堆-cnblog
LeetCode
133. 克隆图
给你无向 连通 图中一个节点的引用,请你返回该图的 深拷贝(克隆)。
图中的每个节点都包含它的值 val(int) 和其邻居的列表(list[Node])。
class Node { public int val; public List<Node> neighbors; }
测试用例格式:
简单起见,每个节点的值都和它的索引相同。例如,第一个节点值为 1(val = 1),第二个节点值为 2(val = 2),以此类推。该图在测试用例中使用邻接列表表示。
邻接列表 是用于表示有限图的无序列表的集合。每个列表都描述了图中节点的邻居集。
给定节点将始终是图中的第一个节点(值为 1)。你必须将 给定节点的拷贝 作为对克隆图的引用返回。
示例 1:
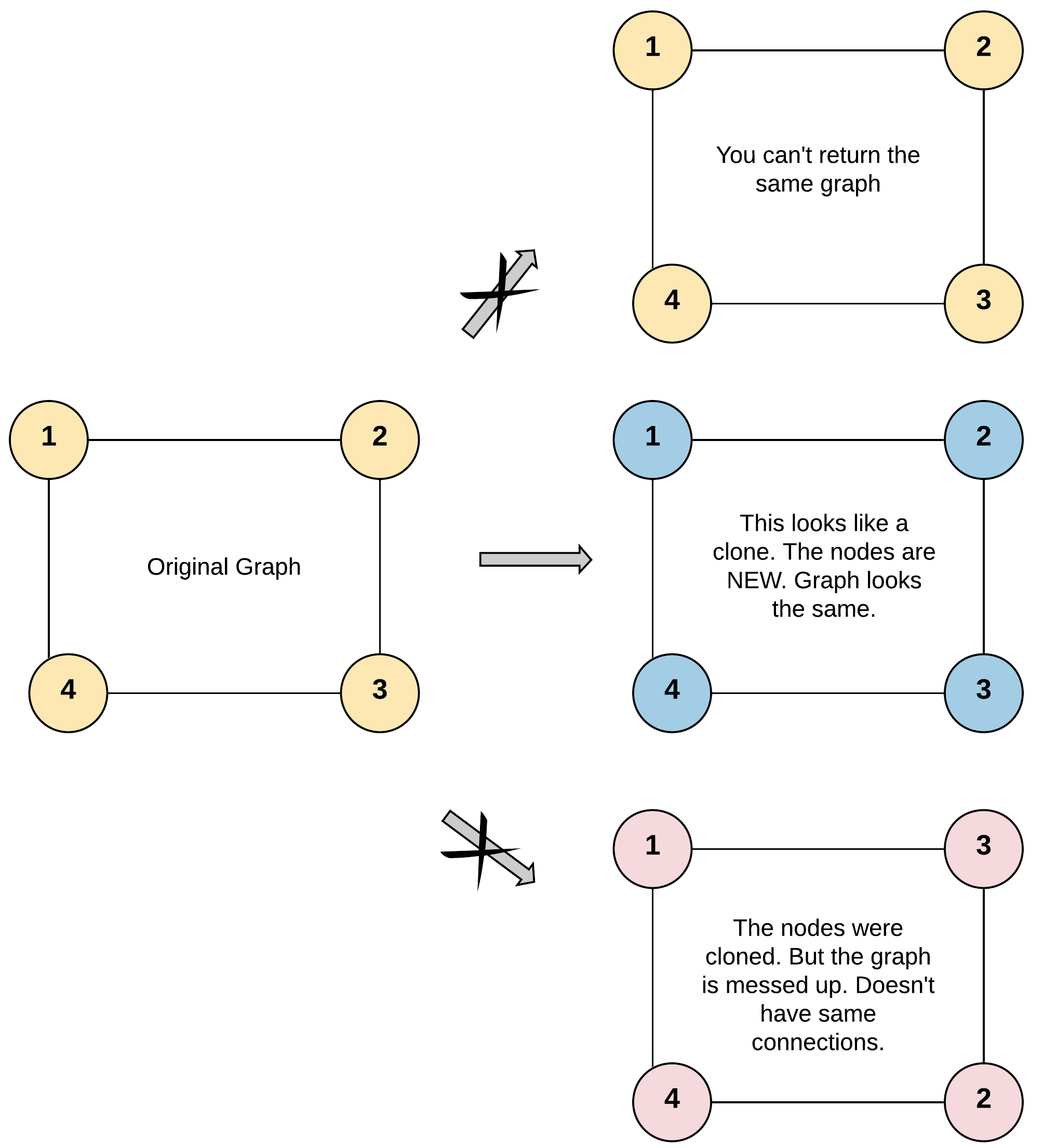
输入:adjList = [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]] 输出:[[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]] 解释: 图中有 4 个节点。 节点 1 的值是 1,它有两个邻居:节点 2 和 4 。 节点 2 的值是 2,它有两个邻居:节点 1 和 3 。 节点 3 的值是 3,它有两个邻居:节点 2 和 4 。 节点 4 的值是 4,它有两个邻居:节点 1 和 3 。
示例 2:
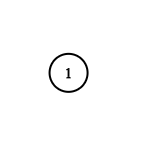
输入:adjList = [[]] 输出:[[]] 解释:输入包含一个空列表。该图仅仅只有一个值为 1 的节点,它没有任何邻居。
示例 3:
输入:adjList = [] 输出:[] 解释:这个图是空的,它不含任何节点。
示例 4:
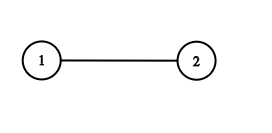
输入:adjList = [[2],[1]] 输出:[[2],[1]]
提示:
- 节点数不超过 100 。
- 每个节点值
Node.val都是唯一的,1 <= Node.val <= 100。 - 无向图是一个简单图,这意味着图中没有重复的边,也没有自环。
- 由于图是无向的,如果节点 p 是节点 q 的邻居,那么节点 q 也必须是节点 p 的邻居。
- 图是连通图,你可以从给定节点访问到所有节点。
解题思路
1. 深度优先搜索或者广度优先搜索 2. 克隆每一个访问的节点 3. 克隆每一个访问的节点所有的边
完整代码
/** * // Definition for a Node. * function Node(val, neighbors) { * this.val = val === undefined ? 0 : val; * this.neighbors = neighbors === undefined ? [] : neighbors; * }; */ /** * @param {Node} node * @return {Node} */ var cloneGraph = function (node) { // console.log(node.neighbors) // console.log(node.neighbors[0].neighbors) // 无向图的搜索 // 每次创建新的节点 // console.log(node) if (!node) { return null } if (node.length === 1 && node.val === 1) { // console.log(1) return new Node(1, []) } // 访问数组集合 const visited = new Set() // 先来一次dfs,将新节点创建出来 // 克隆节点的数组 let nodeList = [] const nodeNew = new Node(node.val, []) // res.neighbors.push(nodeNew) nodeList.push(nodeNew) const dfs = root => { // console.log(root.val) // 加入访问数组 visited.add(root.val) root.neighbors.forEach(node => { if (!visited.has(node.val)) { // 克隆邻居节点 const nodeNew = new Node(node.val, []) // res.neighbors.push(nodeNew) nodeList[node.val - 1] = nodeNew dfs(node) } // 克隆邻居节点所有的边 nodeList[root.val - 1].neighbors.push(nodeList[node.val - 1]) }) } dfs(node) console.log(nodeList) console.log(nodeList[0]) console.log(nodeList[1]) console.log(nodeList[2]) console.log(nodeList[3]) // const res=nodeList[0] return nodeList[0] }
