Linux 需要掌握的一些命令
摘要:
先来看下百度百科的介绍:Linux是一套免费使用和自由传播的类Unix操作系统,是一个基于POSIX和UNIX的多用户、多任务、支持多线程和多CPU的操作系统。它能运行主要的UNIX工具软件、应用程序和网络协议。它支持32位和64位硬件。Linux继承了Unix以网络为核心的设计思想,是一个性能稳定的多用户网络操作系统。先把图片给大家把,图片单击可以放大,也可以自己保存本地查看!图片来源于网络!
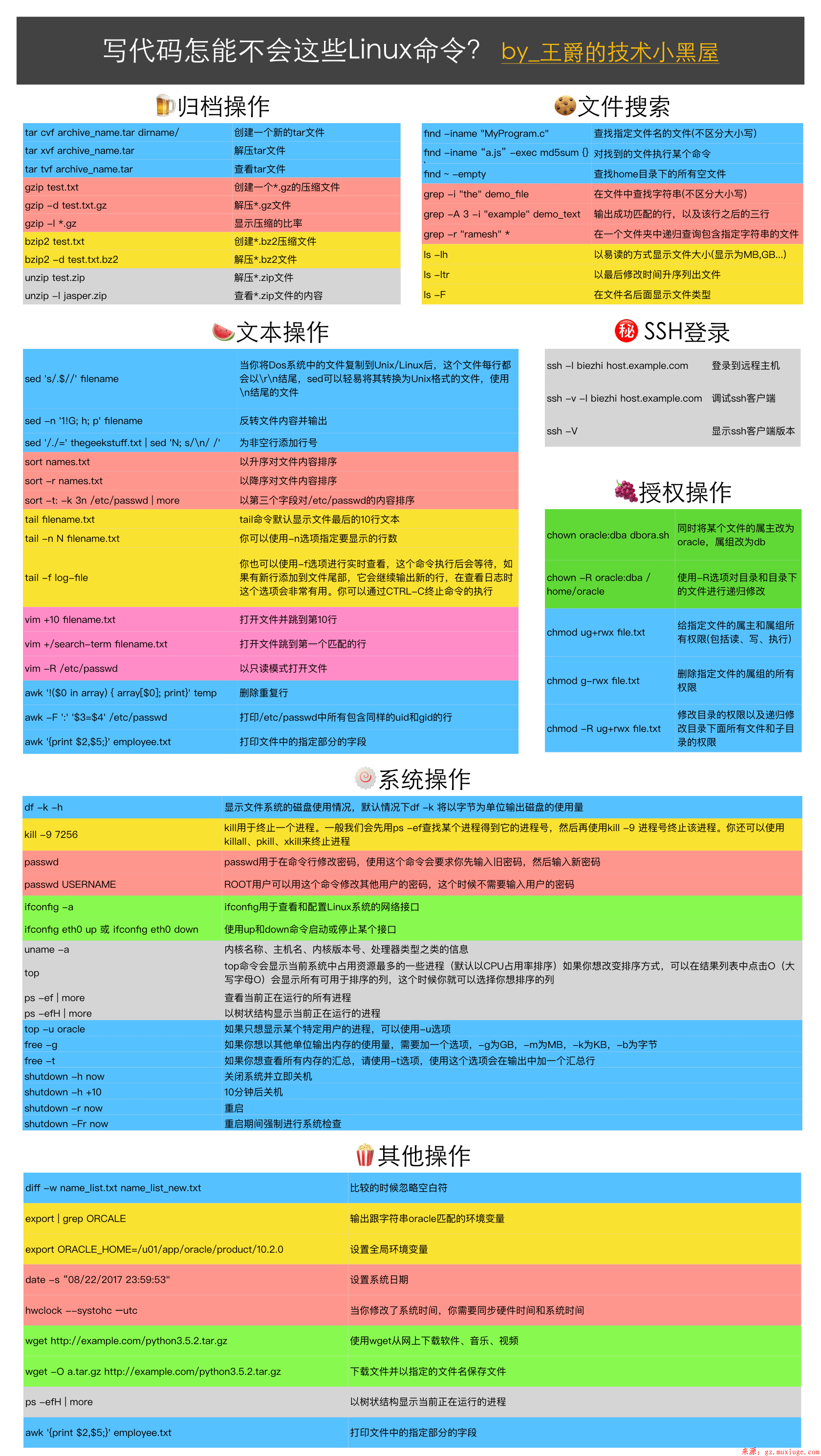 以下为大家准备了常见的命令使用和介绍供大家参考。
以下为大家准备了常见的命令使用和介绍供大家参考。
1. tar
创建一个新的tar文件
Bash
copy$ tar cvf archive_name.tar dirname/
解压tar文件
Bash
copy
$ tar xvf archive_name.tar
查看tar文件
Bash
copy
$ tar tvf archive_name.tar
2. grep
在文件中查找字符串(不区分大小写)
Bash
copy$ grep -i "the" demo_file
输出成功匹配的行,以及该行之后的三行
Bash
copy$ grep -A 3 -i "example" demo_text
在一个文件夹中递归查询包含指定字符串的文件
Bash
copy$ grep -r "ramesh" *
3. find
查找指定文件名的文件(不区分大小写)
Bash
copy$ find -iname "MyProgram.c"
对找到的文件执行某个命令
Bash
copy$ find -iname "MyProgram.c" -exec md5sum {} \;
查找home目录下的所有空文件
Bash
copy
$ find ~ -empty
4. ssh
登录到远程主机
Bash
copy
$ ssh -l jsmith remotehost.example.com
调试ssh客户端
Bash
copy
$ ssh -v -l jsmith remotehost.example.com
显示ssh客户端版本
Bash
copy
$ ssh -V
5. sed
当你将Dos系统中的文件复制到Unix/Linux后,这个文件每行都会以\r\n结尾,sed可以轻易将其转换为Unix格式的文件,使用\n结尾的文件
Bash
copy$ sed 's/.$//' filename
反转文件内容并输出
$ sed -n '1!G; h; p' filename
为非空行添加行号
Bash
copy$ sed '/./=' thegeekstuff.txt | sed 'N; s/\n/ /'
