SLAM14讲 第七章 2D-2D[2] 三角测量

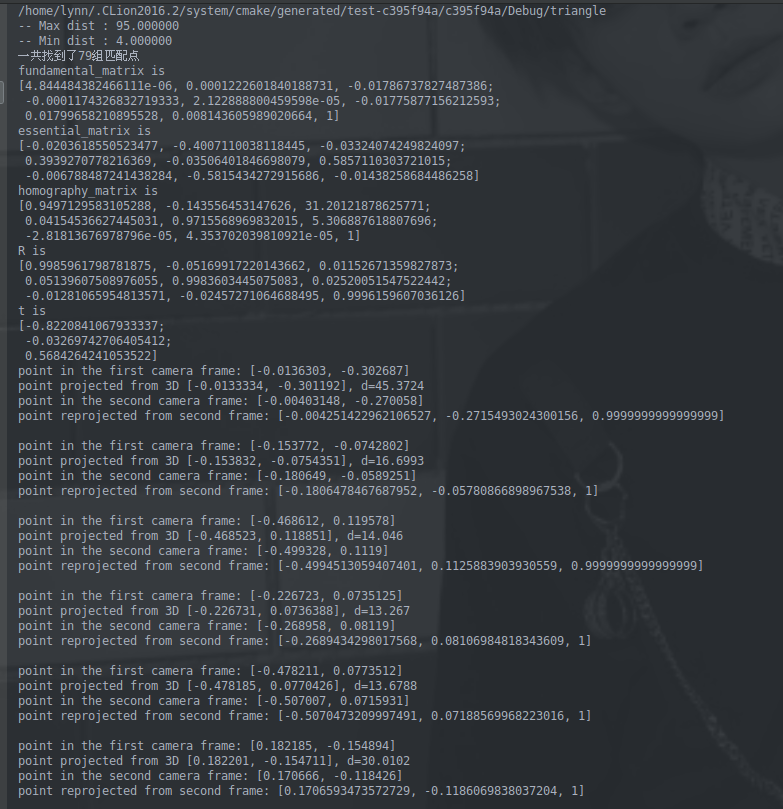
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 | #include <iostream>#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>#include <opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp>#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>#include <opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp>// #include "extra.h" // used in opencv2using namespace std;using namespace cv;//找特征点和描述子void find_feature_matches ( const Mat& img_1, const Mat& img_2, std::vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_1, std::vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_2, std::vector< DMatch >& matches );//DMatch是用于匹配特征关键点的特征描述子的类:查询特征描述子索引, 特征描述子索引, 训练图像索引, 以及不同特征描述子之间的距离.//位姿估计,求R,tvoid pose_estimation_2d2d ( const std::vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_1, const std::vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_2, const std::vector< DMatch >& matches, Mat& R, Mat& t );//三角测量/化,求特征点的三维空间坐标,求double类型的三维点void triangulation ( const vector<KeyPoint>& keypoint_1, const vector<KeyPoint>& keypoint_2, const std::vector< DMatch >& matches, const Mat& R, const Mat& t, vector<Point3d>& points);// 像素坐标转相机归一化坐标,p-O1(相机光心坐标=相机光心标定值/焦距)Point2f pixel2cam( const Point2d& p, const Mat& K );//——————————————————————————————————————//定义float类型的二维点int main ( int argc, char** argv ){ if ( argc != 3 ) { cout<<"usage: triangulation img1 img2"<<endl; return 1; } //-- 读取图像 Mat img_1 = imread ( argv[1], CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR ); Mat img_2 = imread ( argv[2], CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR ); //-- 找匹配点 vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_1, keypoints_2; vector<DMatch> matches; find_feature_matches ( img_1, img_2, keypoints_1, keypoints_2, matches ); cout<<"一共找到了"<<matches.size() <<"组匹配点"<<endl; //-- 估计两张图像间运动 Mat R,t; pose_estimation_2d2d ( keypoints_1, keypoints_2, matches, R, t ); //-- 三角化 vector<Point3d> points; triangulation( keypoints_1, keypoints_2, matches, R, t, points ); //-- 验证三角化点与特征点的重投影关系 Mat K = ( Mat_<double> ( 3,3 ) << 520.9, 0, 325.1, 0, 521.0, 249.7, 0, 0, 1 ); for ( int i=0; i<matches.size(); i++ ) { Point2d pt1_cam = pixel2cam( keypoints_1[ matches[i].queryIdx ].pt, K ); Point2d pt1_cam_3d( points[i].x/points[i].z, points[i].y/points[i].z ); cout<<"point in the first camera frame: "<<pt1_cam<<endl; cout<<"point projected from 3D "<<pt1_cam_3d<<", d="<<points[i].z<<endl; // 第二个图 Point2f pt2_cam = pixel2cam( keypoints_2[ matches[i].trainIdx ].pt, K ); Mat pt2_trans = R*( Mat_<double>(3,1) << points[i].x, points[i].y, points[i].z ) + t; pt2_trans /= pt2_trans.at<double>(2,0); cout<<"point in the second camera frame: "<<pt2_cam<<endl; cout<<"point reprojected from second frame: "<<pt2_trans.t()<<endl; cout<<endl; } return 0;}void find_feature_matches ( const Mat& img_1, const Mat& img_2, std::vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_1, std::vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_2, std::vector< DMatch >& matches ){ //-- 初始化 Mat descriptors_1, descriptors_2; // used in OpenCV3 Ptr<FeatureDetector> detector = ORB::create(); Ptr<DescriptorExtractor> descriptor = ORB::create(); // use this if you are in OpenCV2 // Ptr<FeatureDetector> detector = FeatureDetector::create ( "ORB" ); // Ptr<DescriptorExtractor> descriptor = DescriptorExtractor::create ( "ORB" ); Ptr<DescriptorMatcher> matcher = DescriptorMatcher::create("BruteForce-Hamming"); //-- 第一步:检测 Oriented FAST 角点位置 detector->detect ( img_1,keypoints_1 ); detector->detect ( img_2,keypoints_2 ); //-- 第二步:根据角点位置计算 BRIEF 描述子 descriptor->compute ( img_1, keypoints_1, descriptors_1 ); descriptor->compute ( img_2, keypoints_2, descriptors_2 ); //-- 第三步:对两幅图像中的BRIEF描述子进行匹配,使用 Hamming 距离 vector<DMatch> match; // BFMatcher matcher ( NORM_HAMMING ); matcher->match ( descriptors_1, descriptors_2, match ); //-- 第四步:匹配点对筛选 double min_dist=10000, max_dist=0; //找出所有匹配之间的最小距离和最大距离, 即是最相似的和最不相似的两组点之间的距离 for ( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ ) { double dist = match[i].distance; if ( dist < min_dist ) min_dist = dist; if ( dist > max_dist ) max_dist = dist; } printf ( "-- Max dist : %f \n", max_dist ); printf ( "-- Min dist : %f \n", min_dist ); //当描述子之间的距离大于两倍的最小距离时,即认为匹配有误.但有时候最小距离会非常小,设置一个经验值30作为下限. for ( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ ) { if ( match[i].distance <= max ( 2*min_dist, 30.0 ) ) { matches.push_back ( match[i] ); } }}void pose_estimation_2d2d ( const std::vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_1, const std::vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_2, const std::vector< DMatch >& matches, Mat& R, Mat& t ){ // 相机内参,TUM Freiburg2 Mat K = ( Mat_<double> ( 3,3 ) << 520.9, 0, 325.1, 0, 521.0, 249.7, 0, 0, 1 ); //-- 把匹配点转换为vector<Point2f>的形式 vector<Point2f> points1; vector<Point2f> points2; for ( int i = 0; i < ( int ) matches.size(); i++ ) { points1.push_back ( keypoints_1[matches[i].queryIdx].pt ); points2.push_back ( keypoints_2[matches[i].trainIdx].pt ); } //-- 计算基础矩阵 Mat fundamental_matrix; fundamental_matrix = findFundamentalMat ( points1, points2, CV_FM_8POINT ); cout<<"fundamental_matrix is "<<endl<< fundamental_matrix<<endl; //-- 计算本质矩阵 Point2d principal_point ( 325.1, 249.7 ); //相机主点, TUM dataset标定值 int focal_length = 521; //相机焦距, TUM dataset标定值 Mat essential_matrix; essential_matrix = findEssentialMat ( points1, points2, focal_length, principal_point ); cout<<"essential_matrix is "<<endl<< essential_matrix<<endl; //-- 计算单应矩阵 Mat homography_matrix; homography_matrix = findHomography ( points1, points2, RANSAC, 3 ); cout<<"homography_matrix is "<<endl<<homography_matrix<<endl; //-- 从本质矩阵中恢复旋转和平移信息. recoverPose ( essential_matrix, points1, points2, R, t, focal_length, principal_point ); cout<<"R is "<<endl<<R<<endl; cout<<"t is "<<endl<<t<<endl;}void triangulation ( const vector< KeyPoint >& keypoint_1, const vector< KeyPoint >& keypoint_2, const std::vector< DMatch >& matches, const Mat& R, const Mat& t, vector< Point3d >& points ){ // --变换矩阵T3x4 T1=[I;0],T2=[R;t] Mat T1 = (Mat_<float> (3,4) << 1,0,0,0, 0,1,0,0, 0,0,1,0); Mat T2 = (Mat_<float> (3,4) << R.at<double>(0,0), R.at<double>(0,1), R.at<double>(0,2), t.at<double>(0,0), R.at<double>(1,0), R.at<double>(1,1), R.at<double>(1,2), t.at<double>(1,0), R.at<double>(2,0), R.at<double>(2,1), R.at<double>(2,2), t.at<double>(2,0) ); //相机内参K Mat K = ( Mat_<double> ( 3,3 ) << 520.9, 0, 325.1, 0, 521.0, 249.7, 0, 0, 1 ); vector<Point2f> pts_1, pts_2;//特征点的相机归一化坐标 for ( DMatch m:matches ) { // 将像素坐标转换至相机归一化坐标 pts_1.push_back ( pixel2cam( keypoint_1[m.queryIdx].pt, K) ); pts_2.push_back ( pixel2cam( keypoint_2[m.trainIdx].pt, K) ); } Mat pts_4d; //points4D – 4xN array of reconstructed points in homogeneous coordinates. //输出的3D坐标是齐次坐标,共四个维度,因此需要将前三个维度除以第四个维度以得到非齐次坐标xyz。这个坐标是在相机坐标系下的坐标 cv::triangulatePoints( T1, T2, pts_1, pts_2, pts_4d ); // 转换成非齐次坐标 for ( int i=0; i<pts_4d.cols; i++ ) { Mat x = pts_4d.col(i); x /= x.at<float>(3,0); // 归一化 Point3d p ( x.at<float>(0,0), x.at<float>(1,0), x.at<float>(2,0) ); points.push_back( p );//三角化后的特征点在归一化平面的3D坐标 }}Point2f pixel2cam ( const Point2d& p, const Mat& K ){ return Point2f ( ( p.x - K.at<double>(0,2) ) / K.at<double>(0,0), ( p.y - K.at<double>(1,2) ) / K.at<double>(1,1) );} |






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)