优化(广度优先搜索+Map)
/** * // Definition for a Node. * function Node(val, neighbors) { * this.val = val === undefined ? 0 : val; * this.neighbors = neighbors === undefined ? [] : neighbors; * }; */ /** * @param {Node} node * @return {Node} */ var cloneGraph = function (node) { if (!node) { return null } if (node.length === 1 && node.val === 1) { return new Node(1, []) } // 建立源节点(node,nodeNew)之间的映射关系 const visited = new Map() const nodeNew = new Node(node.val, []) visited.set(node, nodeNew) let queue = [] queue.push(node) while (queue.length) { const node = queue.shift() node.neighbors.forEach(nextNode => { if (!visited.has(nextNode)) { queue.push(nextNode) // 设置映射关系 克隆节点 visited.set(nextNode, new Node(nextNode.val, [])) } // 克隆边 // 获取外层node 对应的 克隆node visited.get(node) // 获取其对应邻居的克隆节点 visited.get(node).neighbors.push(visited.get(nextNode)) }) } return nodeNew // return nodeList[0] }
堆
- 特殊的完全二叉树
- 完全二叉树
- 堆要么是最大堆,要么是最小堆
- 最大堆
- 所有节点都大于它的子节点
- 最小堆
- 所有节点都小于它的子节点
js中表示堆
因为js中没有提供堆直接实现的数据结构

代码实现一个最大堆(最小堆也差不多)
class MaxHeap { constructor() { this.heap = [] } // 获取堆的大小 size() { return this.heap.length } // 获取堆顶 peek() { // 为什么不加判断,因为不存在就是undefined return this.heap[0] } // 获取当前节点的左节点下标 getLeftIndex(index) { return index * 2 + 1 } // 获取当前节点的右节点的下标 getRightIndex(index) { return index * 2 + 2 } // 获取当前节点的父节点下标 getParentIndex(index) { return Math.floor(index / 2) } // 交换节点 swap(index1, index2) { let temp = this.heap[index1] this.heap[index1] = this.heap[index2] this.heap[index2] = temp } // 上移操作 shiftUp(index) { if (index === 0) return const parentIndex = this.getParentIndex(index) // 判断当前节点值是否大于父节点的值 if (this.heap[index] > this.heap[parentIndex]) { // 上移,即交换 this.swap(index, parentIndex) // 继续上移,直到不满足大于条件,或者parentIndex=0 this.shiftUp(parentIndex) } } // 向堆中插入一个新的节点 insert(value) { // 默认插入数组的尾部 this.heap.push(value) // 然后开始上移,如果改节点大于它的父节点,依此类推 this.shiftUp(this.size() - 1) } // 下移节点,如果当前节点小于子节点 shiftDown(index) { const leftIndex = this.getLeftIndex(index) const rightIndex = this.getRightIndex(index) if (this.heap[index] < this.heap[leftIndex]) { this.swap(index, leftIndex) this.shiftDown(leftIndex) } if (this.heap[index] < this.heap[rightIndex]) { this.swap(index, rightIndex) this.shiftDown(rightIndex) } } // 移除堆顶元素 pop() { //为了不破坏原有的结构 this.heap[0] = this.heap.pop() this.shiftDown(0) // 将最后一个在下移一下 } } const heap = new MaxHeap() heap.insert(3) heap.insert(5) heap.insert(8) heap.peek() heap.pop() heap.peek()
