CentOS 8 部署 ELK 8.7真的是方便呀
之前装过一次 ELK 7.7,相比之下装 8.7可方便太多了~
CentOS版本
CentOS-8.5.2111-x86_64-dvd1
JAVA
ELK会自己使用内置版本的JDK
ElasticSearch
8.7.0 下载页面 Download Elasticsearch | Elastic
Kinbana
Logstash
安装ElasticSearch8
加入资源
rpm --import https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch
在/etc/yum.repos.d/位置创建文件elasticsearch.repo
cd /etc/yum.repos.d/
vim elasticsearch.repo
输入如下内容:
[elasticsearch] name=Elasticsearch repository for 8.x packages baseurl=https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/8.x/yum gpgcheck=1 gpgkey=https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch enabled=0 autorefresh=1 type=rpm-md
将镜像从 mirror.centos.org 更改为 vault.centos.org (yum可用,则跳过)
进入到 yum 的 repos 目录
cd /etc/yum.repos.d/
修改 centos 文件内容
sed -i 's/mirrorlist/#mirrorlist/g' /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-* sed -i 's|#baseurl=http://mirror.centos.org|baseurl=http://vault.centos.org|g' /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-*
生成缓存更新
yum makecache
运行 yum update,并且重新安装 vim
yum update -y
yum -y install vim
执行 yum 命令完成 es 安装
yum install --enablerepo=elasticsearch elasticsearch
安装完记得保存如下信息,便于后续使用
Authentication and authorization are enabled. TLS for the transport and HTTP layers is enabled and configured. The generated password for the elastic built-in superuser is : xxxxxxxxx If this node should join an existing cluster, you can reconfigure this with '/usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch-reconfigure-node --enrollment-token <token-here>' after creating an enrollment token on your existing cluster. You can complete the following actions at any time: Reset the password of the elastic built-in superuser with '/usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch-reset-password -u elastic'. Generate an enrollment token for Kibana instances with '/usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch-create-enrollment-token -s kibana'. Generate an enrollment token for Elasticsearch nodes with '/usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch-create-enrollment-token -s node'.
添加用户和用户组 es 并未用户组提供文件夹权限
groupadd es useradd es -g es -p password chown es:es -R /usr/share/elasticsearch chown es:es -R /etc/elasticsearch chown es:es -R /var/lib/elasticsearch chown es:es -R /var/log/elasticsearch
chown es:es -R /var/
chmod 777 /etc/elasticsearch chmod 777 /usr/share/elasticsearch/ chmod 777 /etc/sysconfig/elasticsearch
编辑 elasticsearch.yml 配置文件
