一、配置类导入
1、mybatis-spring-boot-starter 引入了如下图5个依赖
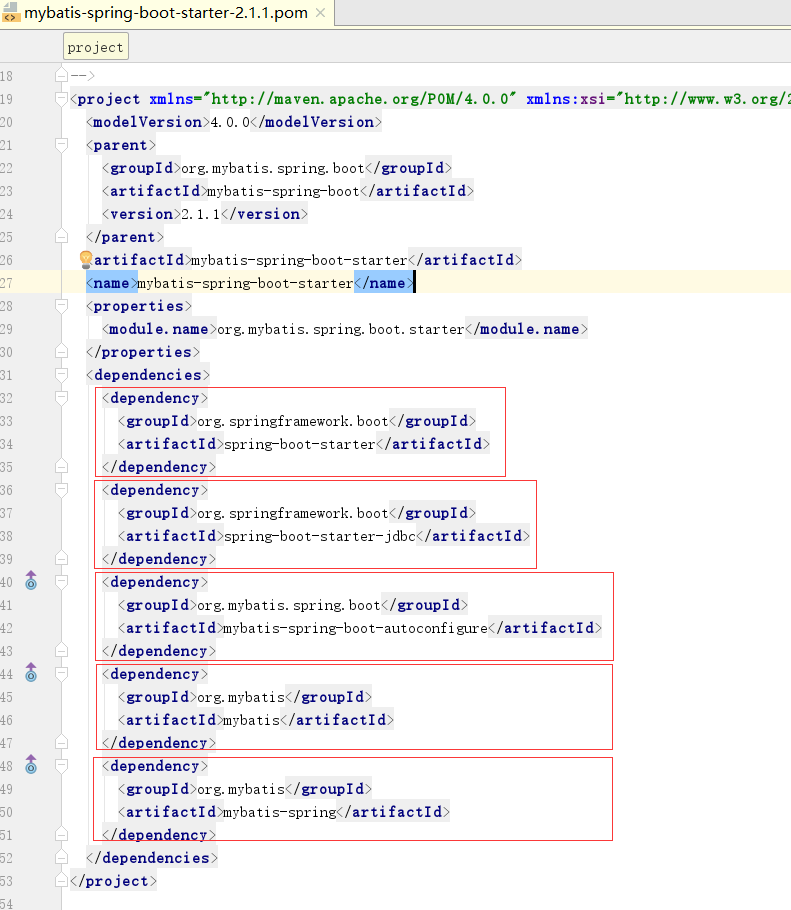
spring-boot-starter是每个starter都要引入的
spring-boot-starter-jdbc 与jdbc相关
后面两个mybatis, mybatis -spring 与mybatis相关
mybatis-spring-boot-autoconfigure 根据之前自定义的starter,它里面spring.factories有一个配置类实现了
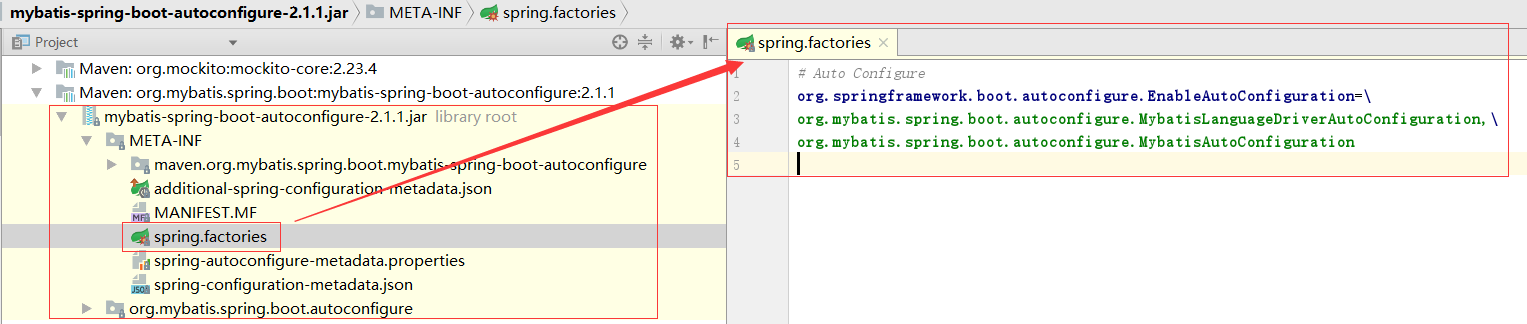
2、进入MyBatisAutoConfiguration类

1)第一个注解是Configuration,标注这个类是配置类
2)接下类是ConditionalOnClass注解,要求容器里有SqlSessionFactory类和SqlSessionfactoryBean类
3)ConditionalOnSingleCandidate注解:要求容器中存在DataSource类
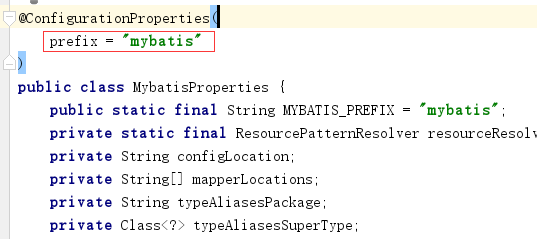
4)接着使用EnableConfigurationProperties注解使MybatisProperties这个类生效。
进入MybatisProperties类
获得mybatis前缀的属性
5)@AutoConfigureAfter({DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class, MybatisLanguageDriverAutoConfiguration.class})
说明当前类要在DataSourceAutoConfiguration和MybatisLanguageDriverAutoConfiguration这两个类之后进行装载
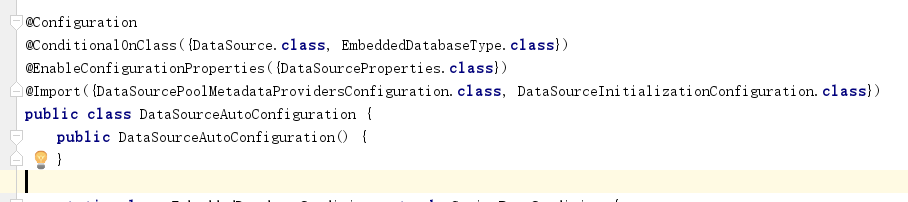
a) DataSourceAutoConfiguration
这个类是对数据源进行配置的
DataSourceProperties获得spring.datasource 的属性
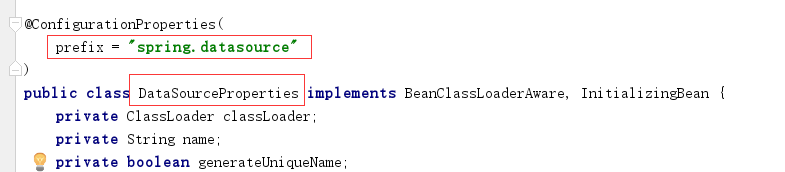
@AutoConfigureAfter({DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class, MybatisLanguageDriverAutoConfiguration.class})
二、关键类注入
MyBatisAutoConfiguration类会注入两个重要的Bean,分别为SqlSessionFactory和sqlSessionTemplate
1、首先进入SqlSessionFactory这个bean方法
sqlSessionFactory是单个数据库映射关系经编译后的内存镜像
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory(DataSource dataSource) throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
factory.setDataSource(dataSource);
factory.setVfs(SpringBootVFS.class);
if(StringUtils.hasText(this.properties.getConfigLocation())) {
factory.setConfigLocation(this.resourceLoader.getResource(this.properties.getConfigLocation()));
}
this.applyConfiguration(factory);
if(this.properties.getConfigurationProperties() != null) {
factory.setConfigurationProperties(this.properties.getConfigurationProperties());
}
if(!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(this.interceptors)) {
factory.setPlugins(this.interceptors);
}
if(this.databaseIdProvider != null) {
factory.setDatabaseIdProvider(this.databaseIdProvider);
}
if(StringUtils.hasLength(this.properties.getTypeAliasesPackage())) {
