1、什么是队列
队列也是一种线性结构
相比数组,队列对应的操作是数组的子集
只能从一端(队尾)添加元素,只能从另一端(队首)取出元素。
队列是一种先进先出的数据结构( 先到先得)
First In First Out(FIFO)
2、自定义队列
1) 定义接口
public interface IQueue<E> {
int getSize(); // 时间复杂度 O(1) 均摊
boolean isEmpty(); // 时间复杂度 O(1)
void enqueue(E e); // 时间复杂度 O(1)
E dequeue(); // 时间复杂度 O(n)
E getFront(); // 时间复杂度 O(1)
}
2、自定义队列实现
基于自定义数组ArrayQueue
public class ArrayQueue<E> implements IQueue<E> {
private CustomArray<E> array;
public ArrayQueue(int capacity){
array = new CustomArray<E>(capacity);
}
public ArrayQueue(){
array = new CustomArray<E>();
}
public int getSize() {
return array.getSize() ;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return array.isEmpty();
}
public int getCapacity(){
return array.getCapacity();
}
public void enqueue(E e) {
array.addLast(e);
}
public E dequeue() {
return array.removeFirst();
}
public E getFront() {
return array.getFirst();
}
@Override
public String toString(){
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(String.format("Queue"));
sb.append("队首 [");
for(int i = 0; i< array.getSize(); i++){
sb.append(array.get(i));
if(i != array.getSize() -1){
sb.append(", ");
}
}
sb.append("] 队尾");
return sb.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayQueue<Integer> queue = new ArrayQueue<Integer>();
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){
queue.enqueue(i);
}
System.out.println(queue); // 输出: Queue队首 [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] 队尾
queue.dequeue();
System.out.println("移除一个队首元素=> " + queue); // 输出: 移除一个队首元素=> Queue队首 [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] 队尾
queue.dequeue();
System.out.println("移除一个队首元素=> " + queue); //输出: 移除一个队首元素=> Queue队首 [2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] 队尾
}
}
3、循环队列
前面的自定义队列,出队列dequeue方法的时间复杂度为O(n), 这个复杂度产生的原因?
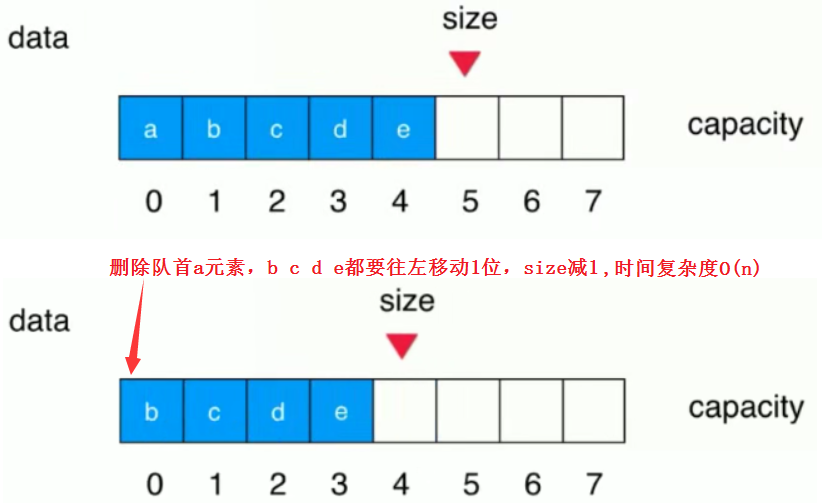
能不能在删除队首元素后,后面的元素不往前移动1位呢?这里就可以用到循环队列
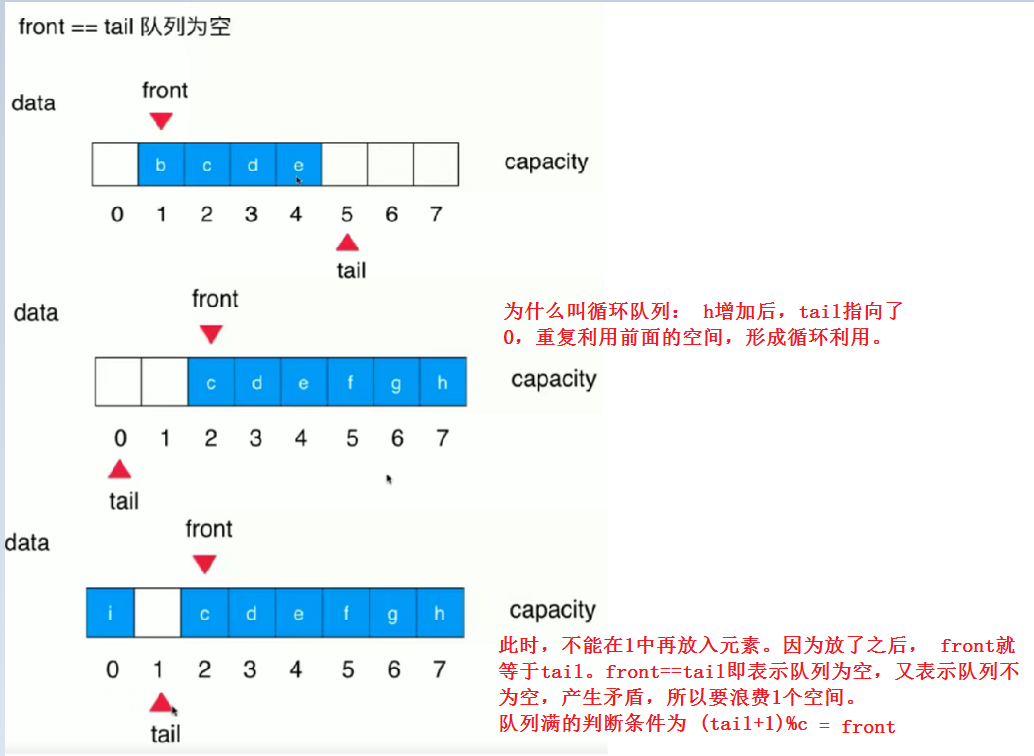
循环队列实现
public class LoopQueue<E> implements IQueue<E> {
private E[] data;
//队首元素的索引
private int front;
//队尾元素的索引+1
private int tail;
private int size;
public LoopQueue(int capacity){
//循环队列,浪费1个空间
data = (E[]) new Object[capacity +1];
front = 0;
tail = 0;
size = 0;
}
public LoopQueue(){
this(10);
}
public int getCapacity(){
return data.length -1;
}
public int getSize() {
return size;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return front == tail;
}
public void enqueue(E e) {
if((tail +1) % data.length == front){
resize(getCapacity() *2);
}
data[tail] = e;
tail = (tail + 1) % data.length;
size++;
}
public E dequeue() {
if(isEmpty()){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot dequeue from an empty queue.");
}
E ret = data[front];
data[front] = null;
front = (front +1) % data.length;
size --;
if(size == getCapacity() / 4 && getCapacity() / 2 != 0){
