容器(集合)
---容器的概念
Java API 所提供的一系列类的实例,用于在程序中存放对象。
容器的API
J2SDK所提供的容器API位于java.util 包内。
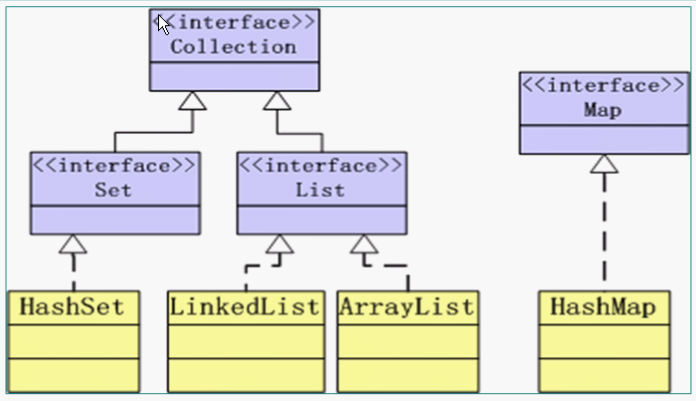
Collection接口--定义了存取一组对象的方法,其子接口Set和List分别定义了存储方式。
Set:类似数学集合,没有顺序,不能重复。
List:有顺序,可以重复。判断重复用equals()判断
在编程语言中List 是标准类库中的一个类,可以简单视之为双向链表,以线性列的方式管理物件集合。
Map接口定义了存储“键(key)--值(value)映射对”的方法
一对一对存储。

package com.collection.test; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collection; import java.util.HashSet; public class CollectionTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Collection c = new HashSet(); //可以放入不同的对象 c.add("Hello world"); c.add(new Integer(100)); c.add(new name("li","mingxian")); c.remove("Hello world"); c.remove(new Integer(100));//重写了object的equals(),所以能去除 System.out.println(c.remove(new name("li","mingxian")));//name没有重写equals(),继承了object的比较方法 System.out.println(c); } } class name{ String firstName, lastName; public name(String firstName, String lastName) { super(); this.firstName = firstName; this.lastName = lastName; } public String getFirstName() { return firstName; } public String getLastName() { return lastName; } @Override public String toString() { return "name [firstName=" + firstName + ", lastName=" + lastName + "]"; } /** * 重写equals方法 */ public boolean equals(Object obj){ if(obj instanceof name){ name name = (name)obj;//字符串已经对这个方法重写 return (firstName.equals(name.firstName))&&(lastName.equals(name.lastName)); } return super.equals(obj); } /** * 重写 hashCode() * hashCode返回一个索引,相同的值索引肯定同 */ public int hashCode(){ return firstName.hashCode(); } }
Collection接口

import java.util.*; public class TestName { public static void main(String[] args){ //子类对象指向父类引用,C不能调用ArrayList的特有方法, //可以大胆的切换其他子类-----大大提高了程序的灵活性 Collection c = new ArrayList(); //可以放入不同类型的对象 c.add("hello"); System.out.println(c.size()); System.out.println(c); } }
Iterator接口

public class CollectionTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Collection c = new HashSet(); //可以放入不同的对象 c.add(new name("f1","l1")); c.add(new name("f2","l2")); c.add(new name("li","mingxian")); Iterator i = c.iterator(); while(i.hasNext()){ //next()返回值为Object类型需要转换为相应类型 name n = (name)i.next(); System.out.println(n.getFirstName()); } } }
增强的for循环

