MPI学习三
1.点对点通信
MPI 的通信模式:是缓冲管理以及发送方和接收方之间的同步方式
MPI支持的4种通信模式:
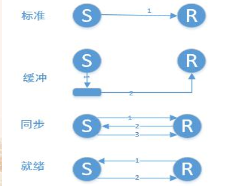
(1)标准通信模式:由MPI决定是否缓冲消息。
实现进程0和进程1中的数据进行相互的通信
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <mpi.h> 3 #include <math.h> 4 #define buf_size 10 5 6 int main(int argc,char **argv) 7 { 8 int myid,numprocs,other,sb[buf_size],rb[buf_size]; 9 MPI_Status status; 10 11 12 MPI_Init(&argc, &argv); 13 14 MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD,&myid); 15 16 MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD,&numprocs); 17 18 for(int i = 0; i < buf_size; i++) 19 { 20 sb[i] = myid + i; 21 } 22 23 printf("------- %d --------\n",myid); 24 25 if(myid == 0) 26 { 27 other = 1; 28 } 29 30 if(myid == 1) 31 { 32 other = 0; 33 } 34 35 36 if(myid == 0) 37 { 38 printf("process: %d tring send...\n",myid); 39 MPI_Send(sb,buf_size,MPI_INT,other,1,MPI_COMM_WORLD); 40 printf("process: %d tring receiving...\n",myid); 41 MPI_Recv(rb,buf_size,MPI_INT,other,1,MPI_COMM_WORLD,&status); 42 for(int j=0;j<buf_size;j++) 43 { 44 printf("0 rb: %d \n",rb[j]); 45 } 46 } 47 if(myid == 1) 48 { 49 printf("process: %d tring receiving...\n",myid); 50 MPI_Recv(rb,buf_size,MPI_INT,other,1,MPI_COMM_WORLD,&status); 51 printf("process: %d tring send...\n",myid); 52 MPI_Send(sb,buf_size,MPI_INT,other,1,MPI_COMM_WORLD); 53 for(int j=0;j<buf_size;j++) 54 { 55 printf(" rb: %d \n",rb[j]); 56 } 57 } 58 printf("hello world ! process %d of %d\n",myid,numprocs); 59 60 61 MPI_Finalize(); 62 return 0; 63 }
运行结果如下:

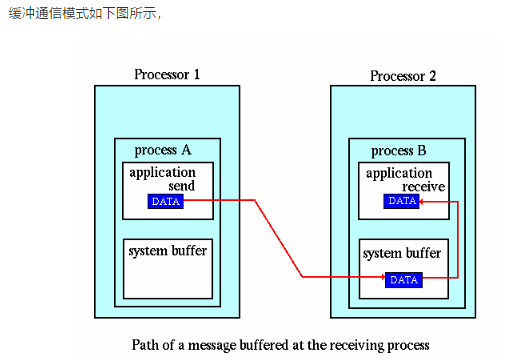
(2)缓冲通信模式
缓冲通信模式主要用于解开阻塞通信的发送和接受之间的耦合。有了缓冲机制,即使在接收端没有启动相应的接收情况下,在完成消息数据到缓冲区的转移后发送端的阻塞发送函数也可以返回。
但缓冲方式带来了额外的内存到内存的复制开销,会导致一定的性能损失和资源占用。的确,每个进程都要在堆里分配内存然后注册成为缓冲区。
缓冲区的使用并不能改变发送和接受之间的语义关系,及不能改变程序的正确性。
与标准模式由于以来MPI环境提供的缓冲机制而受到远端进程状态左右不同,缓冲发送完成与否不会受远端匹配进程状态的影响。但当消息大小超过缓冲区容量时,会报错。
1 #include "mpi.h" 2 #include <stdio.h> 3 #include <stdlib.h> 4 #include <string.h> 5 #define MSG1LEN 7 6 #define MSG2LEN 2 7 #define MSG3LEN 17 8 #define RMSG1LEN 64 9 #define RMSG2LEN 64 10 #define RMSG3LEN 64 11 int main(int argc, char ** argv) 12 { 13 // Communicator. 14 MPI_Comm comm = MPI_COMM_WORLD; 15 // Process number. 16 int src = 0, dest = 1; 17 // Buffer sizes for 3 msg. 18 int s1, s2, s3; 19 // Buffers. 20 char msg1[MSG1LEN], msg3[MSG2LEN], rmsg1[RMSG1LEN], rmsg3[MSG3LEN]; 21 // Buffers. 22 // char msg1[MSG1LEN], msg3[MSG2LEN], rmsg1[RMSG1LEN], rmsg3[MSG3LEN]; 23 double msg2[MSG2LEN], rmsg2[RMSG2LEN]; 24 // Buffer address. 