factory.setTypeAliasesPackage(this.properties.getTypeAliasesPackage());
}
if(this.properties.getTypeAliasesSuperType() != null) {
factory.setTypeAliasesSuperType(this.properties.getTypeAliasesSuperType());
}
if(StringUtils.hasLength(this.properties.getTypeHandlersPackage())) {
factory.setTypeHandlersPackage(this.properties.getTypeHandlersPackage());
}
if(!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(this.typeHandlers)) {
factory.setTypeHandlers(this.typeHandlers);
}
if(!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(this.properties.resolveMapperLocations())) {
factory.setMapperLocations(this.properties.resolveMapperLocations());
}
Set<String> factoryPropertyNames = (Set)Stream.of((new BeanWrapperImpl(SqlSessionFactoryBean.class)).getPropertyDescriptors()).map(FeatureDescriptor::getName).collect(Collectors.toSet());
Class<? extends LanguageDriver> defaultLanguageDriver = this.properties.getDefaultScriptingLanguageDriver();
if(factoryPropertyNames.contains("scriptingLanguageDrivers") && !ObjectUtils.isEmpty(this.languageDrivers)) {
factory.setScriptingLanguageDrivers(this.languageDrivers);
if(defaultLanguageDriver == null && this.languageDrivers.length == 1) {
defaultLanguageDriver = this.languageDrivers[0].getClass();
}
}
if(factoryPropertyNames.contains("defaultScriptingLanguageDriver")) {
factory.setDefaultScriptingLanguageDriver(defaultLanguageDriver);
}
return factory.getObject();
}
2、sqlSessionTemplate类
执行数据库操作的工具类
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public SqlSessionTemplate sqlSessionTemplate(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) {
ExecutorType executorType = this.properties.getExecutorType();
return executorType != null?new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory, executorType):new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory);
}
进入SqlSessionTemplate类,
里面有SqlSessionFactory和sqlSessionProxy
sqlSessionProxy是代理类,里面的增删改查都是通过它来执行的。处理方法都在SqlSessionInterceptor里面

3、SqlSessionInterceptor 类如下
private class SqlSessionInterceptor implements InvocationHandler {
private SqlSessionInterceptor() {
}
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtils.getSqlSession(SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory, SqlSessionTemplate.this.executorType, SqlSessionTemplate.this.exceptionTranslator);
