springboot 配置文件
– Spring Boot使用一个全局的配置文件 • application.properties • application.yml – 配置文件放在src/main/resources目录或者类路径/config下 – .yml是YAML(YAML Ain't Markup Language)语言的文件,以数据为中 心,比json、xml等更适合做配置文件 • http://www.yaml.org/ 参考语法规范 – 全局配置文件的可以对一些默认配置值进行修改
标记语言: 以前的配置文件;大多都使用的是 xxxx.xml文件;
YAML:以数据为中心,比json、xml等更适合做配置文件;
YAML:配置例子
配置文件值注入
yml配置文件
person: lastName: hello age: 18 boss: false birth: 2017/12/12 maps: {k1: v1,k2: 12} lists: ‐ lisi ‐ zhaoliu dog: name: 小狗 age: 12
javaBean:
/** * 将配置文件中配置的每一个属性的值,映射到这个组件中 * @ConfigurationProperties:告诉SpringBoot将本类中的所有属性和配置文件中相关的配置进行绑定; * prefix = "person":配置文件中哪个下面的所有属性进行一一映射 * * 只有这个组件是容器中的组件,才能容器提供的@ConfigurationProperties功能; * */ @Component @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person") public class Person { private String lastName; private Integer age; private Boolean boss; private Date birth; private Map<String,Object> maps; private List<Object> lists; private Dog dog;
我们可以导入配置文件处理器,以后编写配置就有提示了
<!‐‐导入配置文件处理器,配置文件进行绑定就会有提示‐‐>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring‐boot‐configuration‐processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
、@Value获取值和@ConfigurationProperties获取值比较

如果说,我们只是在某个业务逻辑中需要获取一下配置文件中的某项值,使用@Value;
如果说,我们专门编写了一个javaBean来和配置文件进行映射,我们就直接使用@ConfigurationProperties;
3、配置文件注入值数据校验
@Component @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person") @Validated public class Person { /** * <bean class="Person"> * <property name="lastName" value="字面量/${key}从环境变量、配置文件中获取值/# {SpEL}"></property> * <bean/> */ //lastName必须是邮箱格式 @Email //@Value("${person.last‐name}") private String lastName; //@Value("#{11*2}") private Integer age; //@Value("true") private Boolean boss; private Date birth; private Map<String,Object> maps; private List<Object> lists; private Dog dog;
@PropertySource&@ImportResource&@Bean
@PropertySource:加载指定的配置文件;
/** * 将配置文件中配置的每一个属性的值,映射到这个组件中 * @ConfigurationProperties:告诉SpringBoot将本类中的所有属性和配置文件中相关的配置进行绑定; * prefix = "person":配置文件中哪个下面的所有属性进行一一映射 * * 只有这个组件是容器中的组件,才能容器提供的@ConfigurationProperties功能; * @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")默认从全局配置文件中获取值; * */ @PropertySource(value = {"classpath:person.properties"}) @Component @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person") //@Validated public class Person { /** * <bean class="Person"> * <property name="lastName" value="字面量/${key}从环境变量、配置文件中获取值/# {SpEL}"></property> * <bean/> */ //lastName必须是邮箱格式 // @Email //@Value("${person.last‐name}") private String lastName; //@Value("#{11*2}") private Integer age; //@Value("true") private Boolean boss;
@ImportResource:导入Spring的配置文件,让配置文件里面的内容生效; Spring Boot里面没有Spring的配置文件,我们自己编写的配置文件,也不能自动识别;
想让Spring的配置文件生效,加载进来;@ImportResource标注在一个配置类上
@ImportResource(locations = {"classpath:beans.xml"})
导入Spring的配置文件让其生效
不来编写Spring的配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF‐8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema‐instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring‐beans.xsd"> <bean id="helloService" class="com.atguigu.springboot.service.HelloService"></bean> </beans>
SpringBoot推荐给容器中添加组件的方式;
推荐使用全注解的方式
1、配置类@Configuration------>Spring配置文件
2、使用@Bean给容器中添加组件
/** * @Configuration:指明当前类是一个配置类;就是来替代之前的Spring配置文件 * * 在配置文件中用<bean><bean/>标签添加组件 * */ @Configuration public class MyAppConfig { //将方法的返回值添加到容器中;容器中这个组件默认的id就是方法名 @Bean public HelloService helloService02(){ System.out.println("配置类@Bean给容器中添加组件了..."); return new HelloService(); } }
配置文件加载位置
springboot 启动会扫描以下位置的application.properties或者application.yml文件作为Spring boot的默认配置文 件 –file:./config/ –file:./ –classpath:/config/ –classpath:/ 优先级由高到底,高优先级的配置会覆盖低优先级的配置;
自动配置原理
配置文件到底能写什么?怎么写?自动配置原理;
配置文件能配置的属性参照
https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/1.5.19.RELEASE/reference/htmlsingle/#common-application-properties
自动配置原理:
1)、SpringBoot启动的时候加载主配置类,开启了自动配置功能 @EnableAutoConfiguration
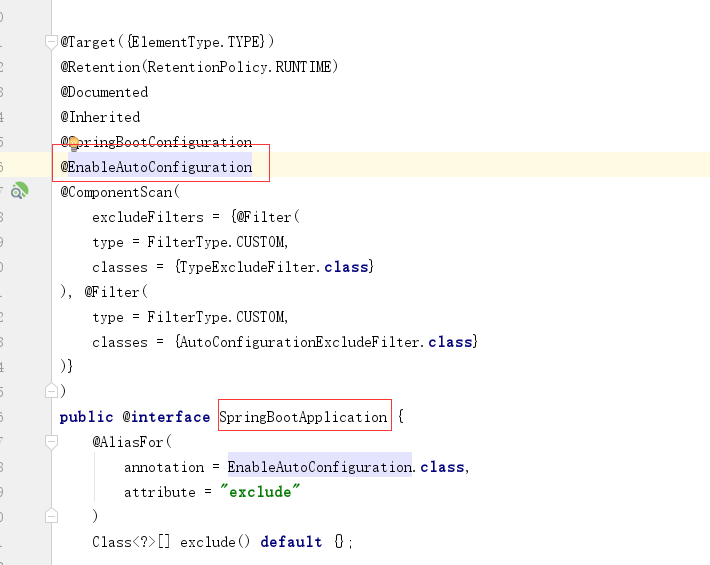
2)、@EnableAutoConfiguration 作用:
利用EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector给容器中导入一些组件?
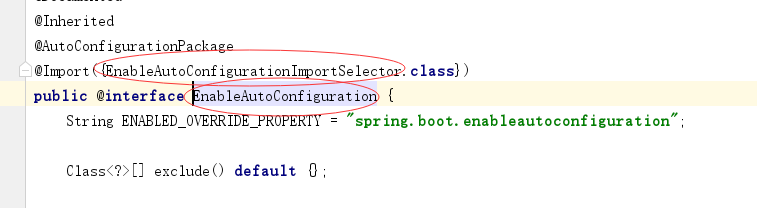
可以查看selectImports()方法的内容;
List configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes);获取候选的配置
SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames() 扫描所有jar包类路径下 META‐INF/spring.factories 把扫描到的这些文件的内容包装成properties对象 从properties中获取到EnableAutoConfiguration.class类(类名)对应的值,然后把他们添加在容器 中

将 类路径下 META-INF/spring.factories 里面配置的所有EnableAutoConfiguration的值加入到了容器中;
# Auto Configure org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.admin.SpringApplicationAdminJmxAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.aop.AopAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.amqp.RabbitAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.batch.BatchAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CacheAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cassandra.CassandraAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cloud.CloudAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.ConfigurationPropertiesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.MessageSourceAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.couchbase.CouchbaseAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.dao.PersistenceExceptionTranslationAutoConfiguration, \ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraDataAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraRepositoriesAutoConfiguration ,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseDataAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseRepositoriesAutoConfiguration ,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchDataAutoConfiguration 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 ,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchRepositoriesAutoConfi guration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.jpa.JpaRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.ldap.LdapDataAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.ldap.LdapRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoDataAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.neo4j.Neo4jDataAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.neo4j.Neo4jRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.solr.SolrRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.rest.RepositoryRestMvcAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.web.SpringDataWebAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.elasticsearch.jest.JestAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.freemarker.FreeMarkerAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.gson.GsonAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.h2.H2ConsoleAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hateoas.HypermediaAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hazelcast.HazelcastAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hazelcast.HazelcastJpaDependencyAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.info.ProjectInfoAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.integration.IntegrationAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jackson.JacksonAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.JdbcTemplateAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.JndiDataSourceAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.XADataSourceAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.JmsAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jmx.JmxAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.JndiConnectionFactoryAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.activemq.ActiveMQAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.artemis.ArtemisAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.flyway.FlywayAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.groovy.template.GroovyTemplateAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jersey.JerseyAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jooq.JooqAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.kafka.KafkaAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.ldap.embedded.EmbeddedLdapAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.ldap.LdapAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.liquibase.LiquibaseAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mail.MailSenderAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mail.MailSenderValidatorAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mobile.DeviceResolverAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mobile.DeviceDelegatingViewResolverAutoConfiguration, \ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mobile.SitePreferenceAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.embedded.EmbeddedMongoAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.MongoAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mustache.MustacheAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.orm.jpa.HibernateJpaAutoConfiguration,\ 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 每一个这样的 xxxAutoConfiguration类都是容器中的一个组件,都加入到容器中;用他们来做自动配置; 3)、每一个自动配置类进行自动配置功能; 4)、以HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration(Http编码自动配置)为例解释自动配置原理; org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.reactor.ReactorAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.SecurityAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.SecurityFilterAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.FallbackWebSecurityAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.OAuth2AutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.sendgrid.SendGridAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.session.SessionAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.social.SocialWebAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.social.FacebookAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.social.LinkedInAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.social.TwitterAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.solr.SolrAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.thymeleaf.ThymeleafAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.TransactionAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.jta.JtaAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.validation.ValidationAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.EmbeddedServletContainerAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.HttpMessageConvertersAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.MultipartAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.ServerPropertiesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.WebClientAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.WebMvcAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.WebSocketAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.WebSocketMessagingAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.webservices.WebServicesAutoConfiguration
每一个这样的 xxxAutoConfiguration类都是容器中的一个组件,都加入到容器中;用他们来做自动配置;
3)、每一个自动配置类进行自动配置功能;
4)、以HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration(Http编码自动配置)为例解释自动配置原理;
@Configuration //表示这是一个配置类,以前编写的配置文件一样,也可以给容器中添加组件 @EnableConfigurationProperties(HttpEncodingProperties.class) //启动指定类的 //ConfigurationProperties功能;将配置文件中对应的值和HttpEncodingProperties绑定起来;并把 //HttpEncodingProperties加入到ioc容器中 @ConditionalOnWebApplication //Spring底层@Conditional注解(Spring注解版),根据不同的条件,如果满足指定的条件,整个配置类里面的配置就会生效; //判断当前应用是否是web应用,如果是,当前配置类生效 @ConditionalOnClass(CharacterEncodingFilter.class) //判断当前项目有没有这个类 CharacterEncodingFilter;SpringMVC中进行乱码解决的过滤器; @ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.http.encoding", value = "enabled", matchIfMissing = true) //判断配置文件中是否存在某个配置 spring.http.encoding.enabled;如果不存在,判断也是成立的 //即使我们配置文件中不配置pring.http.encoding.enabled=true,也是默认生效的; public class HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration { //他已经和SpringBoot的配置文件映射了 private final HttpEncodingProperties properties; //只有一个有参构造器的情况下,参数的值就会从容器中拿 public HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration(HttpEncodingProperties properties) { this.properties = properties; } @Bean //给容器中添加一个组件,这个组件的某些值需要从properties中获取 @ConditionalOnMissingBean(CharacterEncodingFilter.class) //判断容器没有这个组件? public CharacterEncodingFilter characterEncodingFilter() { CharacterEncodingFilter filter = new OrderedCharacterEncodingFilter(); filter.setEncoding(this.properties.getCharset().name()); filter.setForceRequestEncoding