25 char * buf, * bbuf; 26 int errs = 0, rank, bufsize, bsize; 27 MPI_Init(&argc, &argv); 28 MPI_Comm_rank(comm, &rank); 29 MPI_Pack_size(MSG1LEN, MPI_CHAR, comm, &s1); 30 MPI_Pack_size(MSG2LEN, MPI_DOUBLE, comm, &s2); 31 MPI_Pack_size(MSG3LEN, MPI_CHAR, comm, &s3); 32 bufsize = 3*MPI_BSEND_OVERHEAD + s1 + s2 + s3; 33 buf = (char *)malloc(bufsize); 34 MPI_Buffer_attach(buf, bufsize); 35 strncpy(msg1, "012345", MSG1LEN); 36 strncpy(msg3, "0123401234012341", MSG3LEN); 37 msg2[0] = 1.23; 38 msg2[1] = 3.21; 39 if (rank == src) 40 { 41 fprintf(stderr, "Before sending msg1 from proc %d, t = %f\n", rank, MPI_Wtime()); 42 MPI_Bsend(msg1, MSG1LEN, MPI_CHAR, dest, 1, comm); 43 fprintf(stderr, "After sending msg1 from proc %d, t = %f\n", rank, MPI_Wtime()); 44 fprintf(stderr, "Before sending msg2 from proc %d, t = %f\n", rank, MPI_Wtime()); 45 MPI_Bsend(msg2, MSG2LEN, MPI_DOUBLE, dest, 1, comm); 46 fprintf(stderr, "After sending msg2 from proc %d, t = %f\n", rank, MPI_Wtime()); 47 fprintf(stderr, "Before sending msg3 from proc %d, t = %f\n", rank, MPI_Wtime()); 48 MPI_Bsend(msg3, MSG3LEN, MPI_CHAR, dest, 1, comm); 49 fprintf(stderr, "After sending msg3 from proc %d, t = %f\n", rank, MPI_Wtime()); 50 MPI_Buffer_detach(&buf, &bufsize); 51 } 52 else if (rank == dest) 53 { 54 fprintf(stderr, "Before receiving msg1 on proc %d, t = %f\n", rank, MPI_Wtime()); 55 MPI_Recv(rmsg1, MSG1LEN, MPI_CHAR, src, 1, comm, MPI_STATUS_IGNORE); 56 fprintf(stderr, "After receiving msg1 on proc %d, t = %f\n", rank, MPI_Wtime()); 57 fprintf(stderr, "Before receiving msg2 on proc %d, t = %f\n", rank, MPI_Wtime()); 58 MPI_Recv(rmsg2, MSG2LEN, MPI_DOUBLE, src, 1, comm, MPI_STATUS_IGNORE); 59 fprintf(stderr, "After receiving msg2 on proc %d, t = %f\n", rank, MPI_Wtime()); 60 fprintf(stderr, "Before receiving msg3 on proc %d, t = %f\n", rank, MPI_Wtime()); 61 MPI_Recv(rmsg3, MSG3LEN, MPI_CHAR, src, 1, comm, MPI_STATUS_IGNORE); 62 fprintf(stderr, "After receiving msg3 on proc %d, t = %f\n", rank, MPI_Wtime()); 63 MPI_Buffer_detach(&buf, &bufsize); 64 if (strcmp(msg1, rmsg1) != 0) 65 { 66 errs++; 67 fprintf(stderr, "message 1(%s) should be %s\n", rmsg1, msg1); 68 fflush(stderr); 69 } 70 if (rmsg2[0] != msg2[0] || rmsg2[1] != msg2[1]) 71 { 72 errs++; 73 fprintf(stderr, 74 "message 2 incorrect, values are (%f, %f) but should be (%f, %f)\n", 75 rmsg2[0], rmsg2[1], msg2[0], msg2[1]); 76 fflush(stderr); 77 } 78 if (strcmp(msg3, rmsg3) != 0) { 79 errs++; 80 fprintf(stderr, "message 2(%s) should be %s\n", rmsg3, msg3); 81 fflush(stderr); 82 } 83 } 84 free(buf); 85 MPI_Finalize(); 86 87 return 0; 88 }
