C++ 算法竞赛、04 周赛篇 | AcWing 第5场周赛
AcWing 第5场周赛
3726 调整数组
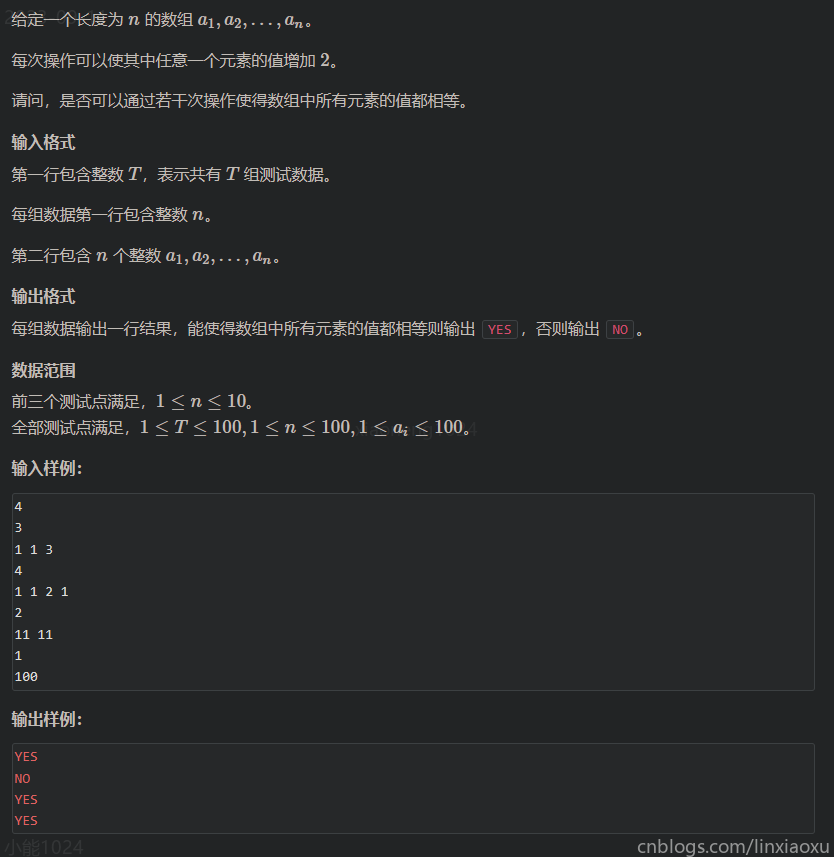
简单题,判断奇偶数是否同时存在
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int t, m;
int main() {
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
cin >> m;
bool f1 = false, f2 = false;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int x;
cin >> x;
if (x & 1)
f1 = true;
else
f2 = true;
}
if (f1 == f2)
puts("NO");
else
puts("YES");
}
return 0;
}
3727⭐乘方相加
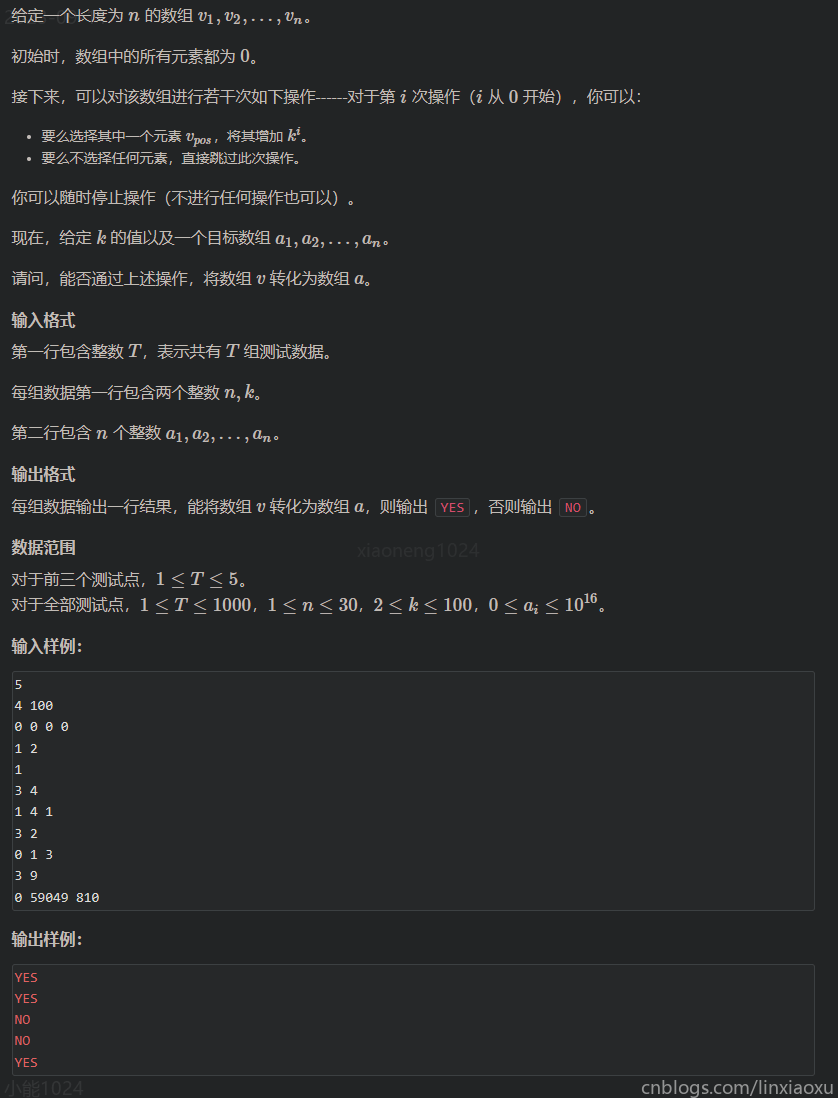
记录每个数据的 k 进制各个位数的值保存到数组,题目要求每位最多为 1,超过 1 则无法达到
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int const N = 1e2;
int t, m, k;
int s[N];
int main() {
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
cin >> m >> k;
memset(s, 0, sizeof s); // 每组测试点初始化
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
long long x;
cin >> x;
for (int j = 0; x; j++, x /= k) {
s[j] += x % k;
}
}
bool flag = true;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
if (s[i] > 1) flag = false;
}
if (flag)
puts("YES");
else
puts("NO");
}
return 0;
}
3728⭐城市通电

