Run command in YMAL build pipeline or Release Pipeline
Azure DevOps CLI in Azure Pipeline YAML
Azure DevOps Services | Azure DevOps Server 2020
If you prefer to use YAML to provide your release pipeline configuration, you can use the following example to understand how YAML can be used to install Azure CLI and add the Azure DevOps extension.
In the example, you will learn how to add the Azure DevOps extension to Azure CLI and run the build and PR list commands on Linux, macOS and Windows hosted agents.
Create the azure-pipelines-steps.yml file
Include the content below.
For macOS: azure-pipelines-steps-mac.yml
steps:
- script: az extension add -n azure-devops
displayName: 'Install Azure DevOps Extension'
- script: echo ${AZURE_DEVOPS_CLI_PAT} | az devops login
env:
AZURE_DEVOPS_CLI_PAT: $(System.AccessToken)
displayName: 'Login Azure DevOps Extension'
- script: az devops configure --defaults organization=$(System.TeamFoundationCollectionUri) project=$(System.TeamProject) --use-git-aliases true
displayName: 'Set default Azure DevOps organization and project'
- script: |
az pipelines build list
git pr list
displayName: 'Show build list and PRs'
For Linux: azure-pipelines-steps-linux.yml
Replace https://dev.azure.com/{OrganizationName} with the URL for your Azure DevOps organization.
steps:
# Updating the python version available on the linux agent
- task: UsePythonVersion@0
inputs:
versionSpec: '3.x'
architecture: 'x64'
# Updating pip to latest
- script: python -m pip install --upgrade pip
displayName: 'Upgrade pip'
# Updating to latest Azure CLI version.
- script: pip install --pre azure-cli --extra-index-url https://azurecliprod.blob.core.windows.net/edge
displayName: 'upgrade azure cli'
- script: az --version
displayName: 'Show Azure CLI version'
- script: az extension add -n azure-devops
displayName: 'Install Azure DevOps Extension'
- script: echo ${AZURE_DEVOPS_CLI_PAT} | az devops login
env:
AZURE_DEVOPS_CLI_PAT: $(System.AccessToken)
displayName: 'Login Azure DevOps Extension'
- script: az devops configure --defaults organization=https://dev.azure.com/{OrganizationName} project="Movie Search Web App" --use-git-aliases true
displayName: 'Set default Azure DevOps organization and project'
- script: |
az pipelines build list
git pr list
displayName: 'Show build list and PRs'
For Windows: azure-pipelines-steps-win.yml
Replace https://dev.azure.com/{OrganizationName} with the URL for your Azure DevOps organization.
steps:
# Updating the python version available on the linux agent
- task: UsePythonVersion@0
inputs:
versionSpec: '3.x'
architecture: 'x64'
# Updating pip to latest which is required by the Azure DevOps extension
- script: python -m pip install --upgrade pip
displayName: 'Upgrade pip'
# Upgrading Azure CLI from 2.0.46 to latest; min version required for Azure DevOps is 2.0.49
- script: pip install --pre azure-cli --extra-index-url https://azurecliprod.blob.core.windows.net/edge
displayName: 'upgrade azure cli'
- script: az --version
displayName: 'Show Azure CLI version'
- script: az extension add -n azure-devops
displayName: 'Install Azure DevOps Extension'
- script: echo $(System.AccessToken) | az devops login
env:
AZURE_DEVOPS_CLI_PAT: $(System.AccessToken)
displayName: 'Login Azure DevOps Extension'
- script: az devops configure --defaults organization=https://dev.azure.com/{OrganizationName} project="Movie Search Web App" --use-git-aliases true
displayName: 'Set default Azure DevOps organization and project'
- script: |
az pipelines build list
git pr list
displayName: 'Show build list and PRs'
Create the azure-pipelines.yml
Include the content below.
jobs:
# Running Azure DevOps extension commands on a hosted Mac agent
- job:
displayName: 'macOS'
pool:
vmImage: 'macOS-latest'
steps:
- template: azure-pipelines-steps-mac.yml
# Running Azure DevOps extension commands on a hosted Linux agent
- job:
displayName: 'Linux'
pool:
vmImage: 'ubuntu-16.04'
steps:
- template: azure-pipelines-steps-linux.yml
# Running Azure DevOps extension commands on a hosted Windows agent
- job:
displayName: 'Windows'
pool:
vmImage: 'vs2017-win2016'
steps:
- template: azure-pipelines-steps-win.yml
Azure DevOps CLI in a release pipeline
Azure DevOps Services | Azure DevOps Server 2020
To use the Azure DevOps CLI in a hosted agent using a Release Pipeline, execute the following steps:
-
Create a release pipeline.

