Linux系统磁盘管理
一、Linux系统磁盘概念
磁盘的结构体系 01. 磁盘的物理结构 (外部结构 内部结构) 工作原理(先切换磁头 让磁头镜像运动) 02. 磁盘阵列说明 (raid0 raid1 raid5 raid10 raid01) 磁盘阵列如何配置 配置LVM L 逻辑 v 卷组 M 管理 逻辑卷管理 --> 实现可以随意调整磁盘分区大小 03. 磁盘分区概念 给容量较小的磁盘进行分区: 小于2T fdisk 给容量较大的磁盘进行分区: 大于2T parted 04. 磁盘格式化操作(创建文件系统) 05. 磁盘维护管理知识(如何使用磁盘 挂载使用)
磁盘层次结构详细说明--物理结构
1、磁盘的外部结构: 看的见摸得到的结构

组成部分 a 磁盘主轴 决定磁盘转速(rpm-round per minute) 家用磁盘转速 7200 rpm 5400 rpm 企业磁盘转速 15k rpm 10k rpm b 磁盘盘片 用于存储数据 c 磁盘磁头 用于读取数据 d 磁盘接口 用于连接主板 用于连接阵列卡
2、磁盘的内部结构: 看不见的结构信息
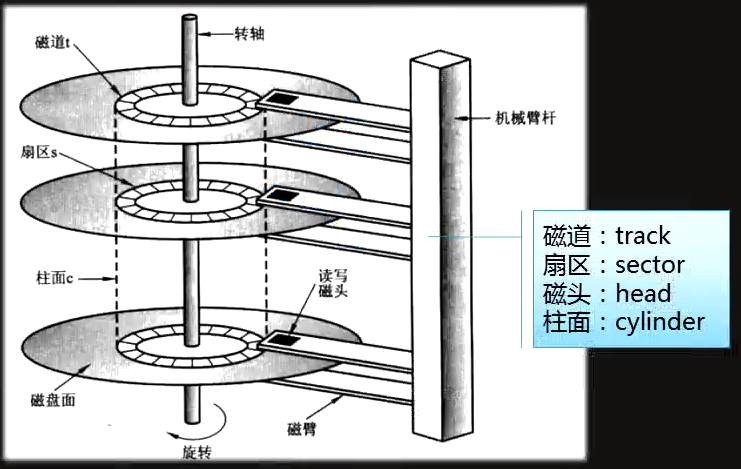
组成部分: a 磁盘(Disk) 磁盘或者分区的大小 = 柱面大小 * 柱面数 b 磁头(Head)(一个柱面有255个) 作用说明:用来写入和读取数据的 特点说明:盘面数量等于磁头数量 工作原理:采用径向运动读写数据 c 磁道(Track)每个磁道划分为63个扇区 作用说明:用来存储用户数据 特点说明:由多个同心圆组成 存储计数:最外面同心圆为0磁道 工作原理:磁盘默认按照磁道寻找数据 重点原理:磁头径向运动为机械运动(寻道) 性能小于固态硬盘(芯片) 原理特点:磁头机械运动较慢 d 扇区(Sector) 作用说明:用来存储用户数据 特点说明:磁盘存储最小单位 存储计数:默认磁盘扇区从1扇区开始,扇区大小为512字节 系统存储最小单位是block e 柱面(Cylinder) 一个柱面的大小=255*63*512字节=8M 作用说明:用来存储用户数据 特点说明:不同盘面上相同的磁道组成(圆柱体) 工作原理:磁盘默认按照柱面进行读写 重点原理:磁头之间的切换为电子切换 原理特点:磁头电子切换较快 f 单元块(Units) 作用说明:用来存储用户数据 特点说明:表示单个柱面大小
磁盘层次结构详细说明--磁盘阵列raid
阵列有什么用?