图是稠密图,用朴素版Prim求,
每点建立发电站的费用转化成:有一个超级原点,每个城市点连向超级原点的边的距离就是建立发电站的费用,如果该点连向该边,就是建立了发电站
用两个 Vector 分别存建立发电站的点 和 接电线的点,distp 用于获取每个点连向连通块的哪个点
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define y second
#define x first
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
int const N = 2e3 + 10;
PII q[N];
int c[N], k[N];
LL dist[N], distp[N]; // distp是每个点连向连通块的边对应的是连通块哪个点
bool st[N];
vector<int> ans1; // 存建发电站
vector<PII> ans2; // 存村庄和村庄之间的边
int n;
inline LL get_dist(int a, int b) {
int dx = q[a].x - q[b].x;
int dy = q[a].y - q[b].y;
return (LL)(abs(dx) + abs(dy)) * (k[a] + k[b]);
}
LL prim() {
// memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist);
LL res = 0;
dist[0] = 0, st[0] = true;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) dist[i] = c[i];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int t = -1;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
if (!st[j] && (t == -1 || dist[t] > dist[j])) t = j;
st[t] = true;
res += dist[t];
if (!distp[t])
ans1.push_back(t);
else
ans2.push_back({distp[t], t});
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
if (!st[j] && dist[j] > get_dist(t, j)) {
dist[j] = get_dist(t, j);
distp[j] = t;
}
}
return res;
}
int main() {
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> q[i].x >> q[i].y;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> c[i];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> k[i];
LL res = prim();
cout << res << endl;
cout << ans1.size() << endl;
for (auto x : ans1) cout << x << " ";
cout << endl;
cout << ans2.size() << endl;
for (auto &t : ans2) cout << t.x << " " << t.y << endl;
return 0;
}
分类:
C/C++
, Algorithm | 比赛,周赛

 标准的错误,经典的零分。考查K进制,Prim朴素版,建图
标准的错误,经典的零分。考查K进制,Prim朴素版,建图


【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· Docker 太简单,K8s 太复杂?w7panel 让容器管理更轻松!