堆-LeetCode
215. 数组中的第K个最大元素
给定整数数组 nums 和整数 k,请返回数组中第 **k** 个最大的元素。
请注意,你需要找的是数组排序后的第 k 个最大的元素,而不是第 k 个不同的元素。
你必须设计并实现时间复杂度为 O(n) 的算法解决此问题。
示例 1:
输入: [3,2,1,5,6,4], k = 2 输出: 5
示例 2:
输入: [3,2,3,1,2,4,5,5,6], k = 4 输出: 4
提示:
1 <= k <= nums.length <= 105-104 <= nums[i] <= 104
解题思路
1. 使用刚学的数据结构-堆 2. 最小堆,因为堆顶元素一直是最小的 3. 但堆的大小达到最大时,每次新的元素添加,必有旧的元素离开(最小的) 4. 那么最后留下了的即是最大的k个数(k为堆长度)
代码实现
- 最小堆堆数据结构
class MinHeap { constructor() { this.heap = [] } swap(i1, i2) { const temp = this.heap[i1] this.heap[i1] = this.heap[i2] this.heap[i2] = temp } getParentIndex(i) { // (i-1)/2 return (i - 1) >> 1 } getLeftIndex(i) { return i * 2 + 1 } getRightIndex(i) { return i * 2 + 2 } shiftUp(index) { if (index == 0) { return } const parentIndex = this.getParentIndex(index) if (this.heap[parentIndex] > this.heap[index]) { this.swap(parentIndex, index) this.shiftUp(parentIndex) } } shiftDown(index) { const leftIndex = this.getLeftIndex(index) const rightIndex = this.getRightIndex(index) if (this.heap[leftIndex] < this.heap[index]) { this.swap(leftIndex, index) this.shiftDown(leftIndex) } if (this.heap[rightIndex] < this.heap[index]) { this.swap(rightIndex, index) this.shiftDown(rightIndex) } } insert(value) { this.heap.push(value) this.shiftUp(this.heap.length - 1) } pop() { this.heap[0] = this.heap.pop() this.shiftDown(0) } peek() { return this.heap[0] } size() { return this.heap.length } } const h = new MinHeap() h.insert(3) h.insert(2) h.insert(1) h.pop()
- 主函数
var findKthLargest = function (nums, k) { // 使用最小堆 // 最小堆的长度固定是,每超过一个,就会移除栈顶(最小的) ,也就是每次超出,都会移除一个最小值(那保留的就是k个最大值) const heap = new MinHeap() /* * 超时了, * 算法是正确的 */ // nums.forEach((item,i)=>{ // console.log(item,i) // heap.insert(item) // if(heap.size()>k){ // heap.pop() // } // }) // 优化版本=> insert之前加上判断 // 减少不必要的push操作 for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { if (i < k) { heap.insert(nums[i]) } else { if (nums[i] >= heap.heap[0]) { heap.heap[0] = nums[i] heap.shiftDown(0) } } } // 循环后,栈顶就是第k个最大值(size长度为k,保留了k个最大的) console.log(heap.heap[0]) return heap.peek() }
347. 前 K 个高频元素