1) 提高磁盘存储效率
2) 提高磁盘存储安全
3) 提高磁盘存储容量
阵列的配置方法:
raid 0 存储数据效率高 存储安全性低
raid 1 存储数据效率低 存储安全性高
raid 5 存储数据效率较高 存储安全性较高
说明: 至少有3块磁盘 raid5阵列中只能最多坏一块磁盘 损耗一块磁盘的容量
300G 300G 300G --> raid5 --> 600G
LVM 实现分区可以弹性缩融 和 扩容
磁盘层次结构详细说明--磁盘分区方法
预备知识: a 系统启动引导记录-- MBR引导记录 用于引导磁盘空间小于2T GPT引导记录 用于引导磁盘空间大于2T b 分区方式 情况一: 可以划分4个主分区 /dev/sda /dev/sda1 .. sda4 mount /dev/sda1 /mnt 情况二: 可以划分3个主分区 /dev/sda /dev/sda1 .. sda3 可以划分1个扩展分区 扩展分区无法直接使用 需要在扩展分区基础上划分逻辑分区: /dev/sda5 /dev/sda6 ...
二、磁盘层次结构--磁盘分区方法

情况一: 磁盘分区实践--磁盘小于2T 第一个里程: 准备磁盘环境 准备了一块新的10G硬盘 第二个里程: 在系统中检查是否识别到了新的硬盘 检查是否有新的磁盘存储文件 [root@oldboyedu ~]# ll /dev/sdb brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 16 Apr 28 08:54 /dev/sdb 第三个里程: 对磁盘进行分区处理(fdisk-- 进行分区处理 查看分区信息) fdisk -l --- 查看分区信息 [root@oldboyedu ~]# fdisk /dev/sdb Welcome to fdisk (util-linux 2.23.2). Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them. Be careful before using the write command. Device does not contain a recognized partition table Building a new DOS disklabel with disk identifier 0x6c918c6d. Command (m for help): 可以对磁盘进行分区了 Command action d delete a partition ***** 删除分区 g create a new empty GPT partition table 创建一个新的空的GPT分区表(可以对大于2T磁盘进行分区) l list known partition types 列出可以分区的类型??? m print this menu 输出帮助菜单 n add a new partition ***** 新建增加一个分区 p print the partition table ***** 输出分区的结果信息 q quit without saving changes 不保存退出 t change a partition's system id 改变分区的系统id==改变分区类型(LVM 增加swap分区大小) u change display/entry units 改变分区的方式 是否按照扇区进行划分 w write table to disk and exit ***** 将分区的信息写入分区表并退出==保存分区信息并退出 开始分区: a 规划分4个主分区 每个分区1G 分区操作过程 Command (m for help): n Partition type: p primary (0 primary, 0 extended, 4 free) e extended Select (default p): p Partition number (1-4, default 1): 1 First sector (2048-20971519, default 2048): Using default value 2048 Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (2048-20971519, default 20971519): +1G Partition 1 of type Linux and of size 1 GiB is set 分区操作检查: Command (m for help): p Disk /dev/sdb: 10.7 GB, 10737418240 bytes, 20971520 sectors Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk label type: dos Disk identifier: 0x3069f1dd Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System /dev/sdb1 2048 2099199 1048576 83 Linux /dev/sdb2 2099200 4196351 1048576 83 Linux /dev/sdb3 4196352 6293503 1048576 83 Linux /dev/sdb4 6293504 8390655 1048576 83 Linux Command (m for help): n If you want to create more than four partitions, you must replace a primary partition with an extended partition first. b 规划分3个主分区 1个扩展分区 每个主分区1G 剩余都给扩展分区 删除分区 Command (m for help): d Partition number (1-4, default 4): 1 Partition 1 is deleted 创建逻辑分区 Command (m for help): p Disk /dev/sdb: 10.7 GB, 10737418240 bytes, 20971520 sectors Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk label type: dos Disk identifier: 