Python爬虫实例
2017-04-10 13:11 linkxu 阅读(3810) 评论(1) 编辑 收藏 举报前言
Python非常适合用来开发网页爬虫,理由如下:
1、抓取网页本身的接口
相比与其他静态编程语言,如java,c#,c++,python抓取网页文档的接口更简洁;相比其他动态脚本语言,如perl,shell,python的urllib2包提供了较为完整的访问网页文档的API。(当然ruby也是很好的选择)
此外,抓取网页有时候需要模拟浏览器的行为,很多网站对于生硬的爬虫抓取都是封杀的。这是我们需要模拟user agent的行为构造合适的请求,譬如模拟用户登陆、模拟session/cookie的存储和设置。在python里都有非常优秀的第三方包帮你搞定,如Requests,mechanize
2、网页抓取后的处理
抓取的网页通常需要处理,比如过滤html标签,提取文本等。python的beautifulsoap提供了简洁的文档处理功能,能用极短的代码完成大部分文档的处理。
其实以上功能很多语言和工具都能做,但是用python能够干得最快,最干净。
Life is short, you need python.
PS:python2.x和python3.x有很大不同.
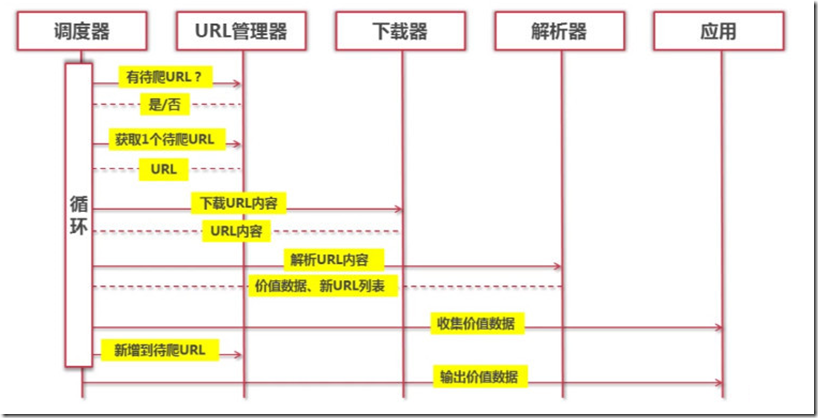
爬虫架构
架构组成

URL管理器:管理待爬取的url集合和已爬取的url集合,传送待爬取的url给网页下载器。
网页下载器(urllib):爬取url对应的网页,存储成字符串,传送给网页解析器。
网页解析器(BeautifulSoup):解析出有价值的数据,存储下来,同时补充url到URL管理器。
运行流程
URL管理器
基本功能
- 添加新的url到待爬取url集合中。
- 判断待添加的url是否在容器中(包括待爬取url集合和已爬取url集合)。
- 获取待爬取的url。
- 判断是否有待爬取的url。
- 将爬取完成的url从待爬取url集合移动到已爬取url集合。
存储方式
1、内存(python内存)
待爬取url集合:set()
已爬取url集合:set()
2、关系数据库(mysql)
urls(url, is_crawled)
3、缓存(redis)
待爬取url集合:set
已爬取url集合:set
大型互联网公司,由于缓存数据库的高性能,一般把url存储在缓存数据库中。小型公司,一般把url存储在内存中,如果想要永久存储,则存储到关系数据库中。
网页下载器(urllib)
将url对应的网页下载到本地,存储成一个文件或字符串。
基本方法
新建baidu.py,内容如下:
import urllib.request response = urllib.request.urlopen('http://www.baidu.com') buff = response.read() html = buff.decode("utf8") print(html)
命令行中执行python baidu.py,则可以打印出获取到的页面。
构造Request
上面的代码,可以修改为:
import urllib.request request = urllib.request.Request('http://www.baidu.com') response = urllib.request.urlopen(request) buff = response.read() html = buff.decode("utf8") print(html)
携带参数
新建baidu2.py,内容如下:
import urllib.request import urllib.parse url = 'http://www.baidu.com' values = {'name': 'voidking','language': 'Python'} data = urllib.parse.urlencode(values).encode(encoding='utf-8',errors='ignore') headers = { 'User-Agent' : 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64; rv:50.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/50.0' } request = urllib.request.Request(url=url, data=data,headers=headers,method='GET') response = urllib.request.urlopen(request) buff = response.read() html = buff.decode("utf8") print(html)
使用Fiddler监听数据
我们想要查看一下,我们的请求是否真的携带了参数,所以需要使用fiddler。
打开fiddler之后,却意外发现,上面的代码会报错504,无论是baidu.py还是baidu2.py。
虽然python有报错,但是在fiddler中,我们可以看到请求信息,确实携带了参数。
经过查找资料,发现python以前版本的Request都不支持代理环境下访问https。但是,最近的版本应该支持了才对。那么,最简单的办法,就是换一个使用http协议的url来爬取,比如,换成http://www.csdn.net。结果,依然报错,只不过变成了400错误。
然而,然而,然而。。。神转折出现了!!!
当我把url换成http://www.csdn.net/后,请求成功!没错,就是在网址后面多加了一个斜杠/。同理,把http://www.baidu.com改成http://www.baidu.com/,请求也成功了!神奇!!!
添加处理器

import urllib.request import http.cookiejar # 创建cookie容器 cj = http.cookiejar.CookieJar() # 创建opener opener = urllib.request.build_opener(urllib.request.HTTPCookieProcessor(cj)) # 给urllib.request安装opener urllib.request.install_opener(opener) # 请求 request = urllib.request.Request('http://www.baidu.com/') response = urllib.request.urlopen(request) buff = response.read() html = buff.decode("utf8") print(html) print(cj)
网页解析器(BeautifulSoup)
从网页中提取出有价值的数据和新的url列表。
解析器选择
为了实现解析器,可以选择使用正则表达式、html.parser、BeautifulSoup、lxml等,这里我们选择BeautifulSoup。
其中,正则表达式基于模糊匹配,而另外三种则是基于DOM结构化解析。
BeautifulSoup
安装测试
1、安装,在命令行下执行pip install beautifulsoup4。
2、测试
import bs4 print(bs4)
使用说明