给你一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数 k ,请你返回其中出现频率前 k 高的元素。你可以按 任意顺序 返回答案。
示例 1:
输入: nums = [1,1,1,2,2,3], k = 2 输出: [1,2]
示例 2:
输入: nums = [1], k = 1 输出: [1]
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 105k的取值范围是[1, 数组中不相同的元素的个数]- 题目数据保证答案唯一,换句话说,数组中前
k个高频元素的集合是唯一的
进阶:你所设计算法的时间复杂度 必须 优于 O(n log n) ,其中 n 是数组大小。
解题思路
和上面一个题目一样
/** * @param {number[]} nums * @param {number} k * @return {number[]} */ class MinHeap { constructor() { this.heap = [] } swap(i1, i2) { const temp = this.heap[i1] this.heap[i1] = this.heap[i2] this.heap[i2] = temp } getParentIndex(i) { // (i-1)/2 return (i - 1) >> 1 } getLeftIndex(i) { return i * 2 + 1 } getRightIndex(i) { return i * 2 + 2 } shiftUp(index) { if (index == 0) { return } const parentIndex = this.getParentIndex(index) if (this.heap[parentIndex]&&this.heap[parentIndex].value > this.heap[index].value) { this.swap(parentIndex, index) this.shiftUp(parentIndex) } } shiftDown(index) { const leftIndex = this.getLeftIndex(index) const rightIndex = this.getRightIndex(index) if (this.heap[leftIndex]&&this.heap[leftIndex].value < this.heap[index].value) { this.swap(leftIndex, index) this.shiftDown(leftIndex) } if (this.heap[rightIndex]&&this.heap[rightIndex].value < this.heap[index].value) { this.swap(rightIndex, index) this.shiftDown(rightIndex) } } insert(value) { this.heap.push(value) this.shiftUp(this.heap.length - 1) } pop() { this.heap[0] = this.heap.pop() this.shiftDown(0) } peek() { return this.heap[0] } size() { return this.heap.length } } const h = new MinHeap() h.insert(3) h.insert(2) h.insert(1) h.pop() // 1.堆排 // 2.快排 var topKFrequent = function(nums, k) { const m=new Map() // 对出现次数进行统计 nums.forEach((item)=>{ m.set(item,m.has(item)? m.get(item)+1:1) }) // 这里可以使用快速排序(Olog(N))或者堆排 // 但是堆排时间复杂度 (O log(K))k<=n let p=new MinHeap() m.forEach((value,key)=>{ p.insert({value,key}) if(p.size()>k){ p.pop() } }) return p.heap.map(item=>item.key) };
23. 合并K个升序链表
给你一个链表数组,每个链表都已经按升序排列。
请你将所有链表合并到一个升序链表中,返回合并后的链表。
示例 1:
输入:lists = [[1,4,5],[1,3,4],[2,6]] 输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4,5,6] 解释:链表数组如下: [ 1->4->5, 1->3->4, 2->6 ] 将它们合并到一个有序链表中得到。 1->1->2->3->4->4->5->6
示例 2:
输入:lists = [] 输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:lists = [[]] 输出:[]
