【每日日报】第十一天
1 今天写了 以点类Point及平面类Plane为基础设计圆类Circle
题目要求:


程序源代码:
package Plane;
public class Point {
double x;
double y;
Point()//无参构造
{
x=0;
y=0;
System.out.println("Point Constructor run");
}
Point(double xv,double yv)//有参构造
{
x=xv;
y=yv;
System.out.println("Point Constructor run");
}
Point(Point p) //拷贝构造
{
x=p.x;
y=p.y;
System.out.println("Point CopyConstructor run");
}
void show() //显示Point信息
{
System.out.print("("+x+","+y+")");
}
void setX(double xv){x=xv;} //设置X坐标
void setY(double yv){y=yv;} //设置Y坐标
double getX() {return x;} //获取X坐标
double getY() {return y;} //获取Y坐标
}
double x;
double y;
Point()//无参构造
{
x=0;
y=0;
System.out.println("Point Constructor run");
}
Point(double xv,double yv)//有参构造
{
x=xv;
y=yv;
System.out.println("Point Constructor run");
}
Point(Point p) //拷贝构造
{
x=p.x;
y=p.y;
System.out.println("Point CopyConstructor run");
}
void show() //显示Point信息
{
System.out.print("("+x+","+y+")");
}
void setX(double xv){x=xv;} //设置X坐标
void setY(double yv){y=yv;} //设置Y坐标
double getX() {return x;} //获取X坐标
double getY() {return y;} //获取Y坐标
}
package Plane;
public class Plane extends Point {
Plane(){}
Plane(double xv,double yv){super(xv,yv);}
Plane(Plane p){super(p);}
double length(){return 0;}
double area(){return 0;}
}
Plane(){}
Plane(double xv,double yv){super(xv,yv);}
Plane(Plane p){super(p);}
double length(){return 0;}
double area(){return 0;}
}
package Plane;
public class Circle extends Plane{
static double PI=3.14159;
double radius;
Circle()
{
System.out.println("Circle Constructor run");
}
Circle(double xx,double yy,double rr)
{
super(xx,yy);
radius=rr;
System.out.println("Circle Constructor run");
}
Circle(Circle cir)
{
super(cir);
radius=cir.radius;
System.out.println("Circle CopyConstructor run");
}
void setR(double r){radius=r;}
double getR() {return radius;}
double length() {return 2*PI*radius;} //用于计算圆的周长
double area() {return PI*radius*radius;} //用于计算圆的面积
void show() {System.out.print("Circle(Point(X="+x+",Y="+y+"),Radius="+getR()+")");}
}
package Plane;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Ma extends Circle{
void show(Circle p){p.show();}
void length(Circle p){System.out.println("Length="+p.length());}
void area(Circle p){System.out.println("Area="+p.area());}
public static void main(String[] arge){
Ma m=new Ma();
double x,y,r;
Circle c1=new Circle();
Circle c2=new Circle(c1);
m.show(c1);
System.out.println();
m.area(c1);
m.length(c1);
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
x=input.nextDouble();
y=input.nextDouble();
r=input.nextDouble();
c2.setX(x);
c2.setY(y);
c2.setR(r);
m.show(c2);
System.out.println();
m.area(c2);
m.length(c2);
input.close();
}
void show(Circle p){p.show();}
void length(Circle p){System.out.println("Length="+p.length());}
void area(Circle p){System.out.println("Area="+p.area());}
public static void main(String[] arge){
Ma m=new Ma();
double x,y,r;
Circle c1=new Circle();
Circle c2=new Circle(c1);
m.show(c1);
System.out.println();
m.area(c1);
m.length(c1);
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
x=input.nextDouble();
y=input.nextDouble();
r=input.nextDouble();
c2.setX(x);
c2.setY(y);
c2.setR(r);
m.show(c2);
System.out.println();
m.area(c2);
m.length(c2);
input.close();
}
}
运行截图:
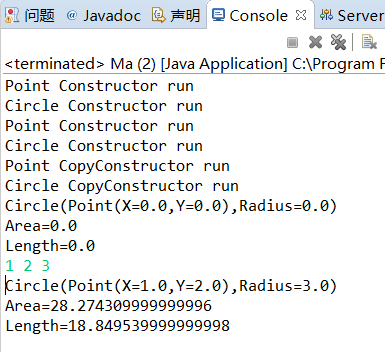
2 今天了解到:
C++ Java
虚函数 -------- 普通函数
纯虚函数 -------- 抽象函数
抽象类 -------- 抽象类虚基类 -------- 接口
虚函数 -------- 普通函数
纯虚函数 -------- 抽象函数
抽象类 -------- 抽象类虚基类 -------- 接口
结论:java类中普通成员函数就是虚函数。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/wuqiuping695/article/details/49069779
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/wuqiuping695/article/details/49069779
3 明天继续写题


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号