-
Choose Empty job.
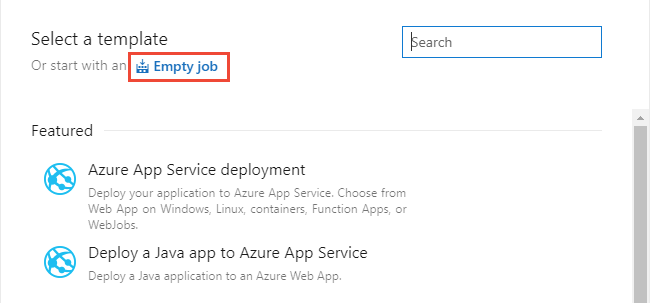
-
Choose Stage 1 to configure the stage.

-
Choose the Tasks page, and configure the job to use Hosted macOS in Agent Pools.
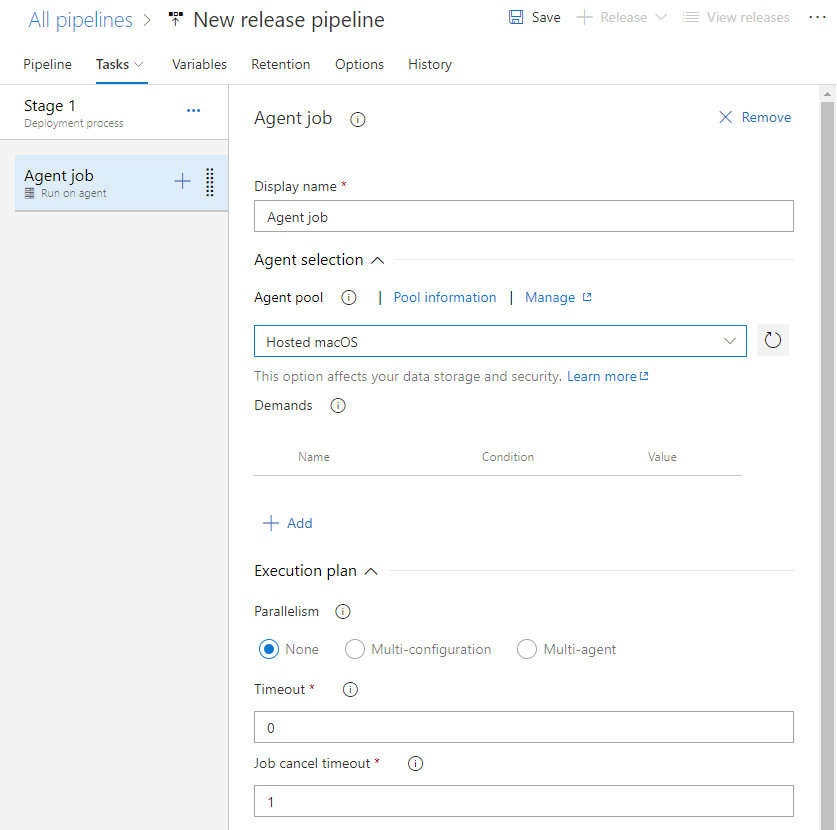
-
Choose the
 plus icon to add another task and configure it as a PowerShell task. Enter Power into the search box to filter the list.