6. awk
删除重复行
Bash
copy$ awk '!($0 in array) { array[$0]; print}' temp
打印/etc/passwd中所有包含同样的uid和gid的行
Bash
copy$ awk -F ':' '$3=$4' /etc/passwd
打印文件中的指定部分的字段
Bash
copy$ awk '{print $2,$5;}' employee.txt
7. vim
打开文件并跳到第10行
Bash
copy
$ vim +10 filename.txt
打开文件跳到第一个匹配的行
Bash
copy
$ vim +/search-term filename.txt
以只读模式打开文件
Bash
copy
$ vim -R /etc/passwd
8. diff
比较的时候忽略空白符
Bash
copy
$ diff -w name_list.txt name_list_new.txt
9. sort
以升序对文件内容排序
Bash
copy$ sort names.txt
以降序对文件内容排序
Bash
copy$ sort -r names.txt
以第三个字段对/etc/passwd的内容排序
Bash
copy$ sort -t: -k 3n /etc/passwd | more
10. export
输出跟字符串oracle匹配的环境变量
Bash
copy$ export | grep ORCALE declare -x ORACLE_BASE="/u01/app/oracle" declare -x ORACLE_HOME="/u01/app/oracle/product/10.2.0" declare -x ORACLE_SID="med" declare -x ORACLE_TERM="xterm"
设置全局环境变量
Bash
copy$ export ORACLE_HOME=/u01/app/oracle/product/10.2.0
11. xargs
将所有图片文件拷贝到外部驱动器
Bash
copy$ ls *.jpg | xargs -n1 -i cp {} /external-hard-drive/directory
将系统中所有jpd文件压缩打包
Bash
copy$ find / -name *.jpg -type f -print | xargs tar -cvzf images.tar.gz
下载文件中列出的所有url对应的页面
Bash
copy$ cat url-list.txt | xargs wget –c
12. ls
以易读的方式显示文件大小(显示为MB,GB...)
Bash
copy$ ls -lh -rw-r----- 1 ramesh team-dev 8.9M Jun 12 15:27 arch-linux.txt.gz
以最后修改时间升序列出文件
Bash
copy$ ls -ltr
在文件名后面显示文件类型
Bash
copy$ ls -F
13. pwd
输出当前工作目录
14. cd
cd -可以在最近工作的两个目录间切换
使用shopt -s cdspell可以设置自动对cd命令进行拼写检查
15. gzip
创建一个*.gz的压缩文件
Bash
copy
$ gzip test.txt
解压*.gz文件
Bash
copy
$ gzip -d test.txt.gz
显示压缩的比率
Bash
copy
$ gzip -l *.gz compressed uncompressed ratio uncompressed_name 23709 97975 75.8% asp-patch-rpms.txt
16. bzip2
创建*.bz2压缩文件
Bash
copy
$ bzip2 test.txt
解压*.bz2文件
Bash
copy
bzip2 -d test.txt.bz2
17. uzip
解压*.zip文件
Bash
copy
$ unzip test.zip
查看*.zip文件的内容
Bash
copy
$ unzip -l jasper.zip Archive: jasper.zip Length Date Time Name -------- ---- ---- ---- 40995 11-30-98 23:50 META-INF/MANIFEST.MF 32169 08-25-98 21:07 classes_ 15964 08-25-98 21:07 classes_names 10542 08-25-98 21:07 classes_ncomp
18. shutdown
关闭系统并立即关机
Bash
copy
$ shutdown -h now
10分钟后关机
Bash
copy
$ shutdown -h +10
重启
Bash
copy
$ shutdown -r now
重启期间强制进行系统检查
Bash
copy
$ shutdown -Fr now
19. ftp
ftp命令和sftp命令的用法基本相似连接ftp服务器并下载多个文件
Bash
copy
$ ftp IP/hostname ftp> mget *.html
显示远程主机上文件列表
Bash
copy
ftp> mls *.html - /ftptest/features.html /ftptest/index.html /ftptest/othertools.html /ftptest/samplereport.html /ftptest/usage.html
20. crontab
查看某个用户的crontab入口
Bash
copy
$ crontab -u john -l
设置一个每十分钟执行一次的计划任务
Bash
copy
*/10 * * * * /home/ramesh/check-disk-space
21. service
service命令用于运行System V init脚本,这些脚本一般位于/etc/init.d文件下,这个命令可以直接运行这个文件夹里面的脚本,而不用加上路径
查看服务状态
Bash
copy
$ service ssh status
查看所有服务状态
Bash
copy
$ service --status-all
重启服务
Bash
copy
$ service ssh restart
22. ps
ps命令用于显示正在运行中的进程的信息,ps命令有很多选项,这里只列出了几个
查看当前正在运行的所有进程
Bash
copy
$ ps -ef | more
以树状结构显示当前正在运行的进程,H选项表示显示进程的层次结构
Bash
copy
$ ps -efH | more
23. free
这个命令用于显示系统当前内存的使用情况,包括已用内存、可用内存和交换内存的情况
默认情况下free会以字节为单位输出内存的使用量
Bash
copy
$ free total used free shared buffers cached Mem: 3566408 1580220 1986188 0 203988 902960 -/+ buffers/cache: 473272 3093136 Swap: 4000176 0 4000176
如果你想以其他单位输出内存的使用量,需要加一个选项,-g为GB,-m为MB,-k为KB,-b为字节
Bash
copy
$ free -g total used free shared buffers cached Mem: 3 1 1 0 0 0 -/+ buffers/cache: 0 2 Swap: 3 0 3
如果你想查看所有内存的汇总,请使用-t选项,使用这个选项会在输出中加一个汇总行
Bash
copy
$ free -t total used free shared buffers cached Mem: 3566408 1592148 1974260 0 204260 912556 -/+ buffers/cache: 475332 3091076 Swap: 4000176 0 4000176 Total: 7566584 1592148 5974436
24. top
top命令会显示当前系统中占用资源最多的一些进程(默认以CPU占用率排序)如果你想改变排序方式,可以在结果列表中点击O(大写字母O)会显示所有可用于排序的列,这个时候你就可以选择你想排序的列
Bash
copyCurrent Sort Field: P for window 1:Def Select sort field via field letter, type any other key to return a: PID = Process Id v: nDRT = Dirty Pages count d: UID = User Id y: WCHAN = Sleeping in Function e: USER = User Name z: Flags = Task Flags ........