resize( getCapacity() / 2);
}
return ret;
}
private void resize(int newCapaCity) {
E[] newData = (E[])new Object[newCapaCity +1];
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++){
//i索引所在的数据,可能发生了偏移
newData[i] = data[(i+ front) % data.length];
}
data = newData;
front = 0;
tail = size;
}
public E getFront() {
if(isEmpty()){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Queue is empty.");
}
return data[front];
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(String.format("Loop Queue size= %d, capacity = %d ", this.size, getCapacity()));
sb.append("队首 [");
for(int i = front; i != tail; i = (i +1) % data.length ){
sb.append(data[i]);
//不是最后一个元素
if( (i + 1) % data.length != tail){
sb.append(", ");
}
}
sb.append("] 队尾");
return sb.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LoopQueue<Integer> queue = new LoopQueue<Integer>();
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){
queue.enqueue(i);
}
System.out.println(queue); // 输出: Loop Queue size= 5, capacity = 10 队首 [0, 1, 2, 3, 4] 队尾
queue.dequeue();
System.out.println("移除一个队首元素=> " + queue); // 输出: 移除一个队首元素=> Loop Queue size= 4, capacity = 10 队首 [1, 2, 3, 4] 队尾
queue.dequeue();
System.out.println("移除一个队首元素=> " + queue); //输出: 移除一个队首元素=> Loop Queue size= 3, capacity = 10 队首 [2, 3, 4] 队尾
queue.dequeue();
System.out.println("移除一个队首元素=> " + queue); //输出: 移除一个队首元素=> Loop Queue size= 2, capacity = 5 队首 [3, 4] 队尾
queue.dequeue();
System.out.println("移除一个队首元素=> " + queue); //输出: 移除一个队首元素=> Loop Queue size= 1, capacity = 2 队首 [4] 队尾
queue.dequeue();
System.out.println("移除一个队首元素=> " + queue); //输出: 移除一个队首元素=> Loop Queue size= 0, capacity = 1 队首 [] 队尾
}
}
总结: 循环队列实现了dequeue为O(1) 均摊 的时间复杂度。
4、数组队列和循环队列的比较
编写如下测试代码:
public class Test {
//测试实验队列q运行opCount个enqueue和dequeue操作所需要的时间,单位: 秒
private static double testQueue(IQueue<Integer> q, int opCount) {
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < opCount; i++) {
q.enqueue(random.nextInt(Integer.MAX_VALUE));
}
for (int i = 0; i < opCount; i++) {
q.dequeue();
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
return (endTime - startTime) / 1000000000.0;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int opCount = 100000;
ArrayQueue<Integer> arrayQueue = new ArrayQueue<Integer>();
double time1 = testQueue(arrayQueue, opCount);
System.out.println("数组队列ArrayQueue, time: " + time1 + "秒");
LoopQueue<Integer> loopQueue = new LoopQueue<Integer>();
double time2 = testQueue(loopQueue, opCount);
System.out.println("循环队列LoopQueue, time: " + time2 + "秒");
}
}
输出结果:
数组队列ArrayQueue, time: 4.540920463秒 循环队列LoopQueue, time: 0.054913962秒
可以看到循环队列比数字队列时间相差近100倍。
作者:Work Hard Work Smart
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/linlf03/
欢迎任何形式的转载,未经作者同意,请保留此段声明!


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号