以下是咕泡公开课的学习笔记
一、创建工程springdemo

二、在pom中配置servlet
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>2.5</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
三、web.xml文件
<!DOCTYPE web-app PUBLIC
"-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Web Application 2.3//EN"
"http://java.sun.com/dtd/web-app_2_3.dtd" >
<web-app>
<display-name>Archetype Created Web Application</display-name>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>mvc</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.example.mvcframework.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>application.properties</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>mvc</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
四、资源文件
application.properties文件
scanPackage=com.example.demo
五、创建注解
1、Autowired
@Target({ElementType.FIELD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Autowired {
String value() default "";
}
2、Controller
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Controller {
String value() default "";
}
3、RequestMapping
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface RequestMapping {
String value() default "";
}
4、RequestParam
@Target({ElementType.PARAMETER})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface RequestParam {
String value() default "";
}
5、Service
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Service {
String value() default "";
}
六、创建DispatcherServlet
public class DispatcherServlet extends HttpServlet {
private Properties contextConfig = new Properties();
private List<String> classNames = new ArrayList<>();
private Map<String, Object> ioc = new HashMap<>();
private Map<String,Method> handlerMapping = new HashMap<>();
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doPost(req, resp);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//运行阶段,根据用户请求的URL进行自动分发和调度
try {
doDispatch(req,resp);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
resp.getWriter().write("500 Detail:" + Arrays.toString(e.getStackTrace()));
}
}
private void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws Exception {
if(this.handlerMapping.isEmpty()){
return;
}
//绝对路径
String url = req.getRequestURI();
//处理成相对路径
String contextPath = req.getContextPath();
url = url.replace(contextPath, "").replaceAll("/+", "/");
if(!this.handlerMapping.containsKey(url)){
resp.getWriter().write("404 Not found");
return;
}
Method method = this.handlerMapping.get(url);
//如何拿到实例?
//唯一的方式从IOC容器中拿
//继续投机取巧
String beanName = lowerFirstCase(method.getDeclaringClass().getSimpleName());
System.out.println("beanName:" + beanName);
Map<String,String[]> params = req.getParameterMap();
method.invoke(ioc.get(beanName), new Object[]{req, resp,params.get("name")[0]});
// System.out.println(method);
}
@Override
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException {
//1、加载配置文件
doLoadConfig(config.getInitParameter("contextConfigLocation"));
//2. 扫描所有相关的类
doScanner(contextConfig.getProperty("scanPackage"));
//3.初始化刚刚扫描到所有相关的类,并且把它保存在IOC容器中
doInstance();
//4. 实现依赖注入 DI 自动赋值
doAutowired();
//5. 初始化handlerMapping
initHandleMapping();
System.out.println("Spring is init");
}
private void initHandleMapping() {
if(ioc.isEmpty()){
return;
}
for(Map.Entry<String, Object> entry: ioc.entrySet()) {
Class<?> clazz = entry.getValue().getClass();
if(!clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Controller.class)){
continue;
}
String baseUrl = "";
if(clazz.isAnnotationPresent(RequestMapping.class)){
RequestMapping requestMapping = clazz.getAnnotation(RequestMapping.class);
baseUrl = requestMapping.value();
}
Method[] methods = clazz.getMethods(); //只认public的方法
for(Method method : methods){
if(!method.isAnnotationPresent(RequestMapping.class)){
continue;
}
RequestMapping requestMapping = method.getAnnotation(RequestMapping.class);
String url = ("/" + baseUrl + "/" + requestMapping.value()).replaceAll("/+", "/");
handlerMapping.put(url,method);
System.out.println("Mapped:" + url +"," + method);
}
Field[] fields = entry.getValue().getClass().getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
if (!field.isAnnotationPresent(Autowired.class)) {
continue;
}
}
}
}