如果只想显示某个特定用户的进程,可以使用-u选项
Bash
copy
$ top -u oracle
25. df
显示文件系统的磁盘使用情况,默认情况下df -k 将以字节为单位输出磁盘的使用量
Bash
copy$ df -k Filesystem 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on /dev/sda1 29530400 3233104 24797232 12% / /dev/sda2 120367992 50171596 64082060 44% /home
使用-h选项可以以更符合阅读习惯的方式显示磁盘使用量
Bash
copy$ df -h Filesystem Size Used Avail Capacity iused ifree %iused Mounted on /dev/disk0s2 232Gi 84Gi 148Gi 37% 21998562 38864868 36% / devfs 187Ki 187Ki 0Bi 100% 648 0 100% /dev map -hosts 0Bi 0Bi 0Bi 100% 0 0 100% /net map auto_home 0Bi 0Bi 0Bi 100% 0 0 100% /home /dev/disk0s4 466Gi 45Gi 421Gi 10% 112774 440997174 0% /Volumes/BOOTCAMP //app@izenesoft.cn/public 2.7Ti 1.3Ti 1.4Ti 48% 0 18446744073709551615 0% /Volumes/public
使用-T选项显示文件系统类型
Bash
copy$ df -T Filesystem Type 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on /dev/sda1 ext4 29530400 3233120 24797216 12% / /dev/sda2 ext4 120367992 50171596 64082060 44% /home
26. kill
kill用于终止一个进程。一般我们会先用ps -ef查找某个进程得到它的进程号,然后再使用kill -9 进程号终止该进程。你还可以使用killall、pkill、xkill来终止进程
Bash
copy$ ps -ef | grep vim ramesh 7243 7222 9 22:43 pts/2 00:00:00 vim $ kill -9 7243
27. rm
删除文件前先确认
Bash
copy$ rm -i filename.txt
在文件名中使用shell的元字符会非常有用。删除文件前先打印文件名并进行确认
Bash
copy$ rm -i file*
递归删除文件夹下所有文件,并删除该文件夹
Bash
copy$ rm -r example
28. cp
拷贝文件1到文件2,并保持文件的权限、属主和时间戳
Bash
copy$ cp -p file1 file2
拷贝file1到file2,如果file2存在会提示是否覆盖
Bash
copy$ cp -i file1 file2
29. mv
将文件名file1重命名为file2,如果file2存在则提示是否覆盖
Bash
copy$ mv -i file1 file2
注意如果使用-f选项则不会进行提示
-v会输出重命名的过程,当文件名中包含通配符时,这个选项会非常方便
Bash
copy$ mv -v file1 file2
30. cat
你可以一次查看多个文件的内容,下面的命令会先打印file1的内容,然后打印file2的内容
Bash
copy$ cat file1 file2
-n命令可以在每行的前面加上行号
Bash
copy$ cat -n /etc/logrotate.conf /var/log/btmp { missingok 3 monthly 4 create 0660 root utmp 5 rotate 1 6 }
31. mount
如果要挂载一个文件系统,需要先创建一个目录,然后将这个文件系统挂载到这个目录上
Bash
copy# mkdir /u01 # mount /dev/sdb1 /u01
也可以把它添加到fstab中进行自动挂载,这样任何时候系统重启的时候,文件系统都会被加载
Bash
copy
/dev/sdb1 /u01 ext2 defaults 0 2
32. chmod
chmod用于改变文件和目录的权限
给指定文件的属主和属组所有权限(包括读、写、执行)
Bash
copy$ chmod ug+rwx file.txt
删除指定文件的属组的所有权限
Bash
copy$ chmod g-rwx file.txt
修改目录的权限,以及递归修改目录下面所有文件和子目录的权限
Bash
copy$ chmod -R ug+rwx file.txt
33. chown
chown用于改变文件属主和属组
同时将某个文件的属主改为oracle,属组改为db
Bash
copy$ chown oracle:dba dbora.sh
使用-R选项对目录和目录下的文件进行递归修改
Bash
copy$ chown -R oracle:dba /home/oracle
34. passwd
passwd用于在命令行修改密码,使用这个命令会要求你先输入旧密码,然后输入新密码
Bash
copy
$ passwd
超级用户可以用这个命令修改其他用户的密码,这个时候不需要输入用户的密码
Bash
copy# passwd USERNAME
passwd还可以删除某个用户的密码,这个命令只有root用户才能操作,删除密码后,这个用户不需要输入密码就可以登录到系统
Bash
copy# passwd -d USERNAME
35. mkdir
在home目录下创建一个名为temp的目录
Bash
copy$ mkdir ~/temp
使用-p选项可以创建一个路径上所有不存在的目录
Bash
copy$ mkdir -p dir1/dir2/dir3/dir4/
36. ifconfig
ifconfig用于查看和配置Linux系统的网络接口
查看所有网络接口及其状态
Bash
copy
$ ifconfig -a
使用up和down命令启动或停止某个接口
Bash
copy
$ ifconfig eth0 up
Bash
copy
$ ifconfig eth0 down
37. uname
uname可以显示一些重要的系统信息,例如内核名称、主机名、内核版本号、处理器类型之类的信息
Bash
copy$ uname -a Linux john-laptop 2.6.32-24-generic #41-Ubuntu SMP Thu Aug 19 01:12:52 UTC 2010 i686 GNU/Linux
