数据结构——栈——求直方图最大面积
原题描述
Given n non-negative integers representing the histogram’s bar height where the width of each bar is 1, find the area of largest rectangle in the histogram.
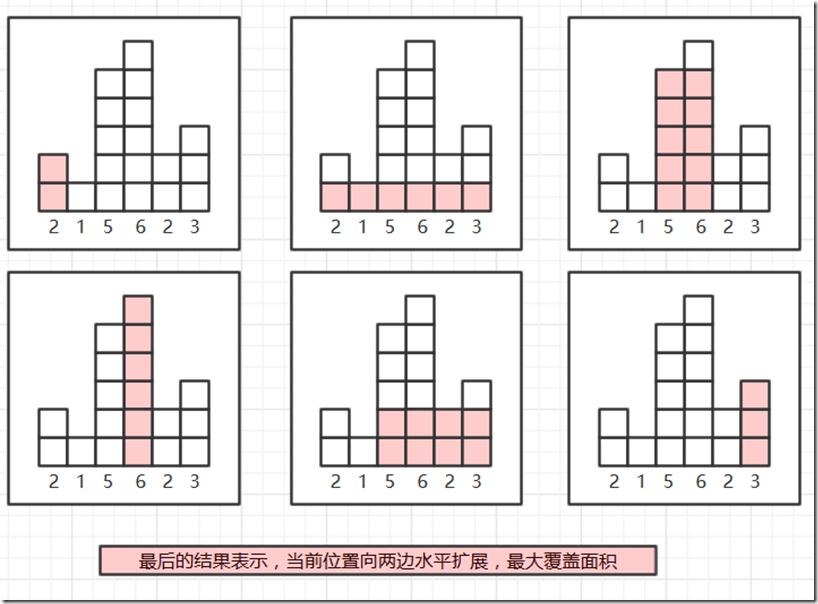
Above is a histogram where width of each bar is 1, given height = [2,1,5,6,2,3].
The largest rectangle is shown in the shaded area, which has area = 10 unit.
For example,
Given height = [2,1,5,6,2,3],
return 10.
简单的说,给出一个直方图,求里面可以画出的最大的矩形的面积
动态规划解题思路
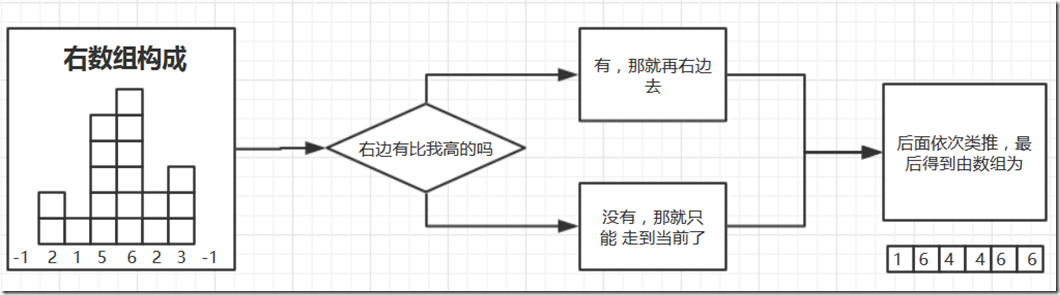
1、求出左数组:左数组的定义为,里面存放,从当前数组下标对应位置尽可能的往左走(前面的元素一定要比自己高),最左边所对应的元素。
2、求出右数组:定义和左数组相同,但是方向向右。
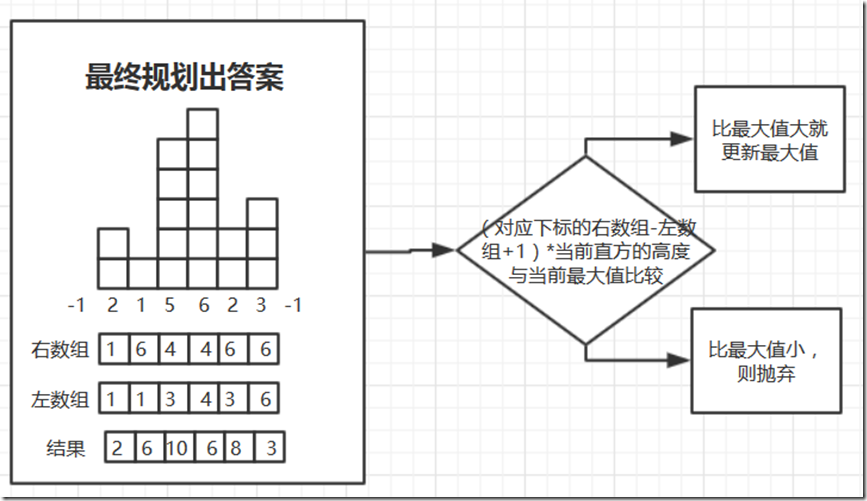
3、利用左右数组和每个位置的高度求出面积的最大值。
这样讲我自己都觉得抽象,还是由图形来说明。
总结一下这个算法的思想:假设当前高度x直方向左走最多走到那里,向右最多走到那里,向左右走的时候都能走比它高的,因为和低的不能组成矩形。
然后就是当前高度下最长的矩形了,然后计算每个高度下最大的矩形就能得到最大值了。
其中利用动态规划思想的地方是在:向左走的时候,如果前一个元素比你高,那么你可以利用前一个元素已经求出的左数组中的值从这个值直接再向前找。
举例来说:165432,现在3的左数组已经求出来的是【2】也就是下标为2的数字6,当要求2对应的左数组的值,因为3大于2,所以你可以直接利用3左数组中的值【2】因为大于3肯定大于2,所以可以瞬间往前走好几步。
如果还是不理解,那就看看代码吧。
动态规划解题代码