Object unwrapped;
try {
Object result = method.invoke(sqlSession, args);
if(!SqlSessionUtils.isSqlSessionTransactional(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory)) {
sqlSession.commit(true);
}
unwrapped = result;
} catch (Throwable var11) {
unwrapped = ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(var11);
if(SqlSessionTemplate.this.exceptionTranslator != null && unwrapped instanceof PersistenceException) {
SqlSessionUtils.closeSqlSession(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory);
sqlSession = null;
Throwable translated = SqlSessionTemplate.this.exceptionTranslator.translateExceptionIfPossible((PersistenceException)unwrapped);
if(translated != null) {
unwrapped = translated;
}
}
throw (Throwable)unwrapped;
} finally {
if(sqlSession != null) {
SqlSessionUtils.closeSqlSession(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory);
}
}
return unwrapped;
}
}
1) 进入getSqlSession这个方法
public static SqlSession getSqlSession(SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory, ExecutorType executorType, PersistenceExceptionTranslator exceptionTranslator) {
Assert.notNull(sessionFactory, "No SqlSessionFactory specified");
Assert.notNull(executorType, "No ExecutorType specified");
SqlSessionHolder holder = (SqlSessionHolder)TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(sessionFactory);
SqlSession session = sessionHolder(executorType, holder);
if(session != null) {
return session;
} else {
LOGGER.debug(() -> {
return "Creating a new SqlSession";
});
session = sessionFactory.openSession(executorType);
registerSessionHolder(sessionFactory, executorType, exceptionTranslator, session);
return session;
}
}
a) 通过资源管理器获得资源 (SqlSessionHolder)TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(sessionFactory);
getResource如下。里面调用了doGetRecource
@Nullable
public static Object getResource(Object key) {
Object actualKey = TransactionSynchronizationUtils.unwrapResourceIfNecessary(key);
Object value = doGetResource(actualKey);