基本用法
1、创建BeautifulSoup对象
import bs4 from bs4 import BeautifulSoup # 根据html网页字符串创建BeautifulSoup对象 html_doc = """ <html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head> <body> <p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p> <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were <a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>, <a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and <a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>; and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p> <p class="story">...</p> """ soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc) print(soup.prettify())
2、访问节点
print(soup.title) print(soup.title.name) print(soup.title.string) print(soup.title.parent.name) print(soup.p) print(soup.p['class'])
3、指定tag、class或id
print(soup.find_all('a')) print(soup.find('a')) print(soup.find(class_='title')) print(soup.find(id="link3")) print(soup.find('p',class_='title'))
4、从文档中找到所有<a>标签的链接
for link in soup.find_all('a'): print(link.get('href'))

出现了警告,根据提示,我们在创建BeautifulSoup对象时,指定解析器即可。
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc,'html.parser')
5、从文档中获取所有文字内容
print(soup.get_text())
6、正则匹配
link_node = soup.find('a',href=re.compile(r"til"))
print(link_node)实例
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- ''' Created on 2017年4月10日 @author: xuxianglin ''' import urllib2, os.path, urllib, random from bs4 import BeautifulSoup def get_soup(url): """ 获取网站的soup对象 """ my_headers = [ 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 5.2) AppleWebKit/534.30 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/12.0.742.122 Safari/534.30', 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 5.1; rv:5.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/5.0', 'Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 8.0; Windows NT 5.2; Trident/4.0; .NET CLR 1.1.4322; .NET CLR 2.0.50727; .NET4.0E; .NET CLR 3.0.4506.2152; .NET CLR 3.5.30729; .NET4.0C)', 'Opera/9.80 (Windows NT 5.1; U; zh-cn) Presto/2.9.168 Version/11.50', 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; zh-CN) AppleWebKit/533.21.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.5 Safari/533.21.1', 'Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 8.0; Windows NT 5.1; Trident/4.0; .NET CLR 2.0.50727; .NET CLR 3.0.04506.648; .NET CLR 3.5.21022; .NET4.0E; .NET CLR 3.0.4506.2152; .NET CLR 3.5.30729; .NET4.0C)'] header={"User-Agent":random.choice(my_headers)} req=urllib2.Request(url, headers=header) html=urllib2.urlopen(req).read() soup=BeautifulSoup(html) return soup def get_pages(url): """ 获取妹子图网站的页数 """ soup=get_soup(url) nums=soup.find_all('a',class_='page-numbers') pages=int(nums[-2].text) return pages def get_menu(url): """ 获取页面的所有妹子图主题的链接名称和地址,记入列表 """ soup=get_soup(url) menu=[] menu_list=soup.find_all('a',target='_blank') for i in menu_list: result=i.find_all('img',class_='lazy') if result: name=result[0]['alt'] address=i['href'] menu.append([name,address]) return menu def get_links(url): """ 获取单个妹子图主题一共具有多少张图片 """ soup=get_soup(url) all_=soup.find_all('a') nums=[] for i in all_: span=i.find_all('span') if span: nums.append(span[0].text) return nums[-2] def get_image(url,filename): """ 从单独的页面中提取出图片保存为filename """ soup=get_soup(url) image=soup.find_all('p')[0].find_all('img')[0]['src'] urllib.urlretrieve(image,filename) def main(page): """ 下载第page页的妹子图 """ print u'正在下载第 %d 页' % page page_url=url+'/page/'+str(page) menu=get_menu(page_url) print u'@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@第 %d 页共有 %d 个主题@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@' %(page,len(menu)) for i in menu: dir_name=os.path.join('MeiZiTu',i[0]) if not os.path.exists(dir_name): os.mkdir(dir_name) pic_nums=int(get_links(i[1])) print u'\n\n\n*******主题 %s 一共有 %d 张图片******\n' %(i[0],pic_nums) for pic in range(1,pic_nums+1): basename=str(pic)+'.jpg' filename=os.path.join(dir_name,basename) pic_url=i[1]+'/'+str(pic) if not os.path.exists(filename): print u'......%s' % basename, get_image(pic_url,filename) else: print filename+u'已存在,略过' if __name__=='__main__': url='http://www.mzitu.com/' pages=get_pages(url) print u'***************妹子图一共有 %d 页******************' %pages if not os.path.exists('MeiZiTu'): os.mkdir('MeiZiTu') page_start=input(u'Input the first page number:\n') page_end=input(u'Input the last page number:\n') if page_end>page_start: for page in range(page_start,page_end): main(page) elif page_end==page_start: main(page_end) else: print u"输入错误,起始页必须小于等于结束页\n"