(3)就绪通信模式

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <mpi.h> 3 4 int main(int argc,char **argv) 5 { 6 MPI_Status status; 7 MPI_Comm comm = MPI_COMM_WORLD; 8 MPI_Init(&argc,&argv); 9 10 int size,rank; 11 MPI_Comm_size(comm,&size); 12 MPI_Comm_rank(comm,&rank); 13 int tag = 1; 14 int buffer[10]; 15 printf("=== : %d\n",rank); 16 if(rank == 0) 17 { 18 for(int i = 0; i < 10;i++) 19 buffer[i] = -1; 20 21 printf("rank ----%d\n",rank); 22 for(int k = 0; k<10; k++) 23 { 24 printf(" %d ",buffer[k]); 25 } 26 printf("\n"); 27 MPI_Recv(buffer,10,MPI_INT,1,tag,comm,&status); 28 29 for(int j = 0;j < 10; j++) 30 { 31 if(buffer[j]!=j) 32 printf("error\n"); 33 } 34 printf("rank %d\n",rank); 35 for(int k = 0; k<10; k++) 36 { 37 printf(" %d ",buffer[k]); 38 } 39 printf("\n"); 40 } 41 42 if(rank ==1) 43 { 44 for(int i=0;i<10;i++) 45 { 46 buffer[i] = i; 47 } 48 MPI_Rsend(buffer,10,MPI_INT,0,tag,comm); 49 } 50 51 MPI_Finalize(); 52 return 0; 53 }
运行结果:
(4)同步通信模式


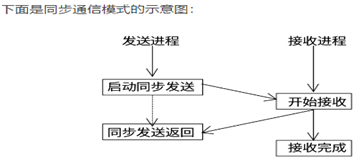
在同步通信模式中,发送进程必须要等到相应的接受进程开始后才可以正确返回。也就是说如果发送的数据一直没有被接受,发送进程就会一直处于等待状态。当同步发送操作返回之后,说明发送缓冲区中的数据已经全被系统缓冲区缓存,并且已经开始发送,这样发送缓冲区就可以被释放或者重新使用。
实例:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <mpi.h> 3 4 int main(int argc,char **argv) 5 { 6 MPI_Status status; 7 MPI_Comm comm = MPI_COMM_WORLD; 8 MPI_Init(&argc,&argv); 9 10 int size,rank; 11 int buffer[10]; 12 int tag = 1; 13 MPI_Comm_size(comm,&size); 14 MPI_Comm_rank(comm,&rank); 15 16 if(rank == 0) 17 { 18 for(int i = 0;i<10;i++) 19 { 20 buffer[i] = i; 21 } 22 printf("proc: %d sending....\n",rank); 23 MPI_Ssend(buffer,10,MPI_INT,1,tag,comm); 24 } 25 26 if(rank == 1) 27 { 28 29 for(int i = 0; i <10;i++) 30 { 31 buffer[i] = -1; 32 } 33 printf("rank--before:%d\n",rank); 34 for(int k=0;k<10;k++) 35 { 36 printf(" %d ",buffer[k]); 37 } 38 printf("\n"); 39 printf("procs: %d receiving....\n",rank); 40 MPI_Recv(buffer,10,MPI_INT,0,tag,comm,&status); 41 for(int j = 0;j<10;j++) 42 { 43 if(buffer[j] != j) 44 { 45 printf("error\n"); 46 } 47 } 48 49 printf("rank--after:%d\n",rank); 50 for(int k=0;k<10;k++) 51 { 52 printf(" %d ",buffer[k]); 53 } 54 printf("\n"); 55 } 56 57 MPI_Finalize(); 58 return 0; 59 }
运行结果:
总结:









