ELKStack入门篇(一)之ELK部署和使用
一、ELKStack简介
1、ELK介绍
中文指南:https://www.gitbook.com/book/chenryn/elk-stack-guide-cn/details
ELK Stack包含:ElasticSearch、Logstash、Kibana
ElasticSearch是一个搜索引擎,用来搜索、分析、存储日志。它是分布式的,也就是说可以横向扩容,可以自动发现,索引自动分片,总之很强大。文档https://www.elastic.co/guide/cn/elasticsearch/guide/current/index.html
Logstash用来采集日志,把日志解析为json格式交给ElasticSearch。
Kibana是一个数据可视化组件,把处理后的结果通过web界面展示
Beats在这里是一个轻量级日志采集器,其实Beats家族有5个成员
早期的ELK架构中使用Logstash收集、解析日志,但是Logstash对内存、cpu、io等资源消耗比较高。相比 Logstash,Beats所占系统的CPU和内存几乎可以忽略不计
x-pack对Elastic Stack提供了安全、警报、监控、报表、图表于一身的扩展包,是收费的。
2、ELK架构图:
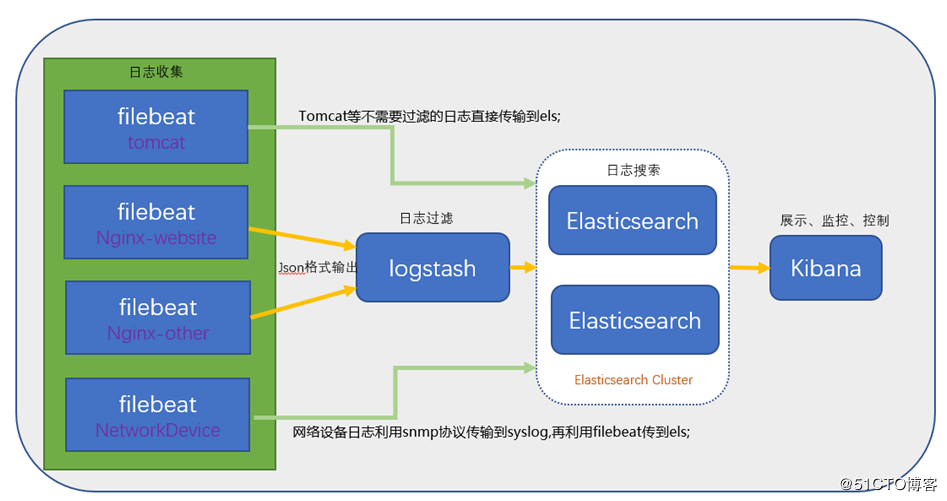
二、Elasticsearch部署
1、安装JDK
方法一:yum安装JDK [root@linux-node1 ~]# yum install -y java [root@linux-node1 ~]# java -version openjdk version "1.8.0_151" OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 1.8.0_151-b12) OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 25.151-b12, mixed mode) 方法二:源码安装JDK 下载 [root@linux-node1 ~]# wget http://download.oracle.com/otn-pub/java/jdk/8u151-b12/e758a0de34e24606bca991d704f6dcbf/jdk-8u151-linux-x64.tar.gz 配置Java环境 [root@linux-node1 ~]# tar zxf jdk-8u151-linux-x64.tar.gz -C /usr/local/ [root@linux-node1 ~]# ln –s /usr/local/jdk1.8.0_91 /usr/local/jdk [root@linux-node1 ~]# vim /etc/profile export JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/jdk export CLASSPATH=.:$JAVA_HOME/lib/dt.jar:$JAVA_HOME/lib/tools.jar export PATH=$PATH:$JAVA_HOME/bin [root@linux-node1 ~]# source /etc/profile [root@linux-node1 ~]# java -version ★★★★注:linux-node2节点上也需要安装JDK
2、安装Elasticsearch
linux-node2节点也需要安装elasticsearch
使用yum安装elasticsearch会很慢,建议先下载:https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-6.0.0.rpm
(1)源码安装elasticsearch:
安装elasticsearch [root@linux-node1 ~]# wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-6.0.0.rpm [root@linux-node1 ~]# yum install -y elasticsearch-6.0.0.rpm 配置elasticsearch,linux-node2配置一个相同的节点,通过组播进行通信,会通过cluster进行查找,如果无法通过组播查询,修改成单播即可。 [root@linux-node1 ~]# vim /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml cluster.name:elk-cluster #集群名称 node.name:elk-node1 #节点名称,一个集群之内节点的名称不能重复 path.data:/data/elkdata #数据路径 path.logs:/data/logs #日志路径 bootstrap.memory_lock:true #锁住es内存,保证内存不分配至交换分区。 network.host:192.168.56.11 #网络监听地址 http.port:9200 #用户访问查看的端口,9300是组件访问使用 discovery.zen,ping.unicast.hosts:["192.168.56.11","192.168.56.12"] #单播(配置一台即可,生产可以使用组播方式) ★★★注:内存锁定需要进行配置需要2G以上内存否则会导致无法启动elasticsearch。6.x版本启用锁定内存,需要进行以下修改操作: [root@linux-node1 ~]# systemctl edit elasticsearch [Service] LimitMEMLOCK=infinity [root@linux-node1 ~]# systemctl daemon-reload [root@linux-node1 ~]# mkdir /data/{elkdata,logs} #创建数据目录和日志目录 [root@linux-node1 ~]# chown elasticsearch.elasticsearch /data -R [root@linux-node1 ~]# systemctl start elasticsearch.service [root@linux-node1 ~]# netstat -tulnp |grep java tcp6 0 0 192.168.56.11:9200 :::* LISTEN 26866/java tcp6 0 0 192.168.56.11:9300 :::* LISTEN 26866/java 将配置文件拷贝到linux-node2 [root@linux-node1 ~]# scp /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml 192.168.56.12:/etc/elasticsearch/ [root@linux-node2 ~]# vim /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml 修改: node.name=elk-node2 network.host=192.168.56.12 [root@linux-node2 ~]# mkdir /data/{elkdata,logs} [root@linux-node2 ~]# chown elasticsearch.elasticsearch /data -R [root@linux-node2 ~]# systemctl start elasticsearch.service [root@linux-node2 ~]# netstat -tulnp |grep java tcp6 0 0 192.168.56.12:9200 :::* LISTEN 16346/java tcp6 0 0 192.168.56.12:9300 :::* LISTEN 16346/java
(2)yum安装elasticsearch
1.下载并安装GPG key [root@linux-node1 ~]# rpm --import https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch 2.添加yum仓库 [root@linux-node1 ~]# vim /etc/yum.repos.d/es.repo [elasticsearch-6.x] name=Elasticsearch repository for 6.x packages baseurl=https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/6.x/yum gpgcheck=1 gpgkey=https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch enabled=1 autorefresh=1 type=rpm-md 3.安装elasticsearch [root@hadoop-node1 ~]# yum install -y elasticsearch
3、Elasticsearch的集群配置和监控
可以使用命令来查看elasticsearch的状态内容

[root@linux-node1 ~]# curl http://192.168.56.11:9200/_cluster/health?pretty=true { "cluster_name" : "elk-cluster", "status" : "green", "timed_out" : false, "number_of_nodes" : 2, "number_of_data_nodes" : 2, "active_primary_shards" : 0, "active_shards" : 0, "relocating_shards" : 0, "initializing_shards" : 0, "unassigned_shards" : 0, "delayed_unassigned_shards" : 0, "number_of_pending_tasks" : 0, "number_of_in_flight_fetch" : 0, "task_max_waiting_in_queue_millis" : 0, "active_shards_percent_as_number" : 100.0 } [root@linux-node2 ~]# curl http://192.168.56.12:9200/_cluster/health?pretty=true { "cluster_name" : "elk-cluster", "status" : "green", "timed_out" : false, "number_of_nodes" : 2, "number_of_data_nodes" : 