private void doAutowired() {
if(ioc.isEmpty()){
return;
}
for(Map.Entry<String, Object> entry: ioc.entrySet()){
Field[] fields = entry.getValue().getClass().getDeclaredFields();
for(Field field: fields){
if(!field.isAnnotationPresent(Autowired.class)){
continue;
}
Autowired autowired = field.getAnnotation(Autowired.class);
String beanName = autowired.value().trim();
if("".equals(beanName)){
beanName = field.getType().getName();
}
field.setAccessible(true); //强制暴力访问
try {
field.set(entry.getValue(), ioc.get(beanName));
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
continue;
}
}
}
}
private void doInstance() {
if(classNames.isEmpty()){
return;
}
try{
for (String className: classNames) {
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(className);
//实例化,把实例化的对象保存到IOC容器之中
if(clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Controller.class)){
Object instance = clazz.newInstance();
String beanName = lowerFirstCase(clazz.getSimpleName());
ioc.put(beanName, instance);
} else if(clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Service.class)){
//因为Service有可能注入的不是它本身,有可能是它的实现类
//1、默认类名首字母小写
//2、自定义的beanName
Service service = clazz.getAnnotation(Service.class);
String beanName = service.value();
if("".equals(beanName)){
beanName = lowerFirstCase(clazz.getSimpleName());
}
Object instance = clazz.newInstance();
ioc.put(beanName, instance);
//3、如果是接口,投机取巧的方式,用它的接口类型作为key
Class<?>[] interfaces = clazz.getInterfaces();
for(Class<?> i : interfaces){
if(ioc.containsKey(i.getName())){
throw new Exception("The beanName is exists");
}
ioc.put(i.getName(), instance);
}
}else{
continue;
}
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 类名首字母小写
*/
private String lowerFirstCase(String simpleName) {
char[] chars = simpleName.toCharArray();
chars[0] += 32;
return String.valueOf(chars);
}
private void doScanner(String scanPackage) {
URL url = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResource("/" + scanPackage.replaceAll("\\.", "/"));
File classDir = new File(url.getFile());
for(File file : classDir.listFiles()){
if(file.isDirectory()){
doScanner(scanPackage + "." + file.getName());
}else{
if(file.getName().endsWith(".class")){
String classname = (scanPackage + "." +file.getName()).replace(".class","");
classNames.add(classname);
}
}
}
}
private void doLoadConfig(String contextConfigLocation) {
InputStream is = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(contextConfigLocation);
try {
contextConfig.load(is);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(is != null){
try {
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
七、使用
1、创建接口
public interface IDemoService {
String get(String name);
}
2、创建服务
@Service
public class DemoService implements IDemoService {
@Override
public String get(String name) {
return "hello," + name;
}
}
3、创建Controller
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/demo")
public class DemoAction {
@Autowired
private IDemoService demoService;
@RequestMapping("/query")
public void query(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp, @RequestParam("name") String name){
String result = demoService.get(name);
try {
resp.getWriter().write(result);
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@RequestMapping("/add")
public void add(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp, @RequestParam("a")Integer a, @RequestParam("b") Integer b){
try {
resp.getWriter().write(a + "+" + b + "=" + (a+b));
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@RequestMapping("/remove")
public void remove(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp, @RequestParam("id")Integer id){
}
}
八、测试
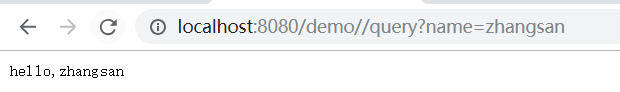
九、Spring十大优势
1、面向接口编程
2、IOC容器的问世
3、AOP思想,使得程序员把大部分精力投入到业务
4、Spring生态完善,Spring不仅仅只是一个框架
5、兼容程度高。只要有Java的地方就有Spring的用武之地
6、Spring的模块化拆分的非常精准,避免过度依赖(低耦合)
7、轻量级,所有的操作都建立在JavaBean之上
8、Spring与时俱进,全面支持Annotation,简化配置。如今的Spring可以实现配置裕兴
9、内部工具类非常丰富,简化开发,提升开发效率
10、Spring与各个开源框架可以实现无缝集成(Dubbo框架也是与Spring集成)
核心:提升开发效
作者:Work Hard Work Smart
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/linlf03/
欢迎任何形式的转载,未经作者同意,请保留此段声明!


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号