1.项目相关要求
•基本功能列表:
-c 统计文件中字符的个数
-w 统计文件中的词数
-l 统计文件中的行数
•拓展功能:
-a 统计文件中代码行数、注释行数、空行
2.PSP2.1
|
PSP2.1 |
Personal Software Process Stages |
预估耗时(小时) |
实际耗时(小时) |
|
Planning |
计划 |
1.0 | 1.5 |
|
· Estimate |
· 估计这个任务需要多少时间 |
0.5 | 1 |
|
Development |
开发 |
30 | 40 |
|
· Analysis |
· 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) |
0.5 | 1 |
|
· Design Spec |
· 生成设计文档 |
0.5 | 0.6 |
|
· Design Review |
· 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) |
0.5 | 0.2 |
|
· Coding Standard |
· 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) |
0.5 | 0.5 |
|
· Design |
· 具体设计 |
1 | 1.5 |
|
· Coding |
· 具体编码 |
30 | 40 |
|
· Code Review |
· 代码复审 |
1 | 2 |
|
· Test |
· 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) |
0.5 | 1 |
|
Reporting |
报告 |
0.5 | 0.5 |
|
· Test Report |
· 测试报告 |
0.5 | 0.5 |
|
· Size Measurement |
· 计算工作量 |
0.5 | 0.5 |
|
· Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan |
· 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 |
0.5 | 1 |
|
合计 |
39 | 52 |
3.解题思路
首先需要读取文件,然后通过命令 计算出字符、词、行、空行、注释行、代码行。
基础功能部分:读取文件后,将读取的文件转换成数组的形式,然后每生成一个数组,就是一行。其中,数组的长度就是字符数。利用正则表达式,判断词的开头结尾,进行计数。
拓展功能部分:利用正则表达式判断是否是注释行。数组长度为0或1为空行。然后代码行=总行数-空行-注释行
4.流程图
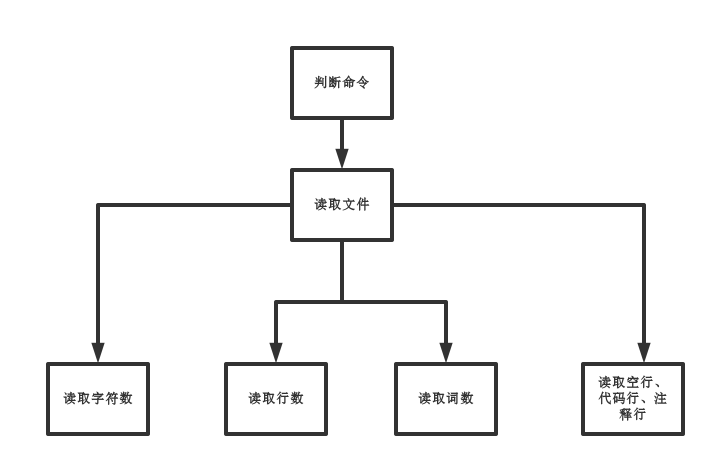
5.代码实现
字符数
public static void charNum()throws Exception
{ //文件导入
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("please input path:");
String path = input.next();
int countChar = 0;
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(path));
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);
while(br.read()!=-1)//read()=-1代表数据读取完毕
{
String s = br.readLine();
countChar += s.length();//字符个数就是字符长度
}
isr.close();//关闭文件
System.out.println("字符个数 "+countChar);
}
词数
public static void wordNum()throws Exception
{Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("please input path:");
String path = input.next();
int countword = 0;
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(path));
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);
while(br.read()!=-1)//read()=-1代表数据读取完毕
{
String s = br.readLine();