2, "active_primary_shards" : 0, "active_shards" : 0, "relocating_shards" : 0, "initializing_shards" : 0, "unassigned_shards" : 0, "delayed_unassigned_shards" : 0, "number_of_pending_tasks" : 0, "number_of_in_flight_fetch" : 0, "task_max_waiting_in_queue_millis" : 0, "active_shards_percent_as_number" : 100.0 } [root@linux-node1 ~]# curl -i -XGET 'http://192.168.56.11:9200/_count?' #查看es里面有什么内容 HTTP/1.1 200 OK content-type: application/json; charset=UTF-8 content-length: 71 {"count":0,"_shards":{"total":0,"successful":0,"skipped":0,"failed":0}} 解释: 返回头部200,执行成功0个,返回0个 curl http://192.168.56.11:9200/_cluster/health?pretty 健康检查 curl http://192.168.56.11:9200/_cluster/state?pretty 集群详细信息 注:但是我们不可能经常通过命令来查看集群的信息,这里就使用elasticsearch的插件--head 插件是为了完成不同的功能,而官方提供了一些插件但大部分是收费的,另外也有一些开发爱好者提供的插件。可以实现对elasticsearch集群的状态与管理配置等功能。
4、Elasticsearch插件–>Head插件
插件作用:主要是做集群管理的插件
Github下载地址:https://github.com/mobz/elasticsearch-head

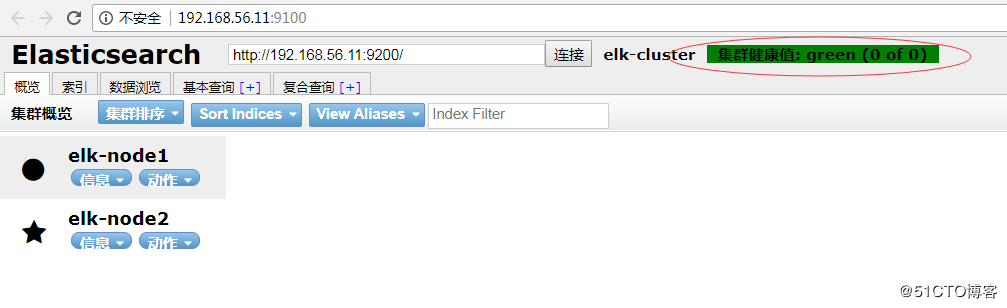
安装Head插件 [root@linux-node1 ~]# wget https://nodejs.org/dist/v8.10.0/node-v8.10.0-linux-x64.tar.xz [root@linux-node1 ~]# tar xf node-v8.10.0-linux-x64.tar.xz [root@linux-node1 ~]# mv node-v8.10.0-linux-x64 /usr/local/node [root@linux-node1 ~]# vim /etc/profile export NODE_HOME=/usr/local/node export PATH=$PATH:$NODE_HOME/bin [root@linux-node1 ~]# source /etc/profile [root@linux-node1 ~]# which node /usr/local/node/bin/node [root@linux-node1 ~]# node -v v8.10.0 [root@linux-node1 ~]# which npm /usr/local/node/bin/npm [root@linux-node1 ~]# npm -v 5.6.0 [root@linux-node1 ~]# npm install -g cnpm --registry=https://registry.npm.taobao.org [root@linux-node1 ~]# npm install -g grunt-cli --registry=https://registry.npm.taobao.org [root@linux-node1 ~]# grunt -version grunt-cli v1.2.0 [root@linux-node1 ~]# wget https://github.com/mobz/elasticsearch-head/archive/master.zip [root@linux-node1 ~]# unzip master.zip [root@linux-node1 ~]# cd elasticsearch-head-master/ [root@linux-node1 elasticsearch-head-master]# vim Gruntfile.js 90 connect: { 91 server: { 92 options: { 93 hostname: '192.168.56.11', 94 port: 9100, 95 base: '.', 96 keepalive: true 97 } 98 } 99 } [root@linux-node1 elasticsearch-head-master]# vim _site/app.js 4354 this.base_uri = this.config.base_uri || this.prefs.get("app-base_uri") || "http://192.168.56.11:9200"; [root@linux-node1 elasticsearch-head-master]# cnpm install [root@linux-node1 elasticsearch-head-master]# grunt --version grunt-cli v1.2.0 grunt v1.0.1 [root@linux-node1 elasticsearch-head-master]# vim /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml 90 # ---------------------------------- Head -------------------------------------增加如下两行: 91 # 92 http.cors.enabled: true 93 http.cors.allow-origin: "*" [root@linux-node1 elasticsearch-head-master]# systemctl restart elasticsearch [root@linux-node1 elasticsearch-head-master]# systemctl status elasticsearch [root@linux-node1 elasticsearch-head-master]# grunt server & (node:2833) ExperimentalWarning: The http2 module is an experimental API. Running "connect:server" (connect) task Waiting forever... Started connect web server on http://192.168.56.11:9100 注:在elasticsearch 2.x以前的版本可以通过/usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/plugin install mobz/elasticsearch-head来安装head插件,在elasticsearch 5.x以上版本需要通过npm进行安装。 浏览器访问:http://192.168.56.11:9100,可以看到各个节点的状态信息,如图:
三、logstash的安装
1、logstash介绍
Logstash是一个开源的数据收集引擎,可以水平伸缩,而且logstash是整个ELK当中拥有最多插件的一个组件,其可以接收来自不同源的数据并统一输入到指定的且可以是不同目的地。
logstash收集日志基本流程: input–>codec–>filter–>codec–>output
1.input:从哪里收集日志。
2.filter:发出去前进行过滤
3.output:输出至Elasticsearch或Redis消息队列
4.codec:输出至前台,方便边实践边测试
5.数据量不大日志按照月来进行收集
2、安装logstash
环境准备:关闭防火墙和Selinux,并且安装java环境 logstash下载地址:https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/logstash/logstash-6.0.0.rpm [root@linux-node1 ~]# wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/logstash/logstash-6.0.0.rpm [root@linux-node1 ~]# yum install -y logstash-6.0.0.rpm [root@linux-node1 ~]# rpm -ql logstash [root@linux-node1 ~]# chown -R logstash.logstash chown -R logstash.logstash /usr/share/logstash/data/queue #权限更改为logstash用户和组,否则启动的时候日志报错 #node2节点安装logstash [root@linux-node2 ~]# yum install -y logstash-6.0.0.rpm [root@linux-node1 ~]# ll /etc/logstash/conf.d/ #logstash的主配置目录 总用量 0
3、测试logstash是否正常
3.1、logstash的基本语法
input {
指定输入
}
output {
指定输出
}
3.2、测试标准输入输出
使用rubydebug方式前台输出展示以及测试
#标准输入输出 [root@linux-node1 ~]# /usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash -e 'input { stdin {} } output { stdout { codec => rubydebug} }' OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM warning: If the number of processors is expected to increase from one, then you should configure the number of parallel GC threads appropriately using -XX:ParallelGCThreads=N WARNING: Could not find logstash.yml which is typically