if(value != null && logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Retrieved value [" + value + "] for key [" + actualKey + "] bound to thread [" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "]");
}
return value;
}
进入doGetResource
@Nullable
private static Object doGetResource(Object actualKey) {
Map<Object, Object> map = (Map)resources.get();
if(map == null) {
return null;
} else {
Object value = map.get(actualKey);
if(value instanceof ResourceHolder && ((ResourceHolder)value).isVoid()) {
map.remove(actualKey);
if(map.isEmpty()) {
resources.remove();
}
value = null;
}
return value;
}
}
resource的数据结构如下
private static final ThreadLocal<Map<Object, Object>> resources = new NamedThreadLocal("Transactional resources");
三、mapper类扫描
1、进入MybatisAutoConfiguration类。
因为没有mapperFactoryBean和MapperScannerConfigurer类,所有会把MapperScannerRegisterarNoFoundConfiguration 注入到容器中,并且导入AutoConfiguredMapperScannerRegistrar类
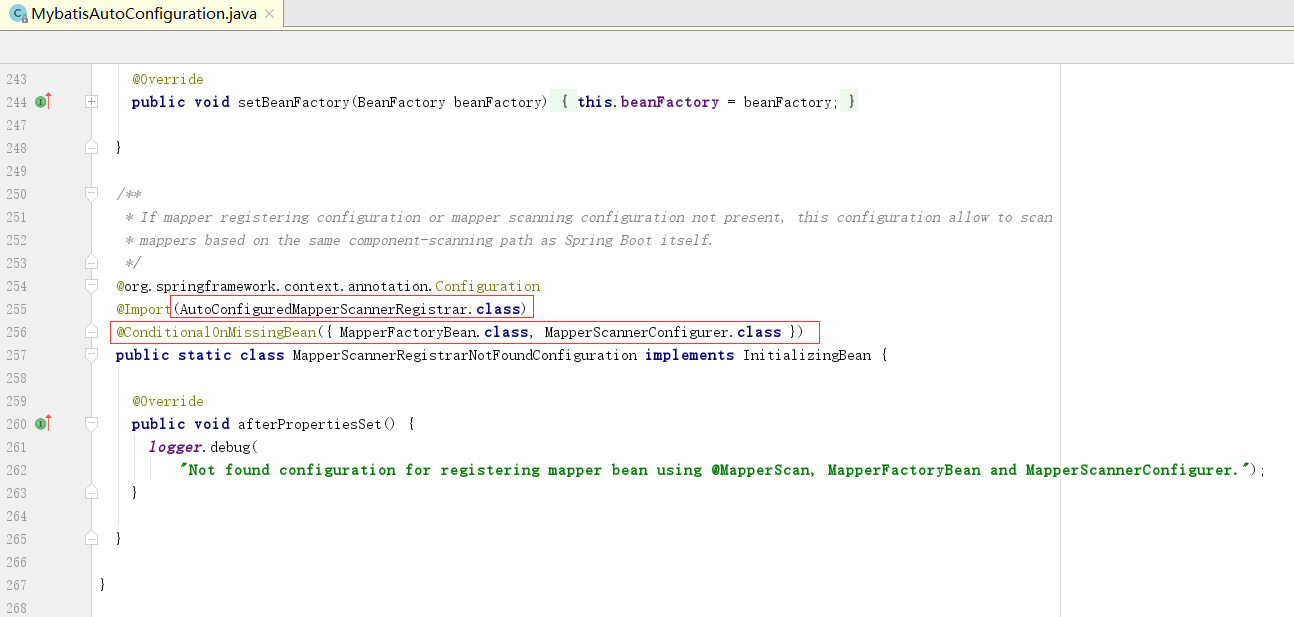
2、进入AutoConfiguredMapperScannerRegistrar类。
实现了ImportBanDefinitionRegistrar接口

最后注册MapperScannerConfigurer这个Bean。
3、MapperScannerConfigurer
作用:扫描mapper接口注册到容器中
1)而MapperScannerConfigurer实现了BeanDefinitionRegitryPostProcessor接口,实现了postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry这个方法


2) 我们进入这个方法scanner.registerFilters();
进入registerFilters
public void registerFilters() {
boolean acceptAllInterfaces = true;
if(this.annotationClass != null) {
this.addIncludeFilter(new AnnotationTypeFilter(this.annotationClass));
acceptAllInterfaces = false;
}
if(this.markerInterface != null) {
this.addIncludeFilter(new AssignableTypeFilter(this.markerInterface) {
protected boolean matchClassName(String className) {
return false;
}
});
acceptAllInterfaces = false;
}
if(acceptAllInterfaces) {
this.addIncludeFilter((metadataReader, metadataReaderFactory) -> {
return true;
});
}
this.addExcludeFilter((metadataReader, metadataReaderFactory) -> {
String className = metadataReader.getClassMetadata().getClassName();
return className.endsWith("package-info");
});
}
3)对包路径进行扫描 scanner.scan(StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(this.basePackage, ",; \t\n"));
public int scan(String... basePackages) {
int beanCountAtScanStart = this.registry.getBeanDefinitionCount();
doScan(basePackages);