0x3069f1dd Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System /dev/sdb1 2048 2099199 1048576 83 Linux /dev/sdb2 2099200 4196351 1048576 83 Linux /dev/sdb3 4196352 6293503 1048576 83 Linux /dev/sdb4 6293504 20971519 7339008 5 Extended 有了扩展分区才能逻辑分区 Command (m for help): n All primary partitions are in use Adding logical partition 5 First sector (6295552-20971519, default 6295552): Using default value 6295552 Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (6295552-20971519, default 20971519): +1G Partition 5 of type Linux and of size 1 GiB is set Command (m for help): p Disk /dev/sdb: 10.7 GB, 10737418240 bytes, 20971520 sectors Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk label type: dos Disk identifier: 0x3069f1dd Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System /dev/sdb1 2048 2099199 1048576 83 Linux /dev/sdb2 2099200 4196351 1048576 83 Linux /dev/sdb3 4196352 6293503 1048576 83 Linux /dev/sdb4 6293504 20971519 7339008 5 Extended /dev/sdb5 6295552 8392703 1048576 83 Linux 第四个里程: 保存退出,让系统可以加载识别分区信息 让系统可以加载识别分区文件 partprobe /dev/sdb

情况二: 磁盘分区实践--磁盘大于2T 第一个里程: 准备磁盘环境 虚拟主机中添加一块3T硬盘 第二个里程: 使用parted命令进行分区 mklabel,mktable LABEL-TYPE create a new disklabel (partition table) 创建一个分区表 (默认为mbr) print [devices|free|list,all|NUMBER] display the partition table, available devices, free space, all found partitions, or a particular partition 显示分区信息 mkpart PART-TYPE [FS-TYPE] START END make a partition 创建一个分区 quit exit program 退出分区状态 rm NUMBER delete partition NUMBER 删除分区 修改磁盘分区类型: mklabel gpt 分区方法: mkpart primary 0 2100G 第三个里程: 加载磁盘分区 partprobe /dev/sdc
三、磁盘层次结构--格式化操作(创建文件系统)
mkfs.xfs /dev/sdb1 mkfs -t xfs /dev/sdb2 创建文件系统: 磁盘分区存储数据的方式 ext3/4 centos6 xfs centos7 格式效率较高 数据存储效率提升(数据库服务器) [root@oldboyedu /]# mkfs.xfs /dev/sdb2 meta-data=/dev/sdb2 isize=512 agcount=4, agsize=65536 blks = sectsz=512 attr=2, projid32bit=1 = crc=1 finobt=0, sparse=0 data = bsize=4096 blocks=262144, imaxpct=25 = sunit=0 swidth=0 blks naming =version 2 bsize=4096 ascii-ci=0 ftype=1 log =internal log bsize=4096 blocks=2560, version=2 = sectsz=512 sunit=0 blks, lazy-count=1 realtime =none extsz=4096 blocks=0, rtextents=0
四、磁盘层次结构--磁盘挂载应用
mount /dev/sdb1 /mount01 mount /dev/sdb2 /mount02 检查确认: [root@oldboyedu /]# df -h /dev/sdb1 1014M 33M 982M 4% /mount01 /dev/sdb2 1014M 33M 982M 4% /mount02
文件查看方式
cat /proc/mounts
/dev/sda1 /boot xfs rw,seclabel,relatime,attr2,inode64,noquota 0 0
如何实现开机自动挂载: 方法一: 将挂载命令放入/etc/rc.local [root@oldboyedu /]# tail -2 /etc/rc.local mount /dev/sdb1 /mount01 mount /dev/sdb2 /mount02 系统开机加载rc.local流程: 加载/etc/rc.local --> /etc/rc.d/rc.local --> 以绝对路径方式执行 /etc/rc.d/rc.local chmod +x /etc/rc.d/rc.local 方法二: 在/etc/fstab文件中进行设置 UUID=e2fc8646-2b36-47cc-a35a-8c13208f4d0b / xfs defaults 0 0 UUID=34fc45ba-c38c-42bc-a120-90f9d5dd2382 /boot xfs defaults 0 0 UUID=62100743-6f8a-4f83-a37d-e2088c4830e2 swap swap defaults 0 0 挂载磁盘文件(存储设备) 挂载点 指定文件系统类型 挂载的参数 是否备份磁盘 是否检查磁盘 mount 挂载的磁盘文件 挂载点 [root@oldboyedu ~]# tail -2 /etc/fstab /dev/sdb1 /mount01 xfs defaults 0 0 UUID=144738ff-0da3-4162-b574-40af379cbe9e /mount02 xfs defaults 0 0