Pattern p = Pattern.compile("\\b[A-Za-z]+\\b");//创建以字母为开头或结尾的模板
Matcher m = p.matcher(s.toString());
while(m.find())
{
countword++;
}
}
isr.close();//关闭文件
System.out.println("单词个数 "+countword );
行数
public static void lineNum()throws Exception
{Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("please input path:");
String path = input.next();
int countline = 0;
int countcommentline = 0;
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(path));
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);
while(br.read()!=-1)//read()=-1代表数据读取完毕
{
String s = br.readLine();
countline++;//因为是按行读取,所以每次增加一即可计算出行的数目
}
isr.close();//关闭文件
System.out.println("行数 "+countline);
}
空行,注释行,代码行
public static void alllineNum()throws Exception
{Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("please input path:");
String path = input.next();
int countline = 0;
int countcommentline = 0;
int countblankline = 0;
int codeNum=0;
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(path));
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);
while(br.read()!=-1)//read()=-1代表数据读取完毕
{
String s = br.readLine();
if(s.length()<=1)
{
countblankline++;
}
Pattern p = Pattern.compile("((/)|(/\\*+)|((^\\s)*\\*)|((^\\s)*\\*+/))+");//创建以注释符为开头或结尾的模板
Matcher m = p.matcher(s.toString());
while(m.find())
{
countcommentline++;
}
countline++;//因为是按行读取,所以每次增加一即可计算出行的数目
}
isr.close();//关闭文件
codeNum=countline-countcommentline-countblankline;
System.out.println("行数 "+countline);
System.out.println("注释行 "+countcommentline );
System.out.println("空行数 "+countblankline);
System.out.println("代码行 "+codeNum);
}
main函数
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
String bString = null;
System.out.println("请输入命令 ");
Scanner ms= new Scanner(System.in);
if (ms.hasNext()) {
bString = ms.next();
}
if (bString.equals("-c"))
{
s.charNum();
}
if (bString.equals("-w"))
{
s.wordNum();
}
if (bString.equals("-l"))
{
s.lineNum();
}
if (bString.equals("-b"))
{
s.blanklineNum();
}
if (bString.equals("-a"))
{
s.alllineNum();
}
}
6.测试运行
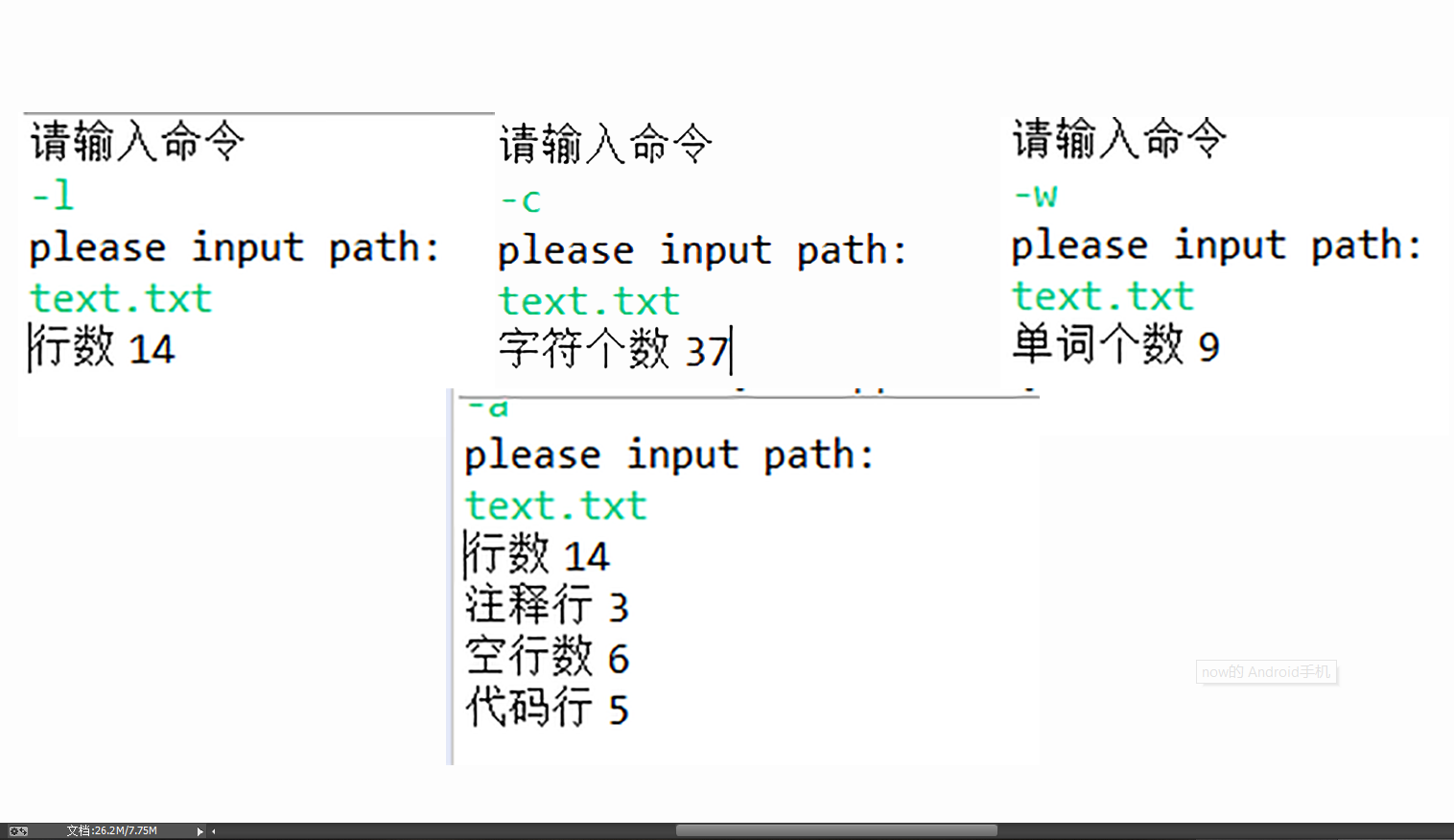
7. 项目总结
通过这次项目,我发现自己知识体系有所欠缺,通过学习书本,和上网查询,请教同学得以解决。也学习到了许多新的知识。