located in $LS_HOME/config or /etc/logstash. You can specify the path using --path.settings. Continuing using the defaults Could not find log4j2 configuration at path /usr/share/logstash/config/log4j2.properties. Using default config which logs errors to the console The stdin plugin is now waiting for input: hello #输入 { "@version" => "1", #@version时间版本号,一个事件就是一个ruby对象 "host" => "linux-node1", #host标记事件发生在哪里 "@timestamp" => 2017-12-08T14:56:25.395Z, #@timestamp,用来标记当前事件发生的时间 "message" => "hello" #消息的具体内容 }
3.3、测试输出到文件
[root@linux-node1 ~]# /usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash -e 'input { stdin{} } output { file { path => "/tmp/test-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}.log"} }' OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM warning: If the number of processors is expected to increase from one, then you should configure the number of parallel GC threads appropriately using -XX:ParallelGCThreads=N WARNING: Could not find logstash.yml which is typically located in $LS_HOME/config or /etc/logstash. You can specify the path using --path.settings. Continuing using the defaults Could not find log4j2 configuration at path /usr/share/logstash/config/log4j2.properties. Using default config which logs errors to the console The stdin plugin is now waiting for input: hello world welcome to beijing! [root@linux-node1 ~]# tailf /tmp/test-2018.03.14.log {"@version":"1","host":"linux-node1","@timestamp":"2018-03-14T07:57:27.096Z","message":"hello world"} {"@version":"1","host":"linux-node1","@timestamp":"2018-03-14T07:58:29.074Z","message":"welcome to beijing!"} 开启gzip压缩输出 [root@linux-node1 ~]# /usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash -e 'input { stdin {} } outpu{ file { path => "/tmp/test-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}.log.tar.gz" gzip => true } }' OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM warning: If the number of processors is expected to increase from one, then you should configure the number of parallel GC threads appropriately using -XX:ParallelGCThreads=N what's your name? [root@linux-node1 ~]# ll /tmp/test-2018.03.14.log.tar.gz -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 117 3月 14 16:00 /tmp/test-2018.03.14.log.tar.gz
3.4、测试输出到elasticsearch
