第二章 快速前进-基础知识
第1讲:算法、数字与表达式
1. 算法
算法就是告诉计算机按照程序员的设计实现既定的事情(类似于食谱的材料+烹饪的方法)。
2.数字、表达式
# 加法 print("2 + 2:",2 + 2 ) # 除法 print(3/2) # 整除 print((3//2)) print(10//3) print(10//3) # 求余 print(1 % 2) # 乘法 print(2 * 3) # 幂 print(2 ** 4) 结果: 2 + 2 = 4 1.5 1 3.3333333333333335 3 1 6 16
3.数据类型
print("整型:",10) print("大数:",1111111111111111111123444555566111) print("浮点型:",0.1123456789008) print("科学计数法:",4e2) print("hello's world!") print("布尔值:",True) print("布尔值比较:",3 > 2) print("布尔值比较:",3 > 5) a = 21334759337882919384 print(type(a)) #type函数,查看变量的类型 结果: 整型: 10 大数: 1111111111111111111123444555566111 浮点型: 0.1123456789008 科学计算法: 400.0 hello's world! 布尔值 True 布尔值比较: True 布尔值比较: False <class 'int'>
4.变量
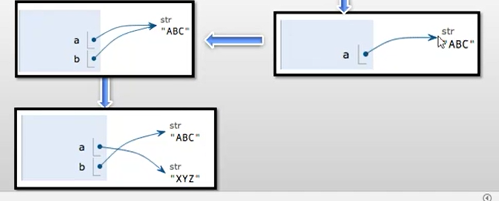
a = "ABC" print(a) b = a print(b) a = "XYZ" print(a) #XYZ print(b) 结果: ABC ABC XYZ ABC
5.变量命名的注意事项
- 变量在程序中就是用一个变量名表示(其指向内存中的某块空间),程序员一般选择有意义的名称作为变量名(以此表示该变量的用途);
- 变量名必须是大小写英文、数字或_的组合,且不能用数字开头(变量名是以小写字母开头的)
- 字母可以是大写或小写,但是大写的变量名与小写的变量名是不同的(Python是区分大小写的),比如Name和name是两个不同的变量名
6.常量:大写字母表示
7.保留字
第2讲 语句与输入、函数
1.语句与表达式
表达式:2+2
语句:print(2+2)
2.input函数的讲解
#input函数,在Python3中,接受的类型都是str类型。 first_num = input("please input the first num:") second_num = input("please input the second num:") print(type(first_num))#type 可以判断变量的类型 print(type(second_num)) print(first_num * second_num)#first_num、second_num str无法计算,报错 结果:报错 please input the first num:2 please input the second num:3 Traceback (most recent call last): <class 'str'> File "C:/Users/lenovo/PycharmProjects/Demo/demo.py", line 6, in <module> <class 'str'> print(first_num * second_num) TypeError: can't multiply sequence by non-int of type 'str' #两种改进方式 #1 first_num = input("please input the first num:") second_num = input("please input the second num:") print(type(first_num)) print(type(second_num)) print(int(first_num)*int(second_num)) 结果: please input the first num:2 please input the second num:5 <class 'str'> <class 'str'> 10 #2 first_num = int(input("please input the first num:")) second_num = int(input("please input the second num:")) print(type(first_num)) print(type(second_num)) print(first_num * second_num) 结果: please input the first num:4 please input the second num:6 <class 'int'> <class 'int'> 24
3.Python的内置函数
# pow()求幂
print(pow(2,2))
print(pow(2,3))
print(pow(2,4))
print(100+pow(2,3))
结果:
4
8
16
108
#abs()求绝对值
print(abs(99))
print(abs(-99))
结果:
99
99
#round()四舍五入取整,而且是最靠近的整数(这点上类似四舍五入)。但是当出现.5的时候,两边的距离都一样,round()取靠近的偶数。
print(round(32.4))
print(round(32.5))
print(round(33.5))
print(round(32.5))
结果:
32
32
34
32
第3讲 模块、程序的运行与字符串
1.导入模块的方式
#形式1 import 模块名 import math print(math.floor(32.6)#模块.函数 print(round(32.6)) #形式2 from 模块名 import 函数名 #注意:确保导入的函数,在接下来的代码中没有重名的 from math import floor print(floor(32.9)) print(round(32.9))
2.注释:
单行注释:#
多行注释:多个#或3个成对的(单引号或双引号),中间的内容视为注释
3.字符串
print(2 + 3) print("2" + "3") print("hello") print('hello') print("let's go") print('hi,"Bell"') print("""let's go.Hi "Bell" """) print('''let's go.Hi "Bell"''') #转义字符 print("hi,\"Bela\"") 结果: 5 23 hello hello let's go hi,"Bell" let's go.Hi "Bell" let's go.Hi "Bell" hi,"Bela"
4.原始字符串
pstr1 = "c:\nowhere" pstr2 = 'c:\nowhere' pstr3 = "c:\\nowhere" pstr4 = "c:\\nowhere\\npp\\now" pstr5 = r"c:\nowhere\npp\now" pstr6 = r"c:\nowhere\npp\now""\\" print(pstr1) print(pstr2) print(pstr3) print(pstr4) print(pstr5) print(pstr6) 结果: c: owhere c: owhere c:\nowhere c:\nowhere\npp\now c:\nowhere\npp\now c:\nowhere\npp\now\
5.跨多行的字符串
lstr =""" 红豆生南国,春来发几枝。 愿君多采撷,此物最相思。 """ lstr1 =''' 红豆生南国,春来发几枝。 愿君多采撷,此物最相思。 ''' print(lstr) print(lstr1) 结果: 红豆生南国,春来发几枝。 愿君多采撷,此物最相思。 红豆生南国,春来发几枝。 愿君多采撷,此物最相思。
第4讲 数据类型
1.常见的数据类型
a = 10 #整型 b = "hello" #字符串 c = 0.00000006 # 科学计数法 print(a) print(b) print(c) print(True) print(False) print(4>2) print(4<2) 结果: 10 hello 6e-08 True False True False
2.类型转换、type、instance(查看是否是某个类型,给出结果True或False)
int_num = 10 str_num = "11" float_num = 12.3 str_num2 = "hello" print(type(int_num)) # type可以查看变量的类型 print(type(str_num)) print(type(float_num)) print("=========================") print(int(str_num)) print(int(float_num)) print("=========================") print(float(int_num)) print(float(str_num)) print("=========================") print(isinstance(int_num,int)) # isinstance 判断是否为某类型 print(isinstance(int_num,str)) print("=========================") print(int(str_num2)) 结果: <class 'int'> <class 'str'> <class 'float'> ========================= 11 12 ========================= 10.0 11.0 ========================= True False
=========================
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "C:/Users/lenovo/PycharmProjects/Demo/demo.py", line 18, in <module>
print(int(str_num2))
ValueError: invalid literal for int() with base 10: 'hello'
第5讲 注释与布尔值的扩充
# ==================== # 作用:计算长方形的面积 # 作者: ling # 时间: 2019-4-2 # ==================== """ ==================== 作用:计算长方形的面积 作者: ling 时间: 2019-4-2 ==================== """ ''' ==================== 作用:计算长方形的面积 作者: ling 时间: 2019-4-2 ==================== ''' length = 10 width = 20 # area表示面积 area = length * width print(area) # 输出面积
2.布尔值
print(True and True) print(True and False) print("==========================") print(True or True) print(True or False) print("==========================") print(not True) print(not False) print("==========================") print(int(True)) print(int(False)) 结果: True False ========================== True True ========================== False True ========================== 1 0



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号