设计模式(二十三)访问者模式
1、定义
封装某些作用于某种数据结构中各元素的操作,它可以在不改变数据结构的前提下定义作用于这些元素的新操作。
2、类型:行为类模式
3、类图
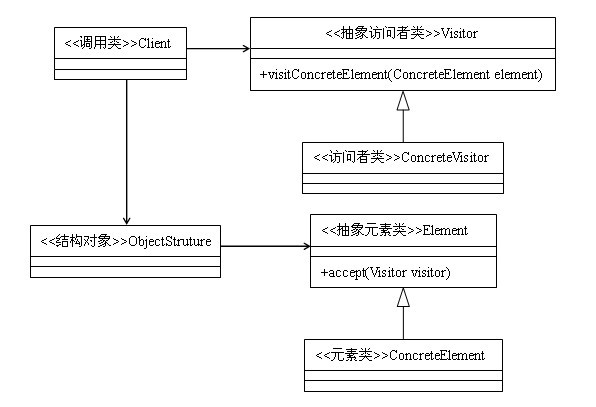
主要角色:
抽象访问者:抽象类或者接口,声明访问者可以访问哪些元素,具体到程序中就是visit方法中的参数定义哪些对象是可以被访问的;
访问者:实现抽象访问者所声明的方法,它影响到访问者访问到一个类后该干什么,要做什么事情;
抽象元素类:抽象类或者接口,声明接受哪一类访问者访问,程序上是通过accept方法中的参数来定义的,抽象类一般有两类方法,一部分是本身的业务逻辑,另外就是允许接收哪类访问者 来访问;
元素类:实现抽象元素类所声明的accept方法,通常都是visitor.visit(this),基本上已经形成一种定式了;
结构对象:一个元素的容器,一般包含一个容纳多个不同类、不同接口的容器,如List、Set、Map等,在项目中一般很少抽象出这个角色。
4、代码实例
1 /** 2 * @author it-小林 3 * @desc 元素接口 4 * @date 2021年10月14日 19:38 5 */ 6 public interface ComputerPart { 7 8 public void accept(ComputerPartVisitor computerPartVisitor); 9 }
1 /** 2 * @author it-小林 3 * @desc 访问者接口 4 * @date 2021年10月14日 19:39 5 */ 6 public interface ComputerPartVisitor { 7 public void visit(Computer computer); 8 public void visit(Mouse mouse); 9 public void visit(Keyboard keyboard); 10 public void visit(Monitor monitor); 11 }
1 /** 2 * @author it-小林 3 * @desc 鼠标 4 * @date 2021年10月14日 19:44 5 */ 6 public class Mouse implements ComputerPart{ 7 8 @Override 9 public void accept(ComputerPartVisitor computerPartVisitor) { 10 computerPartVisitor.visit(this); 11 } 12 }
1 /** 2 * @author it-小林 3 * @desc 键盘 4 * @date 2021年10月14日 19:40 5 */ 6 public class Keyboard implements ComputerPart{ 7 @Override 8 public void accept(ComputerPartVisitor computerPartVisitor) { 9 computerPartVisitor.visit(this); 10 } 11 }
1 /** 2 * @author it-小林 3 * @desc 显示器 4 * @date 2021年10月14日 19:42 5 */ 6 public class Monitor implements ComputerPart{ 7 @Override 8 public void accept(ComputerPartVisitor computerPartVisitor) { 9 computerPartVisitor.visit(this); 10 } 11 }
1 /** 2 * @author it-小林 3 * @desc 电脑 4 * @date 2021年10月14日 19:45 5 */ 6 public class Computer implements ComputerPart{ 7 ComputerPart[] parts; 8 9 public Computer() { 10 parts = new ComputerPart[]{new Mouse(), new Keyboard(), new Monitor()}; 11 } 12 13 @Override 14 public void accept(ComputerPartVisitor computerPartVisitor) { 15 for (ComputerPart computerPart: parts) { 16 computerPart.accept(computerPartVisitor); 17 } 18 computerPartVisitor.visit(this); 19 } 20 }
1 /** 2 * @author it-小林 3 * @desc 具体访问者 4 * @date 2021年10月14日 19:51 5 */ 6 public class ComputerPartDisplayVisitor implements ComputerPartVisitor{ 7 8 @Override 9 public void visit(Computer computer) { 10 System.out.println("Displaying Computer."); 11 } 12 13 @Override 14 public void visit(Mouse mouse) { 15 System.out.println("Displaying Mouse."); 16 } 17 18 @Override 19 public void visit(Keyboard keyboard) { 20 System.out.println("Displaying Keyboard."); 21 } 22 23 @Override 24 public void visit(Monitor monitor) { 25 System.out.println("Displaying Monitor."); 26 } 27 }
1 /** 2 * @author it-小林 3 * @desc 客户端 4 * @date 2021年10月14日 19:54 5 */ 6 public class Client { 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 ComputerPart computer = new Computer(); 9 computer.accept(new ComputerPartDisplayVisitor()); 10 } 11 }
5、优点
- 符合单一职责原则;
- 优秀的扩展性;
- 灵活性。
6、缺点
- 具体元素对访问者公布细节,违反了迪米特原则;
- 具体元素变更比较困难;
- 违反了依赖倒置原则,依赖了具体类,没有依赖抽象。
7、应用场景:
- 对象结构中对象对应的类很少改变,但经常需要在此对象结构上定义新的操作;
- 需要对一个对象结构中的对象进行很多不同的并且不相关的操作,而需要避免让这些操作"污染"这些对象的类,也不希望在增加新操作时修改这些类。
如本文有侵权行为,请及时与本人联系,多多包涵!
小生初出茅庐,多多指教!
本文来自博客园,作者:it-小林,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/linruitao/p/15067890.html