[root@linux-node1 ~]# /usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash -e 'input { stdin {} } output { elasticsearch { hosts => ["192.168.56.110:9200"] index => "logstash-test-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}" } }' OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM warning: If the number of processors is expected to increase from one, then you should configure the number of parallel GC threads appropriately using -XX:ParallelGCThreads=N WARNING: Could not find logstash.yml which is typically located in $LS_HOME/config or /etc/logstash. You can specify the path using --path.settings. Continuing using the defaults Could not find log4j2 configuration at path /usr/share/logstash/config/log4j2.properties. Using default config which logs errors to the console The stdin plugin is now waiting for input: what's your name ? my name is kim. 验证elasticsearch服务器收到数据 [root@linux-node1 ~]# ll /data/elkdata/nodes/0/indices/ 总用量 0 drwxr-xr-x 8 elasticsearch elasticsearch 65 3月 14 16:05 cV8nUO0WSkmR990aBH0RiA drwxr-xr-x 8 elasticsearch elasticsearch 65 3月 14 15:18 Rca-tNpDSt20jWxEheyIrQ
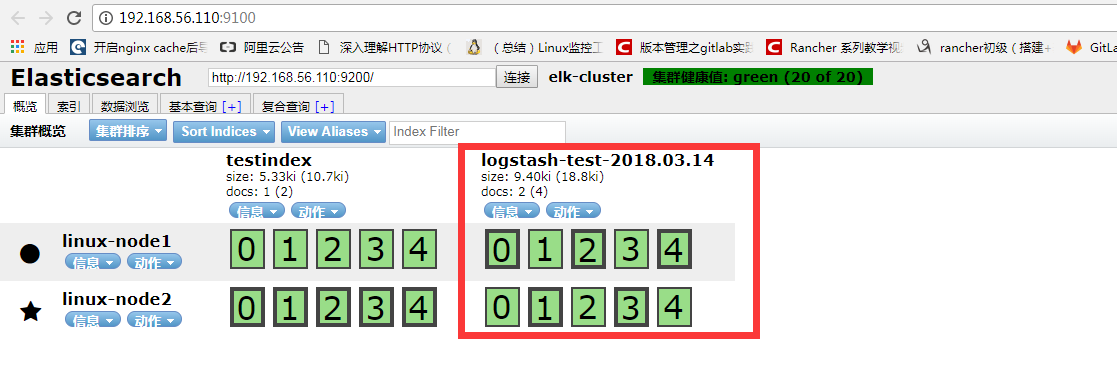

从head插件上可以看到有索引:logstash-test-2018-03-04,并且通过数据浏览可以看到刚才输入的数据。
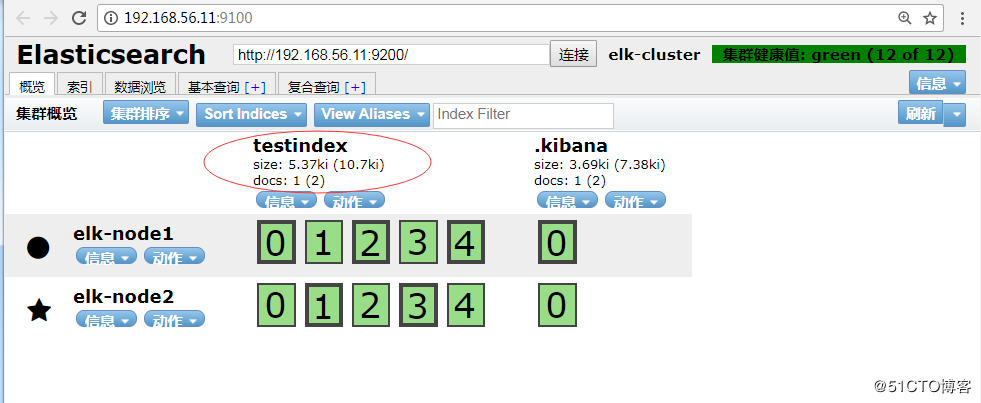
★★★★★
在该界面删除testindex,”动作”–>”删除”,再查看上面目录.
tips:在删除数据时,在该界面删除,切勿在上面的目录删除,因为集群节点上每个都有这样的数据,删除某一个,可能会导致elasticsearch无法启动。
四、Kibana安装
Kibana 是为 Elasticsearch 设计的开源分析和可视化平台。你可以使用 Kibana 来搜索,查看存储在 Elasticsearch 索引中的数据并与之交互。你可以很容易实现高级的数据分析和可视化,以图表的形式展现出来。
kiabana下载地址:https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/kibana/kibana-6.0.0-x86_64.rpm [root@linux-node1 ~]# wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/kibana/kibana-6.0.0-x86_64.rpm [root@linux-node1 ~]# yum install -y kibana-6.0.0-x86_64.rpm [root@linux-node1 ~]# vim /etc/kibana/kibana.yml [root@linux-node1 ~]# grep "^[a-Z]" /etc/kibana/kibana.yml server.port: 5601 #监听端口 server.host: "192.168.56.11" #监听IP地址,建议内网ip elasticsearch.url: "http://192.168.56.11:9200" #elasticsearch连接kibana的URL,也可以填写192.168.56.12,因为它们是一个集群 [root@linux-node1 ~]# systemctl enable kibana Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/kibana.service to /etc/systemd/system/kibana.service. [root@linux-node1 ~]# systemctl start kibana 监听端口为:5601 [root@linux-node1 ~]# ss -tnl State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port LISTEN 0 128 *:9100 *:* LISTEN 0 128 *:22 *:* LISTEN 0 100 127.0.0.1:25 *:* LISTEN 0 128 192.168.56.11:5601 *:* LISTEN 0 128 ::ffff:192.168.56.11:9200 :::* LISTEN 0 128 ::ffff:192.168.56.11:9300 :::* LISTEN 0 128 :::22 :::* LISTEN 0 100 ::1:25 :::* LISTEN 0 80 :::3306 :::*