cd /etc/elasticsearch
vim elasticsearch.yml
配置如下:
network.host: 0.0.0.0 http.port: 9200 xpack.security.enabled: false
使用 es 账号启动 ElasticSearch
cd /usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/
su es
./elasticsearch -d
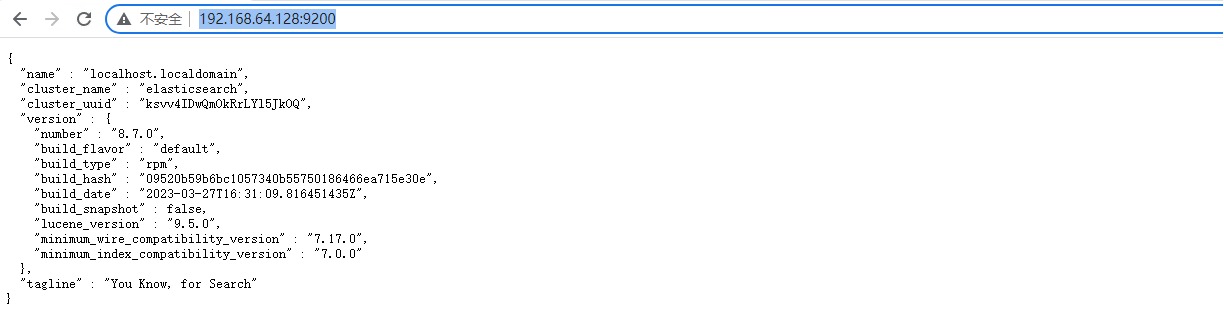
关闭防火墙或者开放9200端口,即可通过 IP:9200 访问
# 查看防火墙状态
systemctl status firewalld.service
# 关闭防火墙
systemctl stop firewalld.service
如果遇到安全提示则选择继续访问,并输入用户名密码这个用到的用户名密码是安装Es后我们保存的那个哦
安装 Kibana
在 /etc/yum.repos.d/ 位置创建文件 kibana.repo
cd /etc/yum.repos.d/
vim kibana.repo
输入如下内容
[kibana-8.x] name=Kibana repository for 8.x packages baseurl=https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/8.x/yum gpgcheck=1 gpgkey=https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch enabled=1 autorefresh=1 type=rpm-md
执行yum命令完成安装
yum install kibana
修改 kibana 配置文件
vim /etc/kibana/kibana.yml
增加如下内容:
server.host: "0.0.0.0"
server.post: 5601
以root后台启动服务
nohup /usr/share/kibana/bin/kibana --allow-root &
在ES安装目录 执行如下代码获取 token (本文 8.7 版本不需要)
/usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch-create-enrollment-token -s kibana
关闭防火墙或者开启5601端口,并使用浏览器访问 IP:5601
安装 Logstash
在 /etc/yum.repos.d/ 位置创建文件 logstash.repo
cd /etc/yum.repos.d/
vim logstash.repo
输入如下内容:
[logstash-8.x] name=Elastic repository for 8.x packages baseurl=https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/8.x/yum gpgcheck=1 gpgkey=https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch enabled=1 autorefresh=1 type=rpm-md
执行yum命令完成安装
yum install logstash
安装完成后的启动目录
/usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash
在 /etc/logstash/ 目录下创建 logstash.conf 配置文件
cd /etc/logstash/
vim logstash.conf
输入如下内容,以搜集 Nginx 的日志
#---------------------------------------------------------------- nginx----------------------------------------------------------------------- input { file { type => "nginx-error-log" path => "/usr/local/nginx/logs/error.log" } file { type => "nginx-access-log" path => "/usr/local/nginx/logs/access.log" codec => json } } filter { if [type] =~ "nginx-error-log" { grok { match => { "message" => "(?<datetime>\d{4}/\d{2}/\d{2} \d{2}:\d{2}:\d{2}) \[(?<errtype>\w+)\] \S+: \*\d+ (?<errmsg>[^,]+), (?<errinfo>.*$)" } } mutate { rename => { "message" => "z_message" "host" => "fromhost" } } } else if [type] =~ "nginx-access-log" { mutate { split => {"upstremtime" => ","} } mutate { convert => { "upstremtime" => "float"} } } if [errinfo] { ruby { code => " new_event = LogStash::Event.new(Hash[event.get('errinfo').split(', ').map{ |l| l.split(': ') }]) new_event.remove('@timestamp') event.append(new_event) " } grok { match => { "request" => '"%{WORD:verb} %{URIPATHPARAM:urlpathparam}?