Create and use Custom APIs in Power Apps
Create and use Custom APIs
[This topic is pre-release documentation and is subject to change.]
Custom APIs offer a new code-first way to define messages that you can add to Dataverse web services. Conceptually, Custom APIs are an extension to Custom Actions that have provided a no-code way to include custom messages. To differentiate between the two different kinds of Custom Action, we will use Workflow Custom Action to refer to the no-code capabilities that depend on workflow. Custom API will refer to the type of custom action that depends on a developer to write a plug-in.
Custom APIs provide a capabilities specifically for developers to define their logic in code. For a full comparison of Workflow Custom Action and Custom API, see Compare Workflow Custom Action and Custom API.
Create a custom API
Because a Custom API requires a plug-in to implement any logic to be defined by the main operation, you can approach the development of your custom API by:
- Write the plug-in first, and then define the Custom API for it.
- Define the Custom API first, then write the plug-in to implement it.
Your Custom API will be completed when the data defining the Custom API is saved and linked to the Plug-in type to define the main operation. In either case, you should understand the data that drives the Custom API.
There are several different ways to create a custom API:
- By manually entering data in available forms. More information: Create a Custom API in the maker portal
- By using the web services, such as the Web API or Organization Service. More information: Create a Custom API with code
- By editing solution files. More information: Create a Custom API with solution files.
Note
Although Custom API data is stored in entities, we do not support creating a model-driven app for these entities. A designer is planned for a future release.
Regardless of the process you use, the following information describes selected attributes for the three entities that contain the data for a Custom API. You should review this as you plan the behavior for your Custom API.
CustomAPI entity attributes
This table includes attributes of the Custom API entity that you can set.
| Display Name Schema Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Allowed Custom Processing Step TypeAllowedCustomProcessingStepType |
Picklist | The type of custom processing steps allowed for this Custom API. This allows you to control whether other plug-ins can be registered
|
Binding TypeBindingType |
Picklist | The binding type of the custom API.
|
Bound Entity Logical NameBoundEntityLogicalName |
String | The logical name of the entity bound to the custom API if it is not Global. Cannot be changed after it is saved. |
Custom APICustomAPIId |
Uniqueidentifier | Unique identifier for custom API instances Cannot be changed after it is saved. |
DescriptionDescription |
String | Localized description for this Custom API. For use when the message is exposed to be called in an app. For example, as a ToolTip. |
Display NameDisplayName |
String | Localized display name for this Custom API. For use when the message is exposed to be called in an app. |
Execute Privilege NameExecutePrivilegeName |
String | (Optional) Name of the privilege that allows execution of the custom API |
Is FunctionIsFunction |
Boolean | Indicates if the custom API is a function. A function requires the HTTP GET method. Otherwise the Http POST method is required.
More information: Use Web API functions Cannot be changed after it is saved. |
Is PrivateIsPrivate |
Boolean | Indicates if the custom API is private (hidden from metadata and documentation) More information: Private Messages
|
NameName |
String | The primary name of the custom API. This will display in the list of custom apis when viewed in the solution. |
OwnerOwnerId |
Owner | A reference to the user or team that owns the API. |
Plugin TypePluginTypeId |
Lookup | A reference to the plug-in type that provides the main operation for this Custom API |
Unique NameUniqueName |
String | Unique name for the custom API. This will be the name of the message created. This value must include a customization prefix that matches the prefix set for your solution publisher. Cannot be changed after it is saved. |
Note
Some values are not valid for update. They cannot be changed after the Custom API is saved. You should have a clear understanding of how your API should work before you begin. If you need to change any values that are not valid for update, you will have to delete the Custom API entity record and start over. Deleting the Custom API record will delete any Custom API Request Parameters or Custom API Response Properties associated with it.
Set the Execute Privilege Name property to the name of the privilege to require it. There is currently no supported way for developers outside of Microsoft to create new privileges, but an existing privilege can be used. More information: Q: Can I create a new privilege for my Custom API?
If you do not set the Plugin Type (PluginTypeId) to specify main operation logic the API can still be called. You might want to do this as a testing step, but any output parameter values will return the default values for the type because there is no code to set them.
Known Issues:
- The Is Private field is not included in the Custom API form
- Custom API functions cannot use Entity or EntityCollection Request Parameters
CustomAPIRequestParameter entity attributes
A custom API isn’t required to have any parameters. There is no specified order for the parameters, they are identified by name.