浏览器访问192.168.56.11:5601,如图:
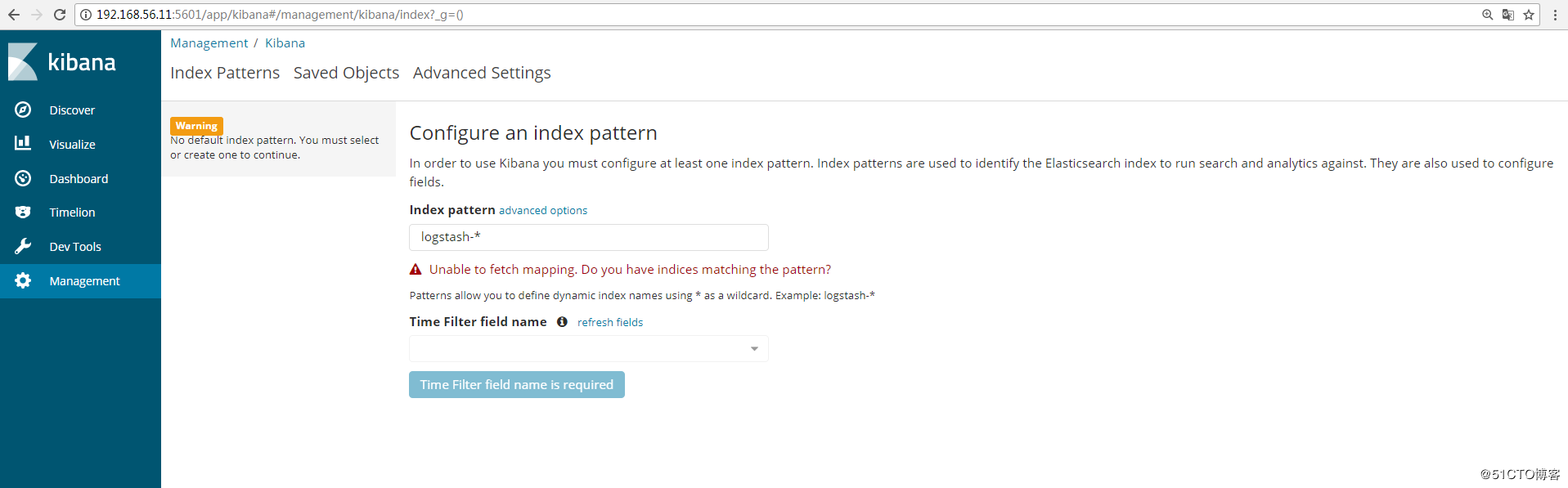
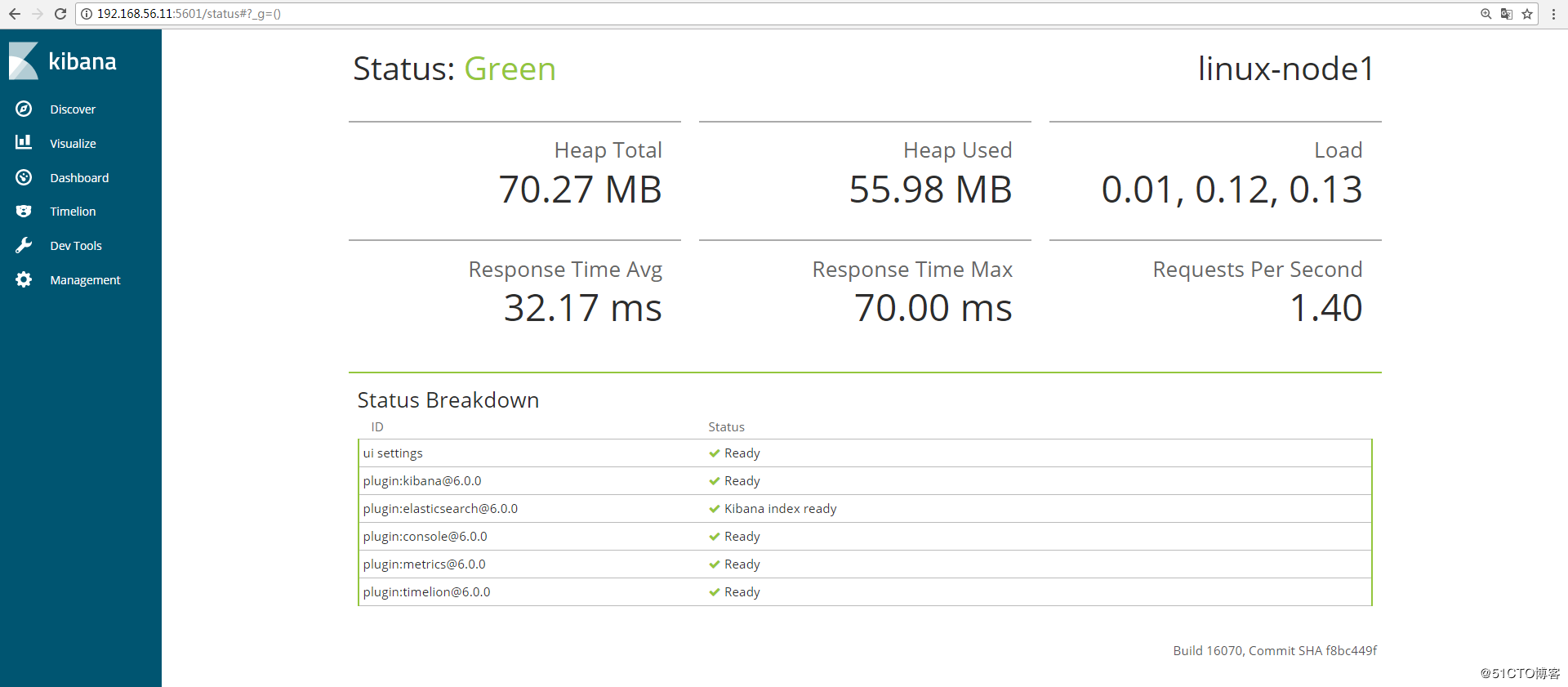
可以通过http://192.168.56.11:5601/status 来查看看是否正常,如果不正常,是无法进入到上图界面
五、通过配置logstash文件收集message日志
1、Kibana展示上一节的日志
在Kibana上展示上一节收集的日志信息,添加索引,如图:
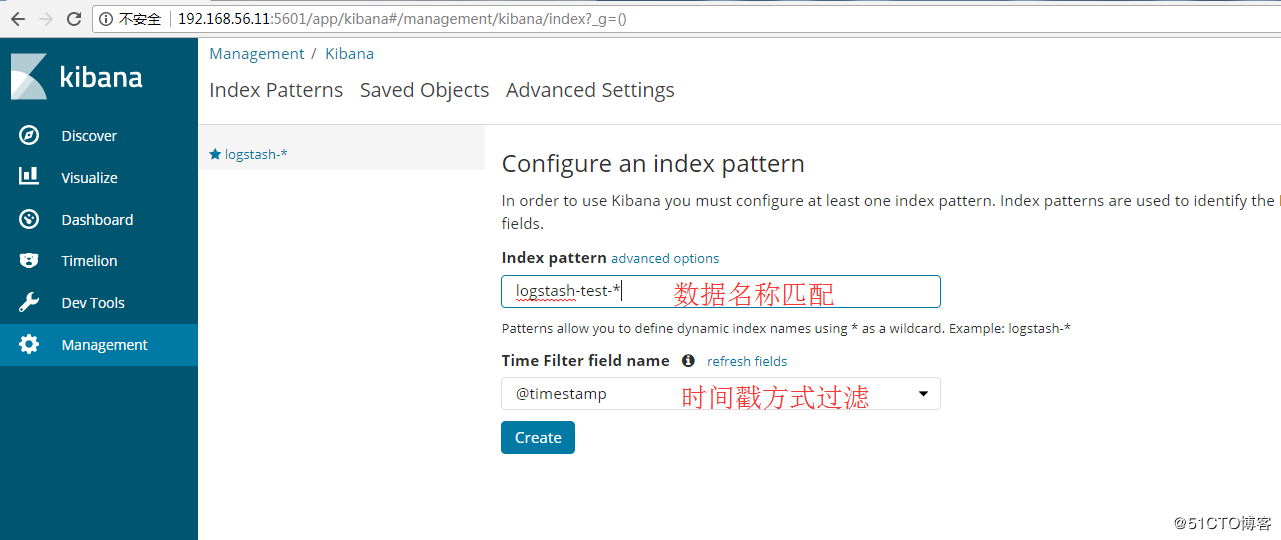
点击“discover”查看收集的信息,如图:

2、使用logstash配置文件收集messages日志
前提需要logstash用户对被收集的日志文件有读的权限并对写入的文件有写权限。
编辑logstash的配置文件: [root@linux-node1 ~]# vim /etc/logstash/conf.d/system.conf input { file { path => "/var/log/messages" #日志路径 type => "systemlog" #类型,自定义,在进行多个日志收集存储时可以通过该项进行判断输出 start_position => "beginning" #logstash 从什么位置开始读取文件数据,默认是结束位置(end),也就是说 logstash 进程会以类似 tail -F 的形式运行。如果你是要导入原有数据,把这个设定改成"beginning",logstash 进程就从头开始读取,类似 less +F 的形式运行。 stat_interval => "2" #logstash 每隔多久检查一次被监听文件状态(是否有更新) ,默认是 1 秒。 } } output { elasticsearch { hosts => ["192.168.56.11:9200"] #指定hosts index => "logstash-systemlog-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}" #索引名称 } } [root@linux-node1 ~]# /usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash -f /etc/logstash/conf.d/system.conf -t #检测配置文件是否有语法错误 OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM warning: If the number of processors is expected to increase from one, then you should configure the number of parallel GC threads appropriately using -XX:ParallelGCThreads=N WARNING: Could not find logstash.yml which is typically located in $LS_HOME/config or /etc/logstash. You can specify the path using --path.settings. Continuing using the defaults Could not find log4j2 configuration at path /usr/share/logstash/config/log4j2.properties. Using default config which logs errors to the console Configuration OK [root@linux-node1 ~]# ll /var/log/messages -rw-------. 1 root root 791209 12月 27 11:43 /var/log/messages #这里可以看到该日志文件是600权限,而elasticsearch是运行在elasticsearch用户下,这样elasticsearch是无法收集日志的。所以这里需要更改日志的权限,否则会报权限拒绝的错误。在日志中查看/var/log/logstash/logstash-plain.log 是否有错误。 [root@linux-node1 ~]# chmod 644 /var/log/messages [root@linux-node1 ~]# systemctl restart logstash
在管理界面查看是否有相应的索引(logstash-systemlog-2017.12.27),如图:

添加到Kibana中展示,创建索引:
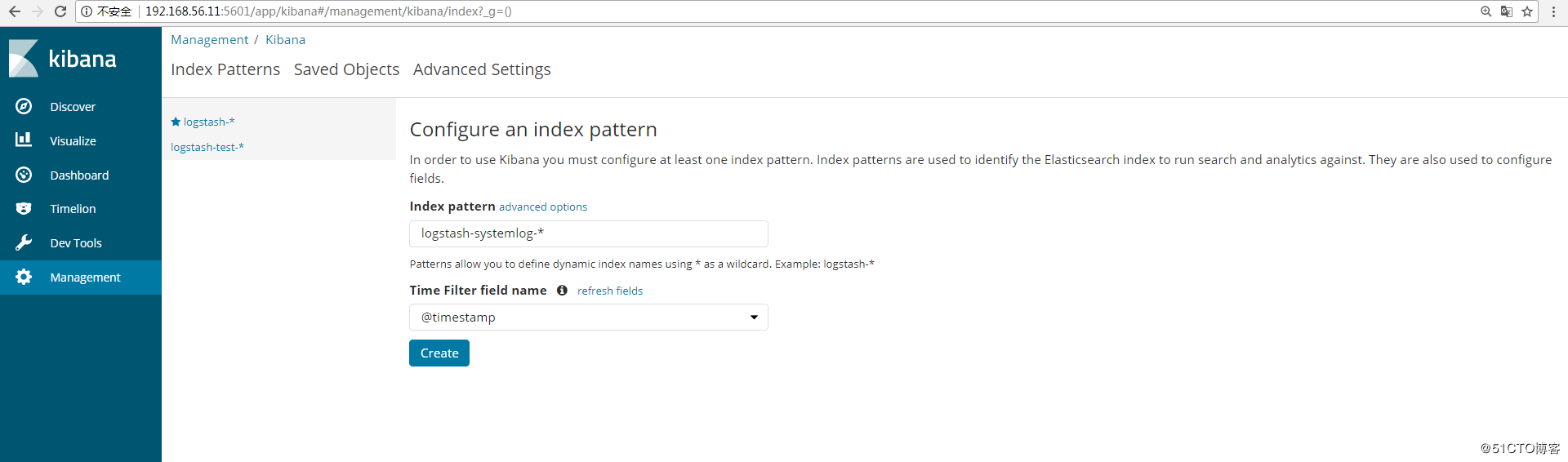
查看日志
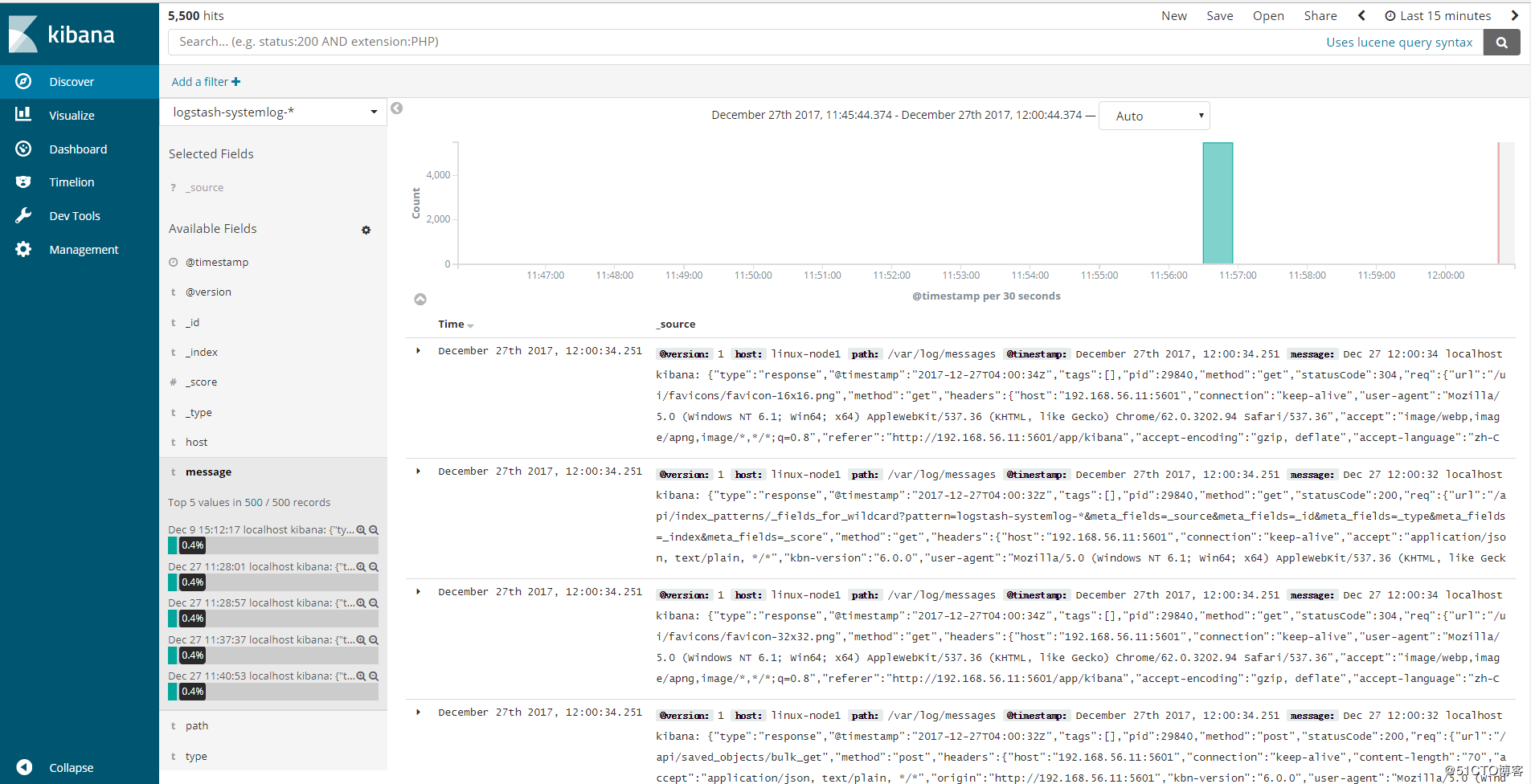
3、使用一个配置文件收集多个日志