提示:
k == lists.length0 <= k <= 10^40 <= lists[i].length <= 500-10^4 <= lists[i][j] <= 10^4lists[i]按 升序 排列lists[i].length的总和不超过10^4
解题思路
1. 堆排序,每次输出最小值 2. 把各个链表头进堆 3. 每次出堆的为最小值,同时把它的后继节点入堆 4. 注意点 当只剩下一个节点时 pop() { // 这里需要修改 // 每次pop需要返回值 if(this.size()===1) return this.heap.shift() const top=this.heap[0] this.heap[0] = this.heap.pop() this.shiftDown(0) return top; }
完整代码
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * function ListNode(val, next) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next) * } */ /** * @param {ListNode[]} lists * @return {ListNode} */ class MinHeap { constructor() { this.heap = [] } swap(i1, i2) { const temp = this.heap[i1] this.heap[i1] = this.heap[i2] this.heap[i2] = temp } getParentIndex(i) { // (i-1)/2 return (i - 1) >> 1 } getLeftIndex(i) { return i * 2 + 1 } getRightIndex(i) { return i * 2 + 2 } shiftUp(index) { if (index == 0) { return } const parentIndex = this.getParentIndex(index) if ( this.heap[parentIndex] && this.heap[parentIndex].val > this.heap[index].val ) { this.swap(parentIndex, index) this.shiftUp(parentIndex) } } shiftDown(index) { const leftIndex = this.getLeftIndex(index) const rightIndex = this.getRightIndex(index) if ( this.heap[leftIndex] && this.heap[leftIndex].val < this.heap[index].val ) { this.swap(leftIndex, index) this.shiftDown(leftIndex) } if ( this.heap[rightIndex] && this.heap[rightIndex].val < this.heap[index].val ) { this.swap(rightIndex, index) this.shiftDown(rightIndex) } } insert(value) { this.heap.push(value) this.shiftUp(this.heap.length - 1) } pop() { // 这里需要修改 // 每次pop需要返回值 if (this.size() === 1) return this.heap.shift() const top = this.heap[0] this.heap[0] = this.heap.pop() this.shiftDown(0) return top } peek() { return this.heap[0] } size() { return this.heap.length } } // 使用堆排序 // 因为只需要每次输出最小值出来,最下堆 var mergeKLists = function (lists) { let h = new MinHeap() lists.forEach(node => { if (node) { h.insert(node) } }) const res = new ListNode(-1) let res1 = res while (h.size()) { // 最小的弹出 const top = h.pop() console.log(top) // res1.next=new ListNode(top.val) res1.next = top res1 = res1.next // 把后面的节点进堆 if (top.next) { h.insert(top.next) } } return res.next }




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· Docker 太简单,K8s 太复杂?w7panel 让容器管理更轻松!