A parameter is related to a single Custom API. You cannot define multiple Custom APIs to use the same parameter definition. You can define multiple request parameter with the same UniqueName value if they are used by different Custom APIs.
Note
If you define a bound entity or entity collection for your Custom API, the parameter will be generated for you. You don’t need to create a parameter for bound entities.
This table includes attributes of the Custom API Request Parameter entity that you can set.
| Display Name Schema Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Custom API Request ParameterCustomAPIRequestParameterId |
Uniqueidentifier | Unique identifier for custom API request parameter instances. Cannot be changed after it is saved. |
Custom API CustomAPIId |
Lookup | Unique identifier for the custom API that this custom API request parameter is associated with. Cannot be changed after it is saved. |
DescriptionDescription |
String | Localized description for custom API request parameter instances. For use when the message parameter is exposed to be called in an app. For example, as a ToolTip. |
Display Name DisplayName |
String | Localized display name for custom API request parameter instances. For use when the message parameter is exposed to be called in an app. |
Is OptionalIsOptional |
Boolean | Indicates if the custom API request parameter is optional. If it is not optional, it is required to pass a value for this parameter when using the message.
|
Logical Entity NameLogicalEntityName |
String | The logical name of the entity bound to the custom API request parameter. Cannot be changed after it is saved. |
NameName |
String | The primary name of the custom API request parameter. This will display in the list of custom api request parameters when viewed in the solution. Use this to differentiate this parameter from others that share a common Unique Name. This naming convention is recommended: {Custom API Unique Name}.{Parameter UniqueName} |
Owner OwnerId |
Owner | A reference to the user or team that owns the API. |
TypeType |
Picklist | The data type of the custom API request parameter.
|
Unique Name UniqueName |
String | Unique name for the custom API request parameter. This will be the name of the parameter when you call the Custom API. Cannot be changed after it is saved. |
Note
Some values are not valid for update. They cannot be changed after the Custom API Request Parameter is saved. If you need to change one of these values, you must delete the Custom API Request Parameter and re-create it with the changes you want to make.
CustomAPIResponseProperty entity attributes
The object returned for your Custom API message will include any response properties you define. It is not required for a Custom API to return any value, but if the custom API is defined as a function it is required.
Important
A Custom API that represents a function with no response properties is not valid and will not appear in the Web API $metadata service document. If you try to use it, you will get a 404 Not Found error similar to this:
{"error":{"code":"0x8006088a","message":"Resource not found for the segment 'your_function_name'."}}.
You must also set the data to be returned in the plug-in for the function. If no data is set to be returned by the plug-in, the operation will return 204 No Content.
If there is only a single Entity or EntityCollection response property defined, the response will be of that type. If there are multiple parameters, or one or more parameter of a simple type, the API will return a complex type where each response property will be a property of that complex type. For example, if your Custom API Unique name is sample_CustomAPIExample, it will return a complex type named sample_CustomAPIExampleResponse with properties for each response property you define.
This table includes attributes of the Custom API Response Property entity that you can set.
| Display Name Schema Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Custom API Response PropertyCustomAPIResponsePropertyId |
Uniqueidentifier | Unique identifier for custom API response property instances. Cannot be changed after it is saved. |
Custom API CustomAPIId |
Lookup | Unique identifier for the custom API that this custom API response property is associated with. Cannot be changed after it is saved. |
DescriptionDescription |
String | Localized description for custom API response property instances. For use when the message parameter is exposed to be called in an app. For example, as a ToolTip. |
Display Name DisplayName |
String | Localized display name for custom API response property instances. For use when the message parameter is exposed to be called in an app. |
Logical Entity NameLogicalEntityName |
String | The logical name of the entity bound to the custom API response property . Cannot be changed after it is saved. |
NameName |
String | The primary name of the custom API response property . This will display in the list of custom api request parameters when viewed in the solution. Use this to differentiate this parameter from others that share a common Unique Name. This naming convention is recommended: {Custom API Unique Name}.{Property UniqueName} |
Owner OwnerId |
Owner | A reference to the user or team that owns the API. |
TypeType |
Picklist | The data type of the custom API response property
|
Unique Name UniqueName |
String | Unique name for the custom API response property . This will be the name of the parameter when you call the Custom API. Cannot be changed after it is saved. |
Note
Some values are not valid for update. They cannot be changed after the Custom API Response Property is saved. If you need to change one of these values, you must delete the Custom API Response Property and re-create it with the changes you want to make.
Invoking Custom APIs
A Custom API creates a new message which can be invoked via the SDK or Web API.
Invoking Custom APIs from SDK based applications or plug-ins
You can choose to use either early-bound or late-bound code to invoke your custom API. Use the CrmSvcUtil tool to generate helper request and response classes to mirror the request and response properties of your custom API.
For late-bound code, create an OrganizationRequest with the unique name of your custom API and add parameters with names matching the unique names of the request properties.
Entity-bound custom APIs have an implicit request property named Target that should be set to an EntityReference of the record to invoke the API on.
You can access response properties from the parameters of the returned response.
var req = new OrganizationRequest("myapi_EscalateCase")
{
["Target"] = new EntityReference("incident", guid),
["Priority"] = new OptionSetValue(1)
};
var resp = svc.Execute(req);
var newOwner = (EntityReference) resp["AssignedTo"];
Invoking Custom APIs from the Web API
Custom APIs can be called in the same way as any standard Web API functions or actions. If your custom API has the IsFunction field set to true then it needs to be invoked as a function using a GET request, otherwise it needs to be used as an action using a POST request:
POST [Organization URI]/api/data/v9.1/myapi_CustomUnboundAPI
OData-MaxVersion: 4.0
OData-Version: 4.0
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
{
"InputParameter": "Value"
}
GET [Organization URI]/api/v9.1/accounts(ed5d4e42-850c-45b7-8b38-2677545107cc)/Microsoft.Dynamics.CRM.myapi_CustomBoundAPI()
OData-MaxVersion: 4.0
OData-Version: 4.0
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
GET [Organization URI]/api/v9.1/accounts/Microsoft.Dynamics.CRM.myapi_CustomEntityCollectionBoundAPI()
OData-MaxVersion: 4.0
OData-Version: 4.0
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
Retrieve data about Custom APIs
You can use the following queries to retrieve data about Custom APIs.
Web API
More information: Query Data using the Web API
GET [Organization URI]/api/data/v9.1/customapis?$select=
uniquename,
allowedcustomprocessingsteptype,
bindingtype,
boundentitylogicalname,
description,
displayname,
executeprivilegename,
isfunction,
isprivate
&$expand=
CustomAPIRequestParameters($select=
uniquename,
name,
description,
displayname,
type,
logicalentityname,
isoptional),
CustomAPIResponseProperties($select=
uniquename,
name,
description,
displayname,
type,
logicalentityname),
PluginTypeId($select=
plugintypeid,
typename,
version,
name,
assemblyname)
FetchXml
More information: Use FetchXML to construct a query
<fetch>
<entity name='customapi' >
<attribute name='isprivate' />
<attribute name='description' />
<attribute name='displayname' />
<attribute name='executeprivilegename' />
<attribute name='isfunction' />
<attribute name='allowedcustomprocessingsteptype' />
<attribute name='boundentitylogicalname' />
<attribute name='bindingtype' />
<attribute name='uniquename' />
<link-entity name='customapirequestparameter' from='customapiid' to='customapiid' link-type='outer' alias='req' >
<attribute name='description' />
<attribute name='displayname' />
<attribute name='logicalentityname' />
<attribute name='name' />
<attribute name='uniquename' />
<attribute name='type' />
<attribute name='isoptional' />
</link-entity>
<link-entity name='customapiresponseproperty' from='customapiid' to='customapiid' link-type='outer' >
<attribute name='description' />
<attribute name='displayname' />
<attribute name='logicalentityname' />
<attribute name='name' />
<attribute name='uniquename' />
<attribute name='type' />
</link-entity>
<link-entity name='plugintype' from='plugintypeid' to='plugintypeid' link-type='outer' alias='plugintype' >
<attribute name='name' />
<attribute name='assemblyname' />
<attribute name='version' />
<attribute name='plugintypeid' />
<attribute name='typename' />
</link-entity>
</entity>
</fetch>
Using SQL
More information: Use SQL to query data (Preview)
SELECT api.customapiid,
api.uniquename,
api.allowedcustomprocessingsteptype,
api.bindingtype,
api.boundentitylogicalname,
api.description,
api.displayname,
api.executeprivilegename,
api.isfunction,
api.isprivate,
req.customapirequestparameterid,
req.uniquename,
req.name,
req.description,
req.displayname,
req.type,
req.logicalentityname,
req.isoptional,
resp.customapiresponsepropertyid,
resp.uniquename,
resp.name,
resp.description,
resp.type,
resp.logicalentityname,
type.plugintypeid,
type.typename,
type.version,
type.name,
type.assemblyname
FROM customapi AS api
LEFT JOIN
customapirequestparameter AS req
ON api.customapiid = req.customapiid
LEFT JOIN
customapiresponseproperty AS resp
ON api.customapiid = resp.customapiid
LEFT JOIN
plugintype AS type
ON api.plugintypeid = type.plugintypeid
Localized values
You can localize the values using the steps documented here: Translate localizable text for model-driven apps and Translating labels and display strings.