38. whereis
当你不知道某个命令的位置时可以使用whereis命令,下面使用whereis查找ls的位置
Bash
copy$ whereis ls ls: /bin/ls /usr/share/man/man1/ls.1.gz /usr/share/man/man1p/ls.1p.gz
当你想查找某个可执行程序的位置,但这个程序又不在whereis的默认目录下,你可以使用-B选项,并指定目录作为这个选项的参数。下面的命令在/tmp目录下查找lsmk命令
Bash
copy
$ whereis -u -B /tmp -f lsmk lsmk: /tmp/lsmk
39. whatis
wathis显示某个命令的描述信息
Bash
copy$ whatis ls ls (1) - list directory contents $ whatis ifconfig ifconfig (8) - configure a network interface
40. locate
locate命名可以显示某个指定文件(或一组文件)的路径,它会使用由updatedb创建的数据库
下面的命令会显示系统中所有包含crontab字符串的文件
Bash
copy
$ locate crontab /etc/anacrontab /etc/crontab /usr/bin/crontab /usr/share/doc/cron/examples/crontab2english.pl.gz /usr/share/man/man1/crontab.1.gz /usr/share/man/man5/anacrontab.5.gz /usr/share/man/man5/crontab.5.gz /usr/share/vim/vim72/syntax/crontab.vim
41. man
显示某个命令的man页面
Bash
copy
$ man crontab
有些命令可能会有多个man页面,每个man页面对应一种命令类型
Bash
copy
$ man SECTION-NUMBER commandname
man页面一般可以分为8种命令类型
-
用户命令
-
系统调用
-
c库函数
-
设备与网络接口
-
文件格式
-
游戏与屏保
-
环境、表、宏
-
系统管理员命令和后台运行命令
例如,我们执行whatis crontab,你可以看到crontab有两个命令类型1和5,所以我们可以通过下面的命令查看命令类型5的man页面
Bash
copy$ whatis crontab crontab (1) - maintain crontab files for individual users (V3) crontab (5) - tables for driving cron $ man 5 crontab 42. tail
tail命令默认显示文件最后的10行文本
Bash
copy$ tail filename.txt 你可以使用-n选项指定要显示的行数
Bash
copy$ tail -n N filename.txt 你也可以使用-f选项进行实时查看,这个命令执行后会等待,如果有新行添加到文件尾部,它会继续输出新的行,在查看日志时这个选项会非常有用。你可以通过CTRL-C终止命令的执行
Bash
copy$ tail -f log-file 43. less
这个命名可以在不加载整个文件的前提下显示文件内容,在查看大型日志文件的时候这个命令会非常有用
Bash
copy$ less huge-log-file.log 当你用less命令打开某个文件时,下面两个按键会给你带来很多帮助,他们用于向前和向后滚屏
Bash
copyCTRL+F – forward one windowCTRL+B – backward one window 44. su
su命令用于切换用户账号,超级用户使用这个命令可以切换到任何其他用户而不用输入密码
Bash
copy$ su - USERNAME 用另外一个用户名执行一个命令下面的示例中用户john使用raj用户名执行ls命令,执行完后返回john的账号
Bash
copy[john@dev-server]$ su - raj -c 'ls'[john@dev-server]$ 用指定用户登录,并且使用指定的shell程序,而不用默认的
Bash
copy$ su -s 'SHELLNAME' USERNAME 45. mysql
mysql可能是Linux上使用最广泛的数据库,即使你没有在你的服务器上安装mysql,你也可以使用mysql客户端连接到远程的mysql服务器
连接一个远程数据库,需要输入密码
Bash
copy$ mysql -u root -p -h 192.168.1.2 连接本地数据库
Bash
copy$ mysql -u root -p 你也可以在命令行中输入数据库密码,只需要在-p后面加上密码作为参数,可以直接写在p后面而不用加空格
46. yum
使用yum安装apache
Bash
copy$ yum install httpd 更新apache
Bash
copy$ yum update httpd 卸载/删除apache
Bash
copy$ yum remove httpd 47. rpm
使用rpm安装apache
Bash
copy# rpm -ivh httpd-2.2.3-22.0.1.el5.i386.rpm 更新apache
Bash
copy# rpm -uvh httpd-2.2.3-22.0.1.el5.i386.rpm 卸载/删除apache
Bash
copy# rpm -ev httpd 48. ping
ping一个远程主机,只发5个数据包
Bash
copy$ ping -c 5 mainblog.cn 49. date
设置系统日期
Bash
copy# date -s "01/31/2010 23:59:53" 当你修改了系统时间,你需要同步硬件时间和系统时间
Bash
copy# hwclock –systohc# hwclock --systohc –utc 50. wget
使用wget从网上下载软件、音乐、视频
Bash
copy$ wget http://prdownloads.sourceforge.net/sourceforge/nagios/nagios-3.2.1.tar.gz 下载文件并以指定的文件名保存文件
Bash
copy$ wget -O taglist.zip http://www.vim.org/scripts/download_script.php?src_id=7701



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步