Set接口
没有顺序,不可重合

public static void main(String[] args) { Set s = new HashSet(); //可以放入不同的对象 s.add("hello"); s.add(new name("f1","l1")); s.add(new name("f2","l2")); s.add(new name("li","mingxian")); s.add("hello");//相同的元素不会被加入 System.out.println(s); }
public static void main(String[] args) { Set s1 = new HashSet(); Set s2 = new HashSet(); //可以放入不同的对象 s1.add("a"); s1.add("b"); s1.add("c"); s2.add("d"); s2.add("a"); s2.add("b"); //Set和list容器类都具有Constructor(Collection c) //构造方法用以初始化容器类 Set sn = new HashSet(s1); sn.retainAll(s2);//判断相交 Set su = new HashSet(s1); su.addAll(s2); System.out.println(sn); System.out.println(su); }
List接口
ArrayList底层是数组实现,LinkedList底层是链表实现
arrayList怎么实现
底层是数组实现
构造体有三种形式:
1)ArrayList带容量大小的
2)ArrayList无参构造函数。默认容量是10
3)创建一个包含collection的ArrayList
元素存储:
ArrayList提供了
set(int index, E element)、add(E e)、add(int index, E element)、addAll(Collection<? extends E> c)、addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c)
这些添加元素的方法
// 将指定的元素添加到此列表的尾部。 public boolean add(E e) { ensureCapacity(size + 1); elementData[size++] = e; return true; }
// 将指定的元素插入此列表中的指定位置。 // 如果当前位置有元素,则向右移动当前位于该位置的元素以及所有后续元素(将其索引加1)。 public void add(int index, E element) { if (index > size || index < 0) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index+", Size: "+size); // 如果数组长度不足,将进行扩容。 ensureCapacity(size+1); // Increments modCount!! // 将 elementData中从Index位置开始、长度为size-index的元素, // 拷贝到从下标为index+1位置开始的新的elementData数组中。 // 即将当前位于该位置的元素以及所有后续元素右移一个位置。 System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1, size - index); //System.arraycopy(elementData,index,elementData,index+1,size-index); elementData[index] = element; size++; }

List<String> l1 = new LinkedList(); for (int i = 0; i <= 5; i++) { l1.add("a" + i); } System.out.println(l1); l1.add(3, "a300");//增加,往后退 System.out.println(l1); l1.set(6, "a400");//设置一个 System.out.println(l1); System.out.println((String)l1.get(2)+"");//获取索引为2的值 System.out.println(l1.indexOf("a3"));//获取索引 l1.remove(1);//删除索引为1的值 System.out.println(l1);

Collections类

/** * List常用算法 */ List l1 = new LinkedList(); List l2 = new LinkedList(); for(int i=0;i<=9;i++){ l1.add("a"+i); } System.out.println(l1); Collections.shuffle(l1);//随机排列 System.out.println(l1); Collections.reverse(l1);//逆序排列 System.out.println(l1); Collections.sort(l1);//排序 System.out.println(l1); System.out.println(Collections.binarySearch(l1, "a5"));//折半查找

此处的是Collections类,不是Collection接口。Collections类提供了静态方法实现了基于List容器的一些常用算法。
链表概念


Comparable 所有可以“排序”的类都实现了java.lang.Comparable接口,Comparable接口中只有一个方法
public int compareTo(object obj);
实现了Comparable接口的类通过实现comparaTo方法从而确定该类对象的排序方法
Comparable接口

/** * 一个类要调用Collections类下的方法进行排序时先得实现Comparable接口 * LinkedList排序速度比ArrayList的排序速度效率高 */ List l1 = new LinkedList(); l1.add(new name("Li","M")); l1.add(new name("Lu","G")); l1.add(new name("Yang","W")); l1.add(new name("Huang","Y")); System.out.println(l1); Collections.sort(l1); System.out.println(l1);
class name implements Comparable { ...... public int compareTo(Object o){ name n = (name) o; int lastCmp = lastName.compareTo(n.lastName);//调用字符串的重写方法 return (lastCmp!=0 ? lastCmp : firstName.compareTo(n.firstName)); }
如何选择数据结构
衡量标准:读的效率和改的效率
Array读快改慢
Linked改快读慢
Hash两者之间(用的很少)

Map接口
实现Map接口的类用来存储键---值 对
Map接口的实现类有HashMap和TreeMap等
Map类中存储的键--值对通过键来标识,所以键值不能重复。

/** * Map练习 */ Map m1 = new HashMap(); Map m2 = new HashMap(); m1.put("one", new Integer(1)); m1.put("two", new Integer(2)); m1.put("three", new Integer(3)); m2.put("A", new Integer(1)); m2.put("B", new Integer(2)); System.out.println(m1.size()); System.out.println(m1.containsKey("one")); System.out.println(m2.containsValue(new Integer(1))); if (m1.containsKey("two")) { int i = ((Integer)m1.get("two")).intValue(); System.out.println(i); } Map m3 = new HashMap(m1); m3.putAll(m2); System.out.println(m3);
自动打包解包技术-------把基础类型转换为对象