This process involves exporting a file that contains the base language values and will include a column for each additional language enabled. You can then edit the values in Excel. After you complete the process to import the translations the labels will be included in your solution.
The following example shows editing the Excel worksheet to add Japanese translations for the English values.
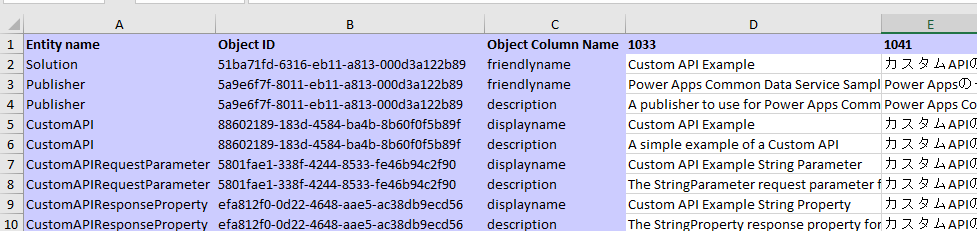
Tip
If you are editing the solution files to create your Custom APIs, you can provide the localized labels directly. More information: Providing Localized Labels with the solution
Setting localized values
If you prefer to set localized labels in code rather than using the manual process described above, you can use the SetLocLabels message using either the Web API SetLocLabels Action or the Organization Service SetLocLabelsRequest.
The following example shows how to use the Web API to set the localized labels for the displayname property of a custom API.
Request
POST [Organization URI]/api/data/v9.1/SetLocLabels HTTP/1.1
Accept: application/json
OData-MaxVersion: 4.0
OData-Version: 4.0
Content-Type: application/json
{
"EntityMoniker": {
"@odata.type": "Microsoft.Dynamics.CRM.customapi",
"customapiid": "86bcd12e-2f30-eb11-a813-000d3a122b89"
},
"AttributeName": "displayname",
"Labels": [
{
"Label": "例え",
"LanguageCode": 1041
},
{
"Label": "Beispiel",
"LanguageCode": 1031
},
{
"Label": "ejemplo",
"LanguageCode": 1034
}
]
}
Response
HTTP/1.1 204 No Content
Retrieving localized values
To retrieve the localized labels use the RetrieveLocLabels message using either the Web API RetrieveLocLabels Function or the Organization Service RetrieveLocLabelsRequest.
The following example shows using the RetrieveLocLabels Function to retrieve the labels for the the displaynameproperty of a Custom API with the customapiid of 88602189-183d-4584-ba4b-8b60f0f5b89f
Request
GET [Organization URI]/api/data/v9.1/RetrieveLocLabels(EntityMoniker=@p1,AttributeName=@p2,IncludeUnpublished=@p3)?
@p1={'@odata.id':'customapis(88602189-183d-4584-ba4b-8b60f0f5b89f)'}&
@p2='displayname'&
@p3=false HTTP/1.1
Response
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
OData-Version: 4.0
{
"@odata.context": "[Organization URI]/api/data/v9.1/$metadata#Microsoft.Dynamics.CRM.RetrieveLocLabelsResponse",
"Label": {
"LocalizedLabels": [
{
"Label": "Custom API Example",
"LanguageCode": 1033,
"IsManaged": null,
"MetadataId": null,
"HasChanged": null
},
{
"Label": "カスタムAPIの例",
"LanguageCode": 1041,
"IsManaged": null,
"MetadataId": null,
"HasChanged": null
}
],
"UserLocalizedLabel": {
"Label": "Custom API Example",
"LanguageCode": 1033,
"IsManaged": null,
"MetadataId": null,
"HasChanged": null
}
}
}
posted on 2021-02-05 12:06 lingdanglfw 阅读(689) 评论(0) 编辑 收藏 举报





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· 探究高空视频全景AR技术的实现原理
· 理解Rust引用及其生命周期标识(上)
· DeepSeek 开源周回顾「GitHub 热点速览」
· 物流快递公司核心技术能力-地址解析分单基础技术分享
· .NET 10首个预览版发布:重大改进与新特性概览!
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 单线程的Redis速度为什么快?