Java IO(七)ByteArrayInputStream 和 ByteArrayOutputStream
Java IO(七)ByteArrayInputStream 和 ByteArrayOutputStream
一、介绍
ByteArrayInputStream 和 ByteArrayOutputStream 是字节数组输入 / 输出流。他们分别继承于 InputStream 和 OutputStream 。
(一)、ByteArrayInputStream
ByteArrayInputStream 是字节数组输入流。它包含一个内部缓冲区,该缓冲区包含从流中读取的字节;通俗点说,它的内部缓冲区就是一个字节数组,而ByteArrayInputStream本质就是通过字节数组来实现的。
我们都知道,InputStream 通过 read() 向外提供接口,供它们来读取字节数据;而 ByteArrayInputStream 的内部额外的定义了一个计数器,它被用来跟踪 read() 方法要读取的下一个字节。
(二)、ByteArrayOutputStream
ByteArrayOutputStream 是字节数组输出流。ByteArrayOutputStream 中的数据被写入一个 byte 数组。缓冲区会随着数据的不断写入而自动增长。可使用 toByteArray() 和 toString() 获取数据。
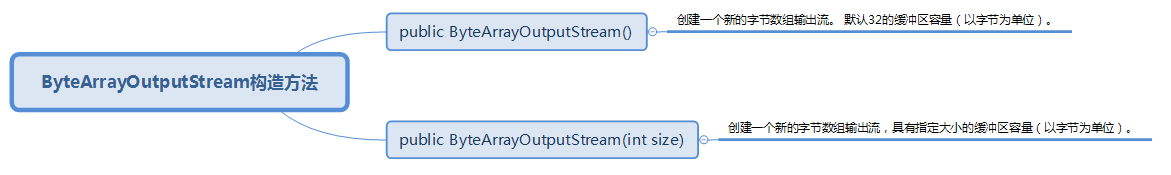
二、构造方法
(一)、ByteArrayInputStream
(二)、ByteArrayOutputStream
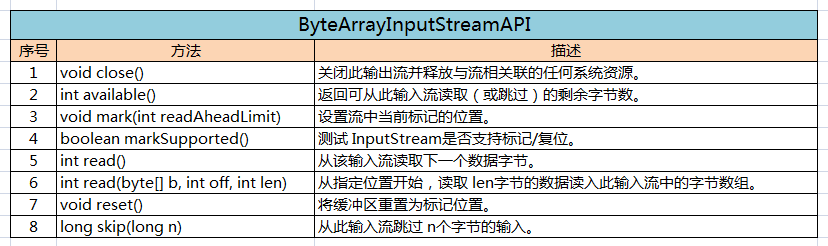
三、常用API
(一)、ByteArrayInputStream
(二)、ByteArrayOutputStream

四、实例
public static void main(String[] args) { write(); read();
} /**
* ByteArrayOutputStream */ private static void write() { ByteArrayOutputStream out = null; byte[] buffer = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz".getBytes(); try { out = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); out.write(99); System.out.println("out = " + out); out.write(buffer, 5, 5); System.out.println("out = " + out); int size = out.size(); System.out.println("size = " + out); byte[] b = out.toByteArray(); System.out.println("byteArray = " + new String(b)); String str = out.toString(); System.out.println("str = " + str); ByteArrayOutputStream out2 = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); out.writeTo((OutputStream)out2); System.out.println("out2 = " + out2); out.reset(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { if(out != null) { out.close(); } }catch(Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } /** * ByteArrayInputStream 测试函数 */ private static void read() { ByteArrayInputStream in = null; byte[] buffer = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz".getBytes(); try { in = new ByteArrayInputStream(buffer); for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { if(in.available() >= 0) { char ch = (char) in.read(); System.out.println(ch); } } in.skip(5); byte[] bu = new byte[10]; in.read(bu); System.out.println(new String(bu)); in.reset(); in.read(bu, 0, 8); System.out.println(new String(bu)); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { if(in != null) { in.close(); } }catch(Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号