python——类与对象
__init__ 方法:
1、Init 初始化方法的返回值必须是None。
3、类没有定义阶段,函数有定义阶段(不调用不执行)。
实例化时触发__init__方法执行,为对象添加属性。【t1=student() ==》 student.__init__(self)】
属性引用:
类里面的函数叫作对象的绑定方法。 对象调用绑定方法时自动传值,类调用函数属性时需要为self传值。 print(Student.__dict__) #查看类的字典 print(t1.__dict__) #查看对象的字典
class Student:
school='偶的博爱' #数据属性
l=[]
def __init__(self,name,age): #函数属性
self.name=name
self.age=age
# Student.l.append(self)
self.l.append(self)
#t1.name='xiaohei'
#t1.age=17
def study(self):
print('%s is studying' %self.name)
t1=Student('alex1',18) #Student.__init__(t1,'alex1',18)
# t2=Student('alex2',18) ==>Student.__init__( Student('alex2',18), 'alex2',18)
# print(Student.study) #类的函数属性
# print(t1.study) #对象的绑定方法
# Student.study(t1) #类调用函数属性需要传值
# t1.study() #Student.study(t1)
对类的属性进行增删改查:
改:Student.school='oldboy'
查:print(Student.school)
增:Student.x='asdfafd'
删:del Student.x
1、 对象的属性是__init__(self)下面的变量。
2、 对象调用属性时先去对象的字典里找,再去类的字典里找
计算这个类共产生了多少个对象:
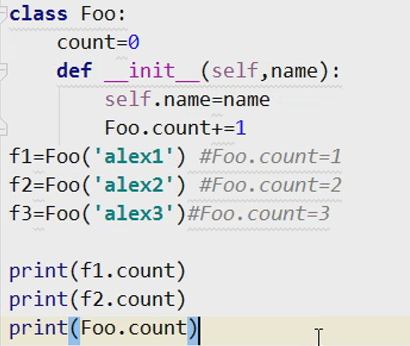
继承:
派生:子类衍生出自己新的属性就叫作派生。
组合:self.birth=Date(year,mon,day)
继承:
class Teacher(People):
People.__init__(self,name,age,year,mon,day)
定义类的时候,括号里面加上要继承的类。
类.__bases__ 查看父类。一个类可以继承多个类。
在Python3中,所有类默认继承object类。
但凡继承了object类的子类,都称为新式类。
没有继承object类的子类称为经典类,在Python2中默认都是经典类。
#!/usr/bin/env python
#继承,组合
#老师和学生都是人,人都有名字,年龄,生日,都会走。所以
class People:
def __init__(self,name,age,year,mon,day):
self.name=name
self.age=age
self.birth=Date(year,mon,day) #组合 people类用到data类。人有生日
def walk(self):
print('%s is walking' % self.name)
class Date:
def __init__(self,year,mon,day):
self.year=year
self.mon=mon
self.day=day
def tell_birth(self):
print('出生于<%s>年 <%s>月 <%s>日'%(self.year,self.mon,self.day))
class Teacher(People):
def __init__(self,name,age,year,mon,day,level,salary):
People.__init__(self,name,age,year,mon,day)
self.level=level
self.salary=salary
def teach(self):
print('%s is teaching' %self.name)
class Student(People):
def __init__(self,name,age,year,mon,day,group):
People.__init__(self,name,age,year,mon,day)
self.group=group
def study(self):
print('%s is studying' %self.name)
t=Teacher('egon',14,2000,12,12,3,'as') #用Teacher类实例化对象
print(t.birth.year) #t.birth其实就是调用Date类
print(t.birth.tell_birth()) #调用Date下面的tell_birth函数属性。
s=Student('linuxws',18,1991,9,19,1)
print(s.birth.year)
print(s.birth.tell_birth())
接口和归一化设计
抽象类:用于限制子类必须要有哪些方法

终极总结:
类的作用:
实例化
调用属性
对象的作用:
调用属性
类与对象的名称空间:
类的名称空间:类名.__dict__
对象的名称空间:对象名.__dict__
绑定方法会自动传值。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号