// Register annotation config processors, if necessary.
if (this.includeAnnotationConfig) {
AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(this.registry);
}
return (this.registry.getBeanDefinitionCount() - beanCountAtScanStart);
}
核心是doScan方法。
首先会调用父类的doScan方法:
public Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> doScan(String... basePackages) {
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions = super.doScan(basePackages);
if(beanDefinitions.isEmpty()) {
LOGGER.warn(() -> {
return "No MyBatis mapper was found in '" + Arrays.toString(basePackages) + "' package. Please check your configuration.";
});
} else {
this.processBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitions);
}
return beanDefinitions;
}
然后调用this.processBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitions);方法
四、mapper类生成
1、进入processBeanDefinitions方法
private void processBeanDefinitions(Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions) {
GenericBeanDefinition definition;
for(Iterator var3 = beanDefinitions.iterator(); var3.hasNext(); definition.setLazyInit(this.lazyInitialization)) {
BeanDefinitionHolder holder = (BeanDefinitionHolder)var3.next();
definition = (GenericBeanDefinition)holder.getBeanDefinition();
String beanClassName = definition.getBeanClassName();
LOGGER.debug(() -> {
return "Creating MapperFactoryBean with name '" + holder.getBeanName() + "' and '" + beanClassName + "' mapperInterface";
});
definition.getConstructorArgumentValues().addGenericArgumentValue(beanClassName);
definition.setBeanClass(this.mapperFactoryBeanClass);
definition.getPropertyValues().add("addToConfig", Boolean.valueOf(this.addToConfig));
boolean explicitFactoryUsed = false;
if(StringUtils.hasText(this.sqlSessionFactoryBeanName)) {
definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionFactory", new RuntimeBeanReference(this.sqlSessionFactoryBeanName));
explicitFactoryUsed = true;
} else if(this.sqlSessionFactory != null) {
definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionFactory", this.sqlSessionFactory);
explicitFactoryUsed = true;
}
if(StringUtils.hasText(this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName)) {
if(explicitFactoryUsed) {
