SGU507. Treediff(树上启发式合并/set)
507. Treediff
Time limit per test: 0.25 second(s)
Memory limit: 262144 kilobytes
input: standard
output: standard
Andrew has just made a breakthrough in complexity theory: he thinks that he can prove P=NP if he can get a data structure which allows to perform the following operation quickly. Naturally, you should help him complete his brilliant research. Consider a rooted tree with integers written in the leaves. For each internal (non-leaf) node v of the tree you must compute the minimum absolute difference between all pairs of numbers written in the leaves of the subtree rooted at v.
Input
The first line of the input file contains two integers n and m — overall number of nodes in the tree and number of leaves in the tree respectively. 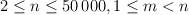 . All nodes are numbered from 1 to n. Node number 1 is always the root of the tree. Each of the other nodes has a unique parent in the tree. Each of the next n - 1 lines of the input file contains one integer — the number of the parent node for nodes 2, 3,..., n respectively. Each of the last mlines of the input file contains one integer ranging from
. All nodes are numbered from 1 to n. Node number 1 is always the root of the tree. Each of the other nodes has a unique parent in the tree. Each of the next n - 1 lines of the input file contains one integer — the number of the parent node for nodes 2, 3,..., n respectively. Each of the last mlines of the input file contains one integer ranging from 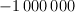 to
to 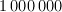 — the value of the corresponding leaf. Leaves of the tree have numbers from n - m + 1 to n.
— the value of the corresponding leaf. Leaves of the tree have numbers from n - m + 1 to n.
Output
Output one line with n - m integers: for each internal node of the tree output the minimum absolute difference between pairs of values written in the leaves of its subtree. If there is only one leaf in the subtree of some internal node, output number 231 - 1 for that node. Output the answers for the nodes in order from node number 1 to n - m.
Example(s)
sample input |
sample output |
|---|---|
5 4 1 1 1 1 1 4 7 9 |
2 |
sample input |
sample output |
|---|---|
5 4 1 1 1 1 1 4 7 10 |
3 |
sample input |
sample output |
|---|---|
7 4 1 2 1 2 3 3 2 10 7 15 |
3 3 8 |
sample input |
sample output |
|---|---|
2 1 1 100 |
2147483647 |
同样是dsu on tree的典型题,整体思想是用set去维护当前以rt为根子树的叶子结点。先搜一遍轻儿子,清空set后再搜重儿子,此时set保存的是重儿子对应的子树的叶子结点。这时候再暴力dfs一遍轻儿子,每当搜到一个叶子结点的时候就可以更新rt的答案了(插入set然后与其他相邻的叶子结点的val值计算更新答案)。
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
#include <cstring>
#define N 50005
using namespace std;
int n, m, tot = 0, head[N], ver[2 * N], Next[2 * N];
int val[N];
int sz[N], son[N];
int ans[N];
set<int> st;
int hson = 0;
void add(int x, int y) {
ver[++tot] = y, Next[tot] = head[x], head[x] = tot;
}
void dfs1(int x, int pre) {
sz[x] = 1;
int mxsz = -1;
for(int i = head[x]; i; i = Next[i]) {
int y = ver[i];
if(y == pre) continue;
dfs1(y, x);
sz[x] += sz[y];
if(sz[y] > mxsz) {
son[x] = y;
mxsz = sz[y];
}
}
}
void Delete() {
st.clear();
}
void process(int x, int pre, int rt) {
if(val[x] != 0x3f3f3f3f) {//叶子结点
if(st.find(val[x]) != st.end()) {
ans[rt] = 0;
} else {
st.insert(val[x]);
set<int>::iterator it = st.find(val[x]);
if(it == st.begin()) {
set<int>::iterator it1 = ++it;
it--;
if(it1 != st.end()) {
ans[rt] = min(ans[rt], abs((*it) - (*it1)));
}
} else {
set<int>::iterator it1 = ++it;
it--;
set<int>::iterator it2 = --it;
it++;
if(it1 != st.end()) {
ans[rt] = min(ans[rt], abs((*it) - (*it1)));
}
ans[rt] = min(ans[rt], abs((*it) - (*it2)));
}
}
} else {
for(int i = head[x]; i; i = Next[i]) {
int y = ver[i];
if(y == pre) continue;
process(y, x, rt);
}
}
}
void dfs2(int x, int pre) {
for(int i = head[x]; i; i = Next[i]) {
int y = ver[i];
if(y == pre || y == son[x]) continue;
dfs2(y, x), Delete();
}
if(son[x]) {
dfs2(son[x], x);
ans[x] = min(ans[x], ans[son[x]]);
}
for(int i = head[x]; i; i = Next[i]) {
int y = ver[i];
if(y == pre || y == son[x] && val[y] == 0x3f3f3f3f) continue;//y == son[x] && val[y] == 0x3f3f3f3f 表示不是叶子的重儿子才不搜
process(y, x, x);
}
}
int main() {
cin >> n >> m;
memset(ans, 0x3f3f3f3f, sizeof(ans));
memset(val, 0x3f3f3f3f, sizeof(val));//因为叶子结点的值可能为0
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
int fa;
cin >> fa;
add(fa, i);
add(i, fa);
}
for(int i = n - m + 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> val[i];
}
dfs1(1, 0);
dfs2(1, 0);
for(int i = 1; i <= n - m; i++) {
if(ans[i] != 0x3f3f3f3f) cout << ans[i] << " ";
else cout << 2147483647 << " ";
}
return 0;
}



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· 探究高空视频全景AR技术的实现原理
· 阿里最新开源QwQ-32B,效果媲美deepseek-r1满血版,部署成本又又又降低了!
· 单线程的Redis速度为什么快?
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· AI编程工具终极对决:字节Trae VS Cursor,谁才是开发者新宠?
· 展开说说关于C#中ORM框架的用法!
2020-11-10 AcWing 1215. 小朋友排队(树状数组)
2020-11-10 AcWing 1214. 波动数列(推柿子+DP)