五、企业磁盘常见问题
1) 磁盘满的情况 No space left on device a 存储的数据过多了 模拟磁盘空间不足 dd if=/dev/zero of=/tmp/oldboy.txt bs=10M count=100 block存储空间不足了 解决方式: 1.删除没用的数据 2.找出大的没用的数据 find / -type f -size +xxx du -sh /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/*|sort -h 补充: 按照数值排序命令 [root@oldboyedu mount01]# cat num.txt |sort -n # 1 # 10 # 11 # 12 # 2 # 3 # 6 # 9 [root@oldboyedu mount01]# cat num.txt |sort -n -k2 # 1 # 2 # 3 # 6 # 9 # 10 # 11 # 12 b 存储的数据过多了 inode存储空间不足了: 出现了大量小文件
六、如何调整swap分区大小
第一个历程: 将磁盘分出一部分空间给swap分区使用 dd if=/dev/zero of=/tmp/1G bs=100M count=10 第二个历程: 将指定磁盘空间作为swap空间使用 [root@oldboyedu tmp]# mkswap /tmp/1G Setting up swapspace version 1, size = 1023996 KiB no label, UUID=6dd70684-dec2-48cf-8fd9-f311548bbb4f 第三个历程: 加载使用swap空间 [root@oldboyedu tmp]# swapon /tmp/1G swapon: /tmp/1G: insecure permissions 0644, 0600 suggested. [root@oldboyedu tmp]# free -h total used free shared buff/cache available Mem: 1.9G 225M 575M 9.6M 1.2G 1.5G Swap: 2.0G 0B 2.0G [root@oldboyedu tmp]# swapoff /tmp/1G [root@oldboyedu tmp]# free -h total used free shared buff/cache available Mem: 1.9G 224M 576M 9.6M 1.2G 1.5G Swap: 1.0G 0B 1.0G [root@oldboyedu tmp]# rm /tmp/1G -f
Linux inode
https://www.cnblogs.com/llife/p/11470668.html
fdisk -l显示信息详解
[root@www.linuxidc.com ~]# fdisk -l
Disk /dev/sda: 10.7 GB, 10737418240 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 1305 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0x00044938
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sda1 * 1 638 5120000 83 Linux
Partition 1 does not end on cylinder boundary.
/dev/sda2 638 893 2048000 83 Linux
Partition 2 does not end on cylinder boundary.
/dev/sda3 893 1020 1024000 82 Linux swap / Solaris
Partition 3 does not end on cylinder boundary.
/dev/sda4 1020 1306 2292736 5 Extended
/dev/sda5 1021 1306 2291712 83 Linux
解析:
Disk /dev/sda: 10.7 GB, 10737418240 bytes
块设备名称为/dev/sda,此设备的大小为10.7GB,这个数字不是特别精确,我系统是10GB;10737418240 bytes这是转换成字节后的大小,即:10737418240/1024/1024/1024=10GB (注:bytes=B,表示“字节”,bit=b,表示“位”)
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 1305 cylinders
255 heads:表示磁头数为255
63 sectors/track:表示每磁道上有63个扇区
1305 cylinders:表示共有1305个柱面,柱面是分区的最小单位
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
16065=255*63 因为每一个磁头都是在同一个柱面的,63表示每个磁道上的扇区数量,这两个数的乘积表示一个柱面上的扇区数量;所以16065*512表示一个柱面的大小是8225280字节
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
表示一个扇区的大小是512字节
总结:所以一个磁盘的大小=一个柱面大小*柱面的总数=磁头数量*每个磁道上的扇区数*一个扇区大小*柱面总数
即:磁盘大小=8225280*1305=10733990400bytes=9.99GB=255*63*512*1305
上例中显示出我们的磁盘只有1305个柱面,但下边的分区信息中出现了1306个柱面数,不必太在意,linux显示的这些数据不会十分精确。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号