C++ 拷贝构造
12 拷贝构造
- Create a new object from an existing one
- For example, when calling a function
// Currency as pass-by-value argument
void func(Currency p)
{
cout << "X = " << p.dollars();
}
Currency bucks(100, 0);
func(bucks); // bucks is copied into p
- 示例二:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
static int objectCount = 0;
class HowMany {
public:
HowMany() { objectCount++; print("HowMany()"); }
void print(const string& msg = "") {
if (msg.size() != 0) {
cout << msg << ": ";
}
cout << "objectCount = "
<< objectCount << endl;
}
~HowMany() {
objectCount--;
print("~HowMany()");
}
};
HowMany f(HowMany x) {
cout << "begin of f " << endl;
x.print("x argument inside f() ");
cout << "end of f" << endl;
return x;
}
int main() {
HowMany h;
h.print("after construction of h");
HowMany h2 = f(h);
h.print("after call to f()");
}
- 示例三:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
static int objectCount = 0;
class HowMany {
public:
HowMany() { objectCount++; print("HowMany()"); }
HowMany(int i) { objectCount++; print("HowMany(int)"); }
// 拷贝构造
HowMany(const HowMany& o) { objectCount++; print("HowMany(HM)"); }
void print(const string& msg = "") {
if (msg.size() != 0) {
cout << msg << ": ";
}
cout << "objectCount = "
<< objectCount << endl;
}
~HowMany() {
objectCount--;
print("~HowMany()");
}
};
HowMany f(HowMany x) {
cout << "begin of f " << endl;
x.print("x argument inside f() ");
cout << "end of f" << endl;
return x;
}
int main() {
HowMany h;
h.print("after construction of h");
// 这种方式,是可以初始化 h2 的
HowMany h2 = 10;
// HowMany h2 = h;
HowMany h3 = f(h);
h.print("after call to f()");
}
12.1 The copy cosntructor
- Copying is implemented by the copy cosntructor
- Has the unique signature:
T::T(cosnt T&);- Call-by-reference is used for the explicit argument
- C++ builds a copy constructor for you if you don't provide one!
- Copies each member variable
- Good for numbers, objects, arrays
- Copies each pointer
- Data may become shared!
- Copies each member variable
12.2 class contains pointers
- 示例一:
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
class Person {
public:
Person(const char *s);
~Person();
void print();
// private:
char *name;
};
Person::Person(const char *s) {
name = new char[::strlen(s) + 1];
::strcpy(name, s);
}
Person::~Person() {
delete []name;
}
int main()
{
Person p1("John");
Person p2(p1);
printf("p1.name = %p\n", p1.name);
printf("p2.name = %p\n", p2.name);
return 0;
}
// p1.name 和 p2.name 指向同一个地址,析构的时候,会析构两次;
// 程序运行会报错。
- 示例二:
Person copy constructor
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
class Person {
public:
Person(const char *s);
// 自定义拷贝构造
Person(const Person& w);
~Person();
void print();
// private:
char *name;
};
Person::Person(const char *s) {
name = new char[::strlen(s) + 1];
::strcpy(name, s);
}
Person::Person(const Person& w) {
name = new char[::strlen(w.name) + 1];
::strcpy(name, w.name);
}
Person::~Person() {
delete []name;
}
int main()
{
Person p1("John");
Person p2(p1);
printf("p1.name = %p\n", p1.name);
printf("p2.name = %p\n", p2.name);
return 0;
}
- 总结:
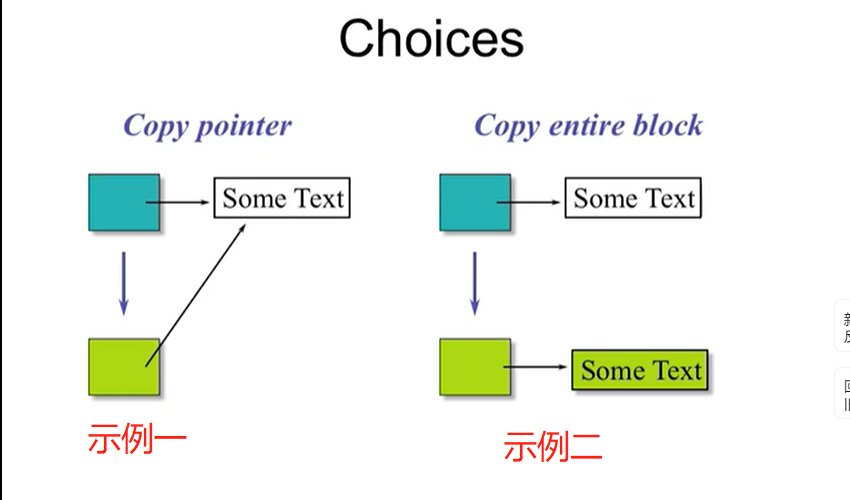
12.3 When are copy constructor called?
- During call by value
void roster(Person); // 函数声明
Person child("Tom"); // 创建对象
roster(child); // 调用函数,参数为对象本身
- During initialization
Person baby_a("Fred");
// 以下需要使用 copy constructor
Person baby_b = baby_a; // not an assignment
Person baby_c(baby_a); // not an assignment
- During function return
Person f()
{
Person player("Musk");
return player;
}
int main()
{
Person p = f();
return 0;
}
12.3.1 编译器对拷贝的优化
- Compilers can "optimize out" copies when safe!
// 示例一:
Person copy_func(char *who) {
Person local(who);
local.print();
return local; // copy constructor called!
}
// 示例二:
Person nocopy_func(char *who) {
return Person(who); // no copy needed!
}
12.4 Construction vs. assignment
- Every object is constructed once.
- Every object should be destroyed once
- Failure to invoke delete()
- Invoking delete() more than once
- Once an object is constructed, it can be the target of many assignment operations.
12.5 Copy constructor guidelines
- In general, be explicit
- Create your own copy constructor -- don't rely on the default
- If you don't need one, declare a private copy constructor
- prevents creation of a default copy constructor
- generates a compiler error if try to pass-by-value
- don't need a definition
参考资料:




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号