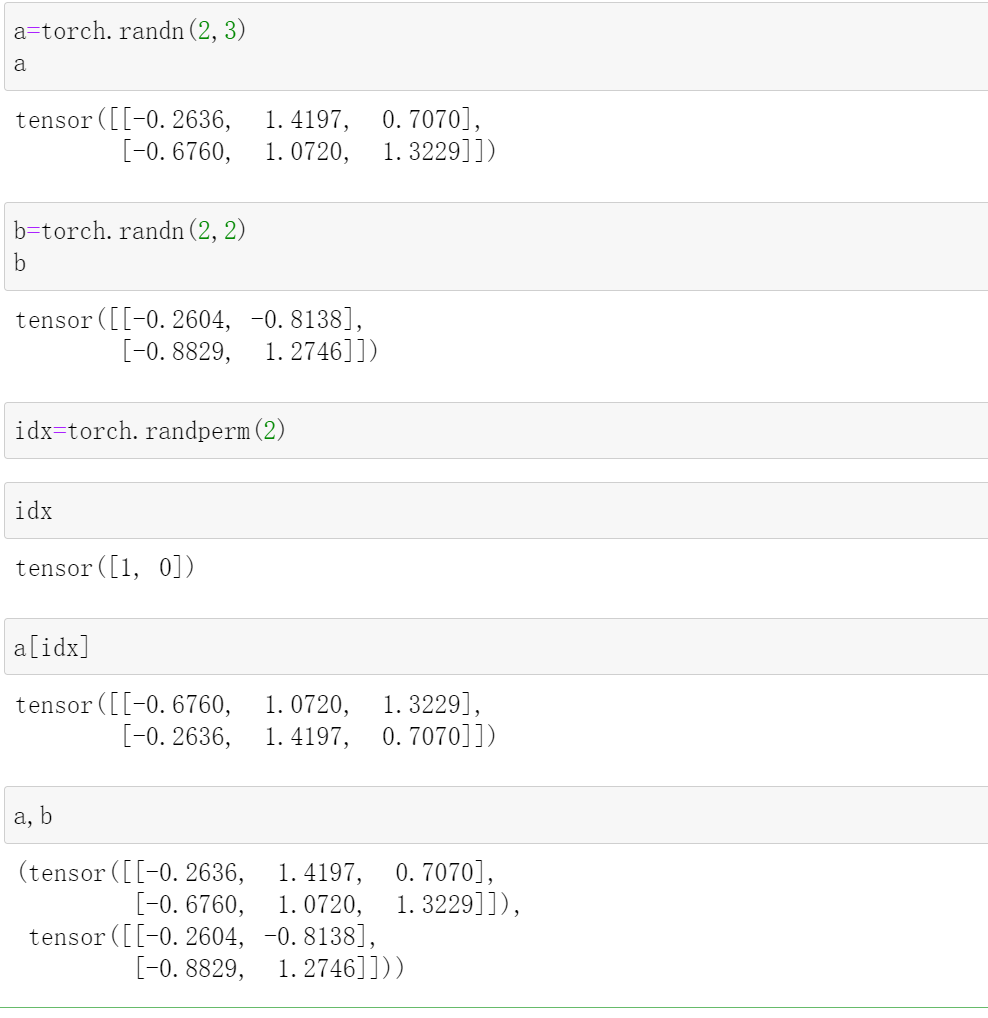
randperm
这个起到打散的作用
random.randperm(k)
就是[0,k)随机打散
torch.randperm(10)
#tensor([7, 0, 1, 3, 9, 5, 2, 8, 4, 6])
torch.randperm(10)
#tensor([4, 7, 8, 5, 3, 6, 1, 9, 2, 0])