/** *求直方图最大面积-dp **/ #include <cstdio> #include <cstdlib> #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; //数组元素个数 int n=6; //保存直方图的高度 (前后用一个-1标记) int high[8]={-1,2,1,5,6,2,3,-1}; //定义左右数组 int leftArray[8]={-1,0,0,0,0,0,0,-1}; int rightArray[8]={-1,0,0,0,0,0,0,-1}; void getLeft() { for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { int k = i; while(high[i] <= high[k-1]) k = leftArray[k-1]; leftArray[i] = k; } } void getRight() { for(int i=n;i>=1;i--) { int k = i; while(high[i] <= high[k+1]) k = rightArray[k+1]; rightArray[i] = k; } } int getMax() { int maxArea = 0; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { int temp=0; temp = (rightArray[i]-leftArray[i]+1) * high[i]; if(temp > maxArea) maxArea = temp; } return maxArea; } int main() { //求左数组 getLeft(); //求右数组 getRight(); //求最大值 cout<<getMax()<<endl; return 0; }
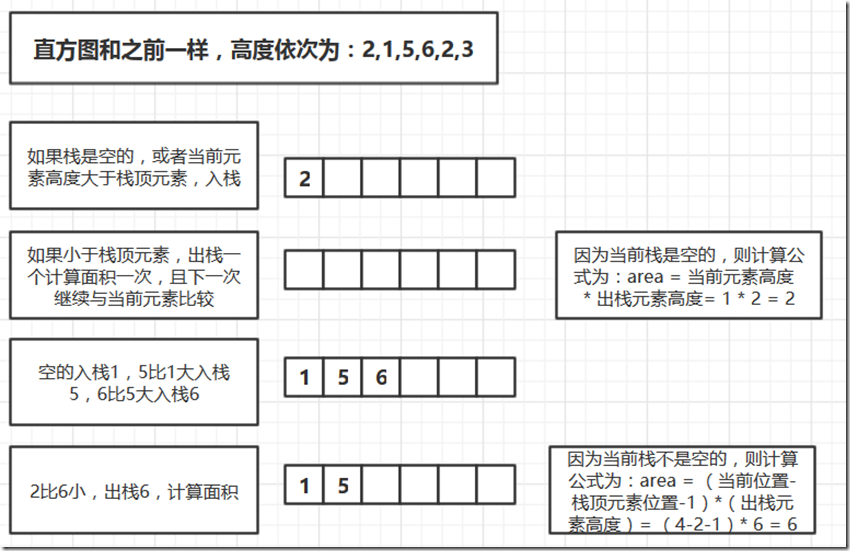
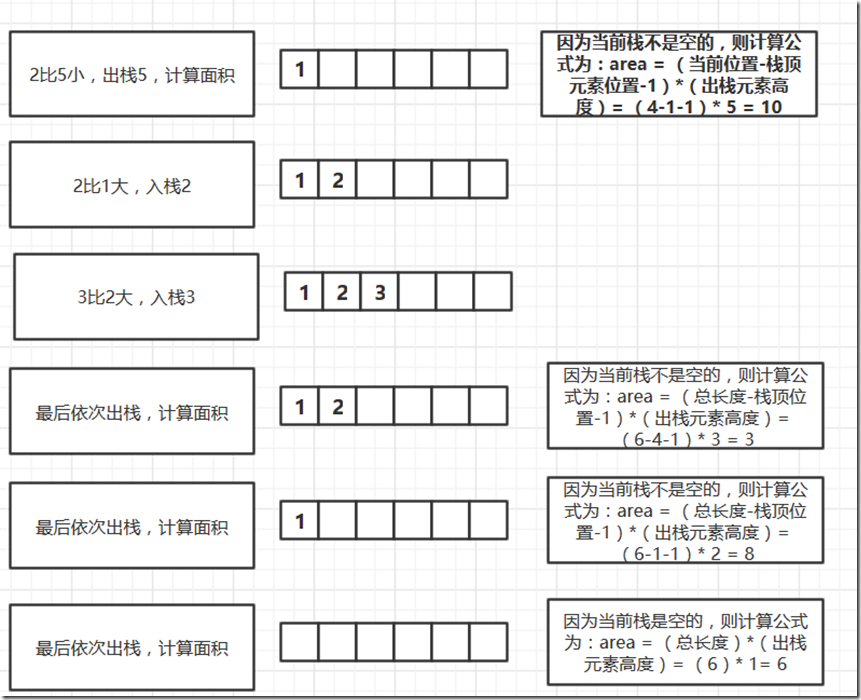
利用栈解题思路
下面是栈的解题思路。巧妙的利用栈里计算全部可能的面积,求最大值。
利用栈解题的代码