Map m1 = new HashMap(); Map m2 = new HashMap(); //m1.put("one", new Integer(1)); m1.put("one", 1); //m1.put("two", new Integer(2)); m1.put("two", 2); //m1.put("three", new Integer(3)); m1.put("three",3); //m2.put("A", new Integer(1)); m2.put("A", 1); //m2.put("B", new Integer(2)); m2.put("B", 2); System.out.println(m1.size()); System.out.println(m1.containsKey("one")); //System.out.println(m2.containsValue(new Integer(1))); System.out.println(m2.containsValue(1)); if (m1.containsKey("two")) { //int i = ((Integer)m1.get("two")).intValue(); int i = ((Integer)m1.get("two")); System.out.println(i); } Map m3 = new HashMap(m1); m3.putAll(m2); System.out.println(m3);
收摘自----http://www.cnblogs.com/blest-future/p/4628871.html
import java.util.HashMap; 2 import java.util.Iterator; 3 import java.util.Map; 4 5 public class TestMap { 6 public static void main(String[] args) { 7 Map<Integer, String> map = new HashMap<Integer, String>(); 8 map.put(1, "a"); 9 map.put(2, "b"); 10 map.put(3, "ab"); 11 map.put(4, "ab"); 12 map.put(4, "ab");// 和上面相同 , 会自己筛选 13 System.out.println(map.size()); 14 // 第一种: 15 /* 16 * Set<Integer> set = map.keySet(); //得到所有key的集合 17 * 18 * for (Integer in : set) { String str = map.get(in); 19 * System.out.println(in + " " + str); } 20 */ 21 System.out.println("第一种:通过Map.keySet遍历key和value:"); 22 for (Integer in : map.keySet()) { 23 //map.keySet()返回的是所有key的值 24 String str = map.get(in);//得到每个key多对用value的值 25 System.out.println(in + " " + str); 26 } 27 // 第二种: 28 System.out.println("第二种:通过Map.entrySet使用iterator遍历key和value:"); 29 Iterator<Map.Entry<Integer, String>> it = map.entrySet().iterator(); 30 while (it.hasNext()) { 31 Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry = it.next(); 32 System.out.println("key= " + entry.getKey() + " and value= " + entry.getValue()); 33 } 34 // 第三种:推荐,尤其是容量大时 35 System.out.println("第三种:通过Map.entrySet遍历key和value"); 36 for (Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry : map.entrySet()) { 37 //Map.entry<Integer,String> 映射项(键-值对) 有几个方法:用上面的名字entry 38 //entry.getKey() ;entry.getValue(); entry.setValue(); 39 //map.entrySet() 返回此映射中包含的映射关系的 Set视图。 40 System.out.println("key= " + entry.getKey() + " and value= " 41 + entry.getValue()); 42 } 43 // 第四种: 44 System.out.println("第四种:通过Map.values()遍历所有的value,但不能遍历key"); 45 for (String v : map.values()) { 46 System.out.println("value= " + v); 47 } 48 } 49 }
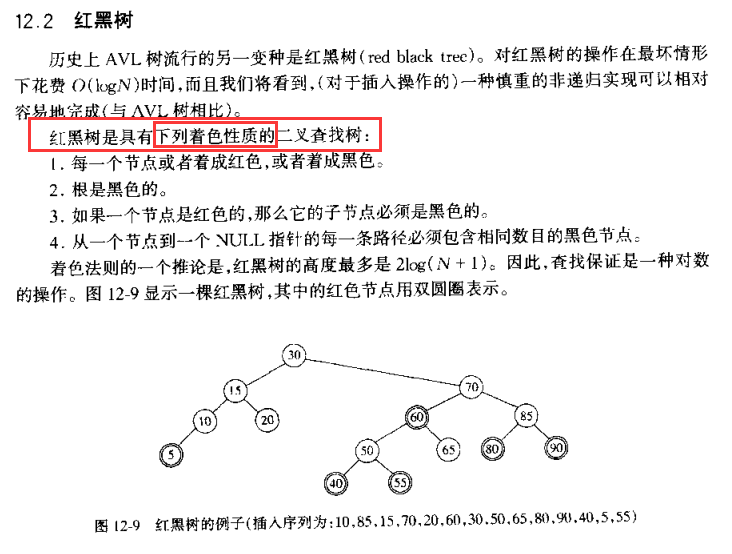
TreeMap底层是通过红黑树来实现的---
对于大量的输入数据,链表的线性访问时间太慢,不宜使用,所以引入了树这种数据结构。


自动打包/解包
泛型