LOGGER.warn(() -> {
return "Cannot use both: sqlSessionTemplate and sqlSessionFactory together. sqlSessionFactory is ignored.";
});
}
definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionTemplate", new RuntimeBeanReference(this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName));
explicitFactoryUsed = true;
} else if(this.sqlSessionTemplate != null) {
if(explicitFactoryUsed) {
LOGGER.warn(() -> {
return "Cannot use both: sqlSessionTemplate and sqlSessionFactory together. sqlSessionFactory is ignored.";
});
}
definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionTemplate", this.sqlSessionTemplate);
explicitFactoryUsed = true;
}
if(!explicitFactoryUsed) {
LOGGER.debug(() -> {
return "Enabling autowire by type for MapperFactoryBean with name '" + holder.getBeanName() + "'.";
});
definition.setAutowireMode(2);
}
}
}
里面会将beanClass替换为mapperFactoryBeanClass 。definition.setBeanClass(this.mapperFactoryBeanClass);
2、进入MapperFactoryBean方法
里面有一个getObject方法
public T getObject() throws Exception {
return this.getSqlSession().getMapper(this.mapperInterface);
}
进入getMapper方法,类型为接口TestMapper
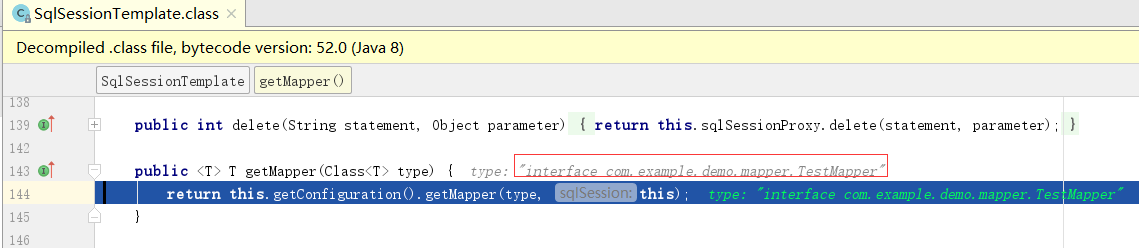
进入getMapper方法
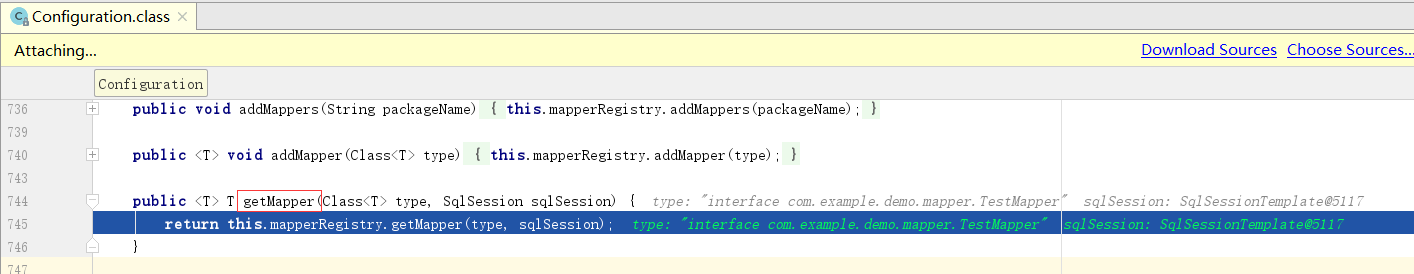
进入getMapper

进入newInstance方法。最终返回一个代理对象。MapperProxy是Mybatis源码里的内容,这里不做过多的介绍。
五、mapper类执行
1、进入MapperProxy中的invoke方法

进入execute方法
进入增删改查其中一种类型,然后通过sqlSession进行执行,执行完毕后将结果返回
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
switch (command.getType()) {
case INSERT: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case UPDATE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case DELETE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case SELECT:
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {
result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
if (method.returnsOptional()
&& (result == null || !method.getReturnType().equals(result.getClass()))) {
result = Optional.ofNullable(result);
}
}
break;
case FLUSH:
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
}
作者:Work Hard Work Smart
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/linlf03/
欢迎任何形式的转载,未经作者同意,请保留此段声明!


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号