/** *求直方图最大面积-stack **/ #include <cstdio> #include <cstdlib> #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <stack> using namespace std; //数组元素个数 int n=6; //保存直方图的高度 (前后用一个-1标记) int high[6]={2,1,5,6,2,3}; int main() { int i=0, maxArea=0,tempArea=0,popNum=0; stack<int> map; for(i=0; i<n; i++) { if(map.empty() || high[i] > high[map.top()]) map.push(i); else { popNum = map.top(); map.pop(); if(map.empty()) { tempArea = i * high[popNum]; } else { tempArea = (i-map.top()-1) * high[popNum]; } if(tempArea > maxArea) maxArea = tempArea; i--; } } while(!map.empty()) { popNum = map.top(); map.pop(); if(map.empty()) { tempArea = n * high[popNum]; } else { tempArea = (n-map.top()-1) * high[popNum]; } if(tempArea > maxArea) maxArea = tempArea; } cout<<"max area = "<<maxArea<<endl; return 0; }
总结和思考
个人认为其实dp的方式更容易让人理解一些,但是从代码量上面来说,确实用栈会快一些。
不够只能说下一次解题如果没有栈这个模版的话,比较容易写出的还是dp的方式。
另外说一下,虽然dp的方式有for循环嵌套while循环,但是还是能保证时间复杂度还是O(N),和栈的方式是相同的。
只能说栈这个方法确实很巧妙,所以要记录一下。






 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号