修改logstash的配置文件,这里增加收集数据库mariadb的日志: [root@linux-node1 ~]# vim /etc/logstash/conf.d/system.conf input { file { path => "/var/log/messages" type => "systemlog" start_position => "beginning" stat_interval => "2" } file { path => "/var/log/mariadb/mariadb.log" type => "mariadblog" start_position => "beginning" stat_interval => "2" } } output { if [type] == "systemlog" { #使用if来判断类型,并输出到elasticsearch和file,展示一个out可以作多样输出 elasticsearch { hosts => ["192.168.56.11:9200"] index => "logstash-systemlog-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}" } file { path => "/tmp/logstash-systemlog-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}" }} if [type] == "mariadblog" { elasticsearch { hosts => ["192.168.56.11:9200"] index => "logstash-mariadblog-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}" } file { path => "/tmp/logstash-mariadblog-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}" }} } 配置文件检测语法是否正常: [root@linux-node1 ~]# /usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash -f /etc/logstash/conf.d/system.conf -t OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM warning: If the number of processors is expected to increase from one, then you should configure the number of parallel GC threads appropriately using -XX:ParallelGCThreads=N WARNING: Could not find logstash.yml which is typically located in $LS_HOME/config or /etc/logstash. You can specify the path using --path.settings. Continuing using the defaults Could not find log4j2 configuration at path /usr/share/logstash/config/log4j2.properties. Using default config which logs errors to the console Configuration OK 重启logstash: [root@linux-node1 ~]# systemctl restart logstash 修改mariadb的日志权限: [root@linux-node1 ~]# ll /var/log/mariadb/ -d drwxr-x--- 2 mysql mysql 24 12月 4 17:43 /var/log/mariadb/ [root@linux-node1 ~]# chmod 755 /var/log/mariadb/ [root@linux-node1 ~]# ll /var/log/mariadb/mariadb.log -rw-r----- 1 mysql mysql 114993 12月 27 14:23 /var/log/mariadb/mariadb.log [root@linux-node1 ~]# chmod 644 /var/log/mariadb/mariadb.log
通过head插件查看:
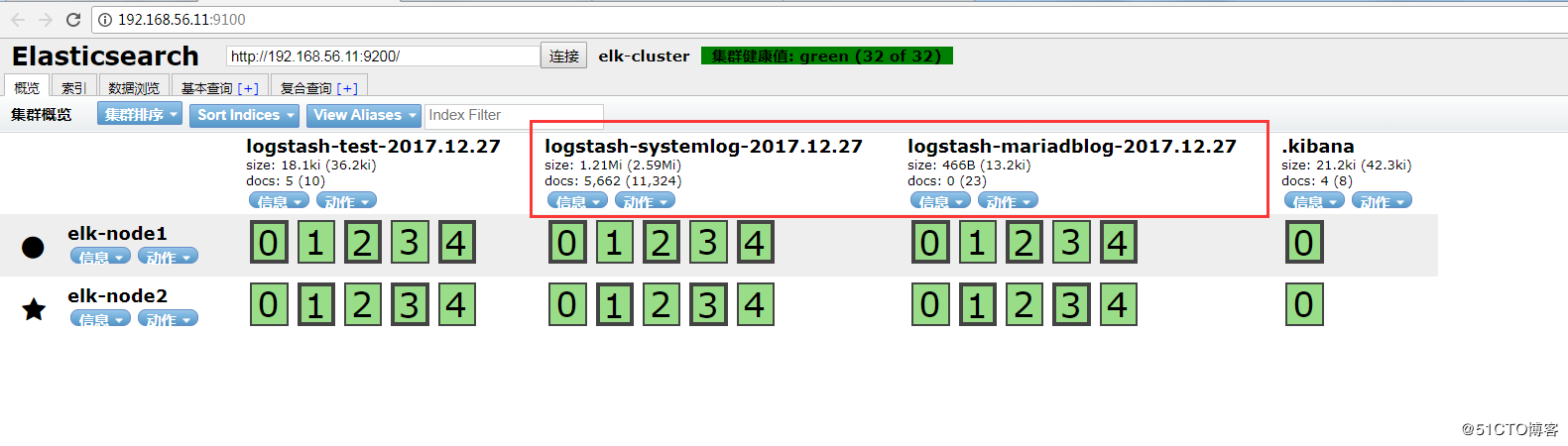
查看是否在/tmp下收集到了日志数据
[root@linux-node1 ~]# ll /tmp/logstash-* -rw-r--r-- 1 logstash logstash 288449 12月 27 14:27 /tmp/logstash-mariadblog-2017.12.27 -rw-r--r-- 1 logstash logstash 53385 12月 27 14:28 /tmp/logstash-systemlog-2017.12.27
Kibana创建索引:
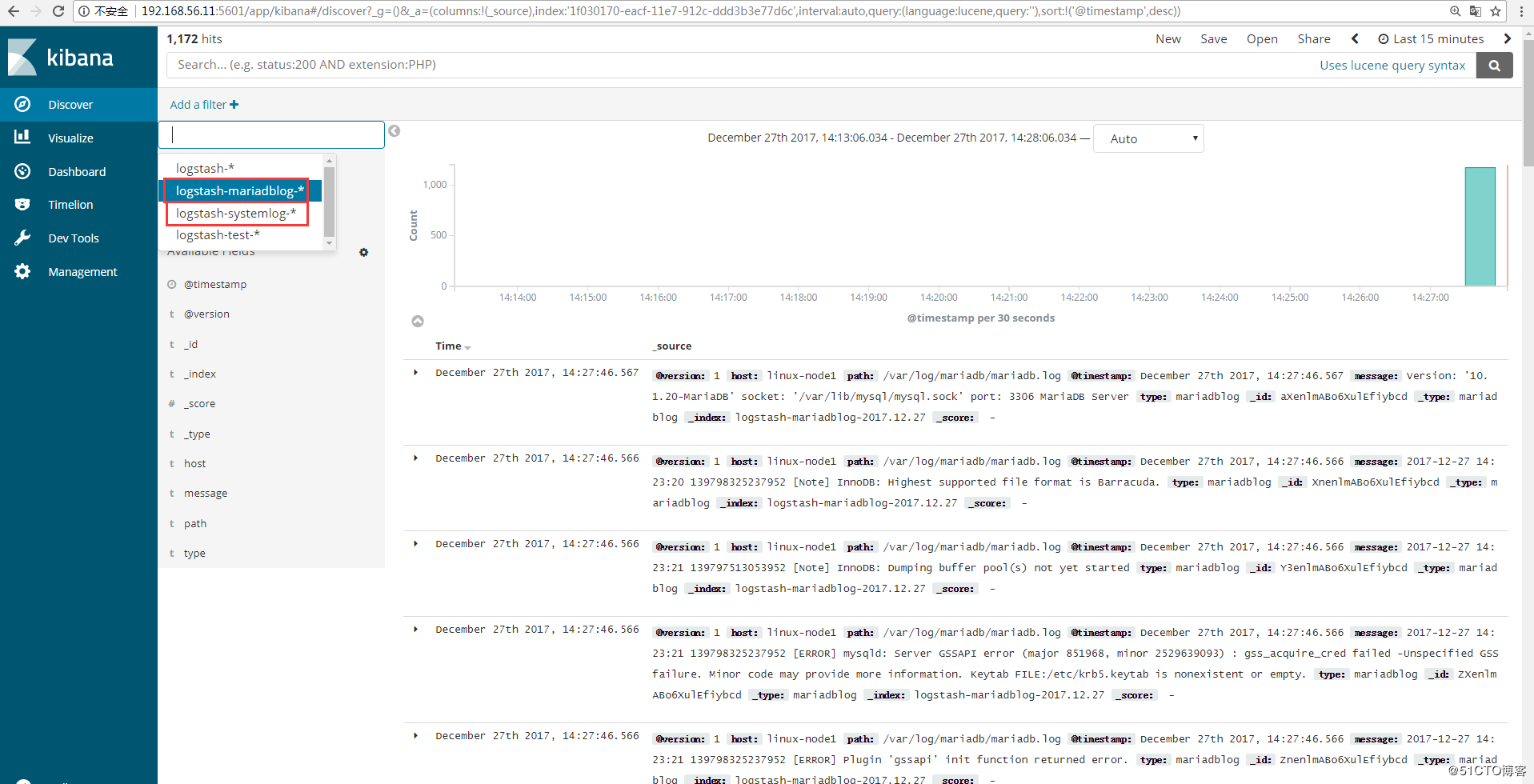



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号