方法有以下几种:
主线程等待法
使用Thread类的join()阻塞当前线程以等待子线程处理完毕
通过Callable接口实现: 通过FutureTask Or线程池获取
一、主线程等待法
如下代码
public class CycleWait implements Runnable {
private String name;
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
name = "zhang san";
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
CycleWait cw = new CycleWait();
Thread t = new Thread(cw);
t.start();
System.out.println("name: " + cw.name);
}
}
打印的结果为
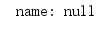
将它改造成主线程等待法
public class CycleWait implements Runnable {
private String name;
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
name = "zhang san";
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
CycleWait cw = new CycleWait();
Thread t = new Thread(cw);
t.start();
while (cw.name == null){
Thread.sleep(100);
}
System.out.println("name: " + cw.name);
}
}
这样,5秒后就能打印name的值

二、使用Thread类的join()阻塞当前线程以等待子线程处理完毕
修改上上面的方法

三、通过Callable接口实现: 通过FutureTask Or线程池获取
1、通过FutureTask
创建MyCallback 类,实现Callable接口
public class MyCallback implements Callable<String>{
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
String value = "nick";
System.out.println("Read to work");
Thread.sleep(5000);
System.out.println("task done");
return value;
}
}
使用FutureTask的方式
public class FutureTaskDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
FutureTask<String> task = new FutureTask<String>(new MyCallback());
new Thread(task).start();
if(!task.isDone()){
System.out.println("任务没有完成,请等待");
}
System.out.println("任务返回:" + task.get());
}
}
打印结果
任务没有完成,请等待 Read to work task done 任务返回:nick
2、使用线程池的方式
public class SomeCallable {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Callable<String> callbale = new Callable<String>() {
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
Thread.sleep(2000);
return "ok";
}
};
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
//执行任务并获取Future对象
Future<String> future = executorService.submit(callbale);
try {
String result = future.get();
System.out.println("result:" + result);
}catch (Exception e){}
finally {
//关闭线程池
executorService.shutdown();
}
}
}
作者:Work Hard Work Smart
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/linlf03/
欢迎任何形式的转载,未经作者同意,请保留此段声明!


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号