(?: HTTP/%{NUMBER:httpversion})"' } patterns_dir => ["/home/data/logstash/patterns/"] remove_field => [ "errinfo","request" ] } } } output { #elasticsearch { host => localhost } stdout { codec => rubydebug } if [type] =~ "nginx-error-log" { elasticsearch { hosts => ["http://ES的域名或者IP地址"] index => "logstash-nginx-error-log-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}" document_type => "data" user => "es用户名" password => "es密码" } }else if [type] =~ "nginx-access-log" { elasticsearch { hosts => ["http://ES的域名或者IP地址"] index => "logstash-nginx-access-log-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}" document_type => "data" user => "es用户名" password => "es密码" } } }
指定配置文件,启动 logstash
/usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash -f /etc/logstash/logstash.conf
# 后台启动
nohup /usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash -f /etc/logstash/logstash.conf &
格式化 Nginx 日志
进入 nginx 配置文件(以各自的文件目录、文件名为准)
cd /usr/local/nginx/conf/
vim nginx.conf
在 http 里输入如下内容:
log_format main '{"@timestamp":"$time_iso8601",' '"host":"$server_addr",' ' "clientip" : "$remote_addr",' ' "size" : "$body_bytes_sent" ,' '"respnsetime":"$request_time",' '"upstremtime":"$upstream_response_time",' '"upstremhost":"$upstream_addr",' '"httphost":"$host",' '"referer":"$http_referer",' '"xff":"$http_x_forwarded_for",' '"agent":"$http_user_agent",' '"clientip":"$remote_addr",' '"request":"$request",' '"uri":"$uri",' '"status":"$status"}'; access_log /usr/local/nginx/logs/access.log main; error_log /usr/local/nginx/logs/error.log error;
重新加载 Nginx
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload
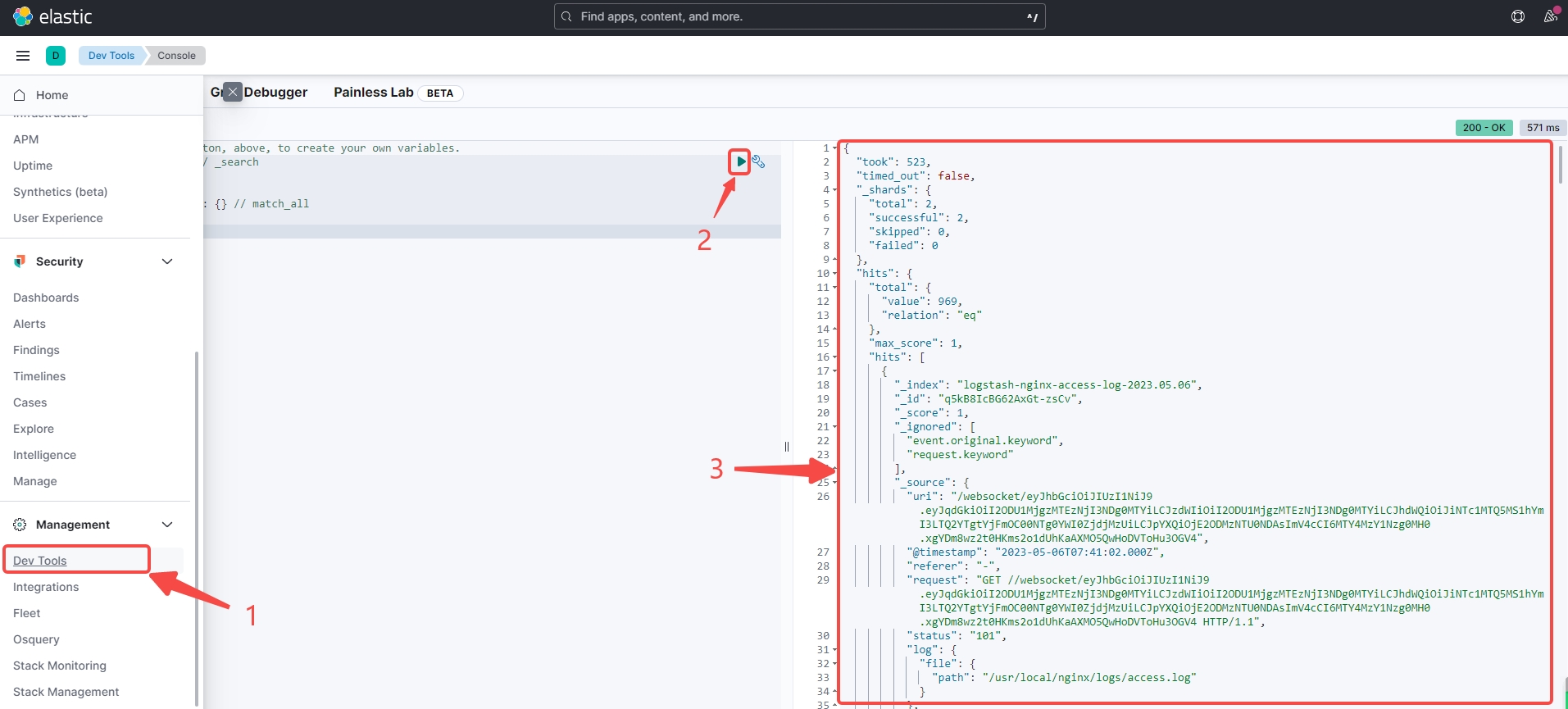
进入 kibana,就能看到推过来的 Nginx 的日志
安装 filebeat
logstash 占用的资源比较大,没有 filebeat 轻量,所以官方也推荐使用beats来作为日志采集工具。而且beats可扩展,支持自定义构建。
yum install filebeat -y
备份其配置文件,并新建
mv /etc/filebeat/filebeat.yml /etc/filebeat/filebeat.yml.bek
vim /etc/filebeat/filebeat.yml
输入如下内容:
- type: log paths: - /var/log/messages # 指定需要收集的日志文件的路径 output.elasticsearch: hosts: ["127.0.0.1:9200"] # 配置 Elasticsearch 服务器的 IP 地址
命令
systemctl start filebeat #启动
systemctl enable filebeat #开机启动
systemctl status filebeat #查看
systemctl stop filebeat #停止
告辞~


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号