plus icon to add another task and configure it as a PowerShell task. Enter Power into the search box to filter the list.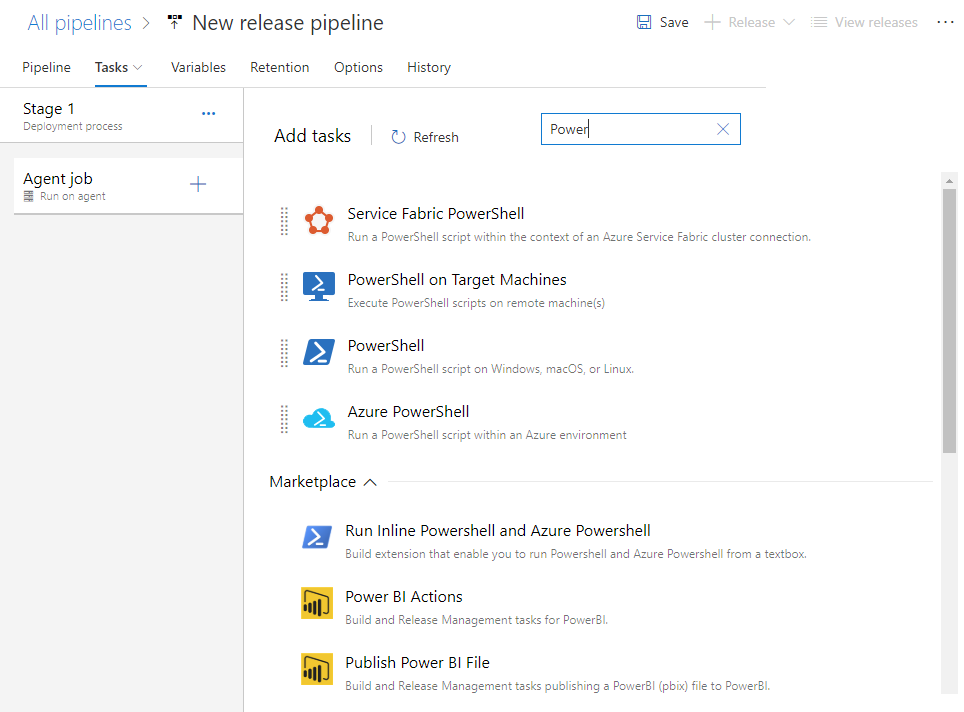
-
Add the script, either via file or inline. For the example, the script has been included inline.
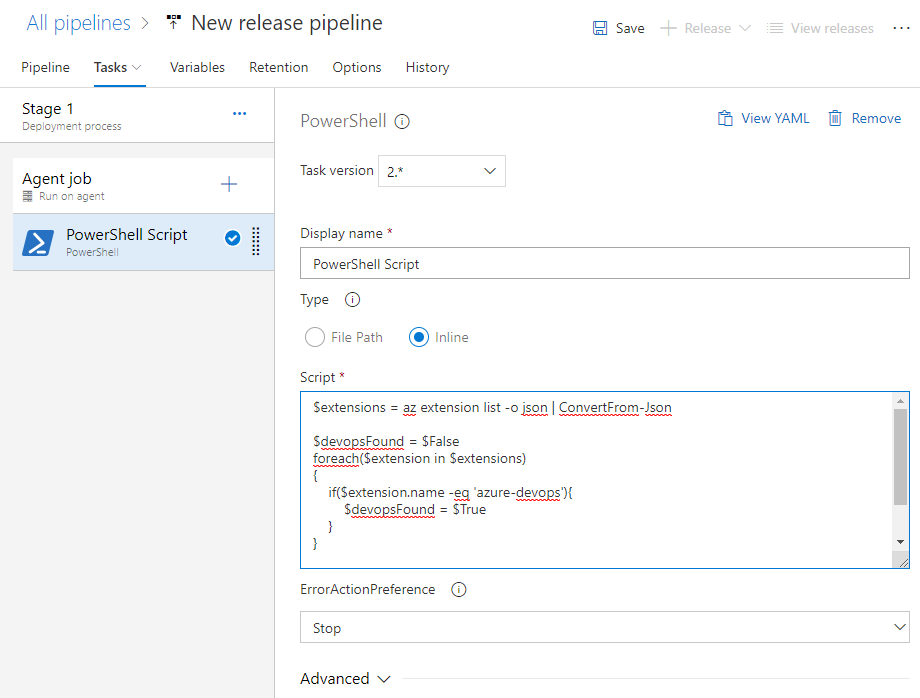
For reference, here is the inline script:
$extensions = az extension list -o json | ConvertFrom-Json
$devopsFound = $False
foreach($extension in $extensions)
{
if($extension.name -eq 'azure-devops'){
$devopsFound = $True
}
}
if ($devopsFound -eq $False){
az extension add -n azure-devops
}
posted on 2021-01-25 13:15 lingdanglfw 阅读(259) 评论(0) 编辑 收藏 举报





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· 探究高空视频全景AR技术的实现原理
· 理解Rust引用及其生命周期标识(上)
· DeepSeek 开源周回顾「GitHub 热点速览」
· 物流快递公司核心技术能力-地址解析分单基础技术分享
· .NET 10首个预览版发布:重大改进与新特性概览!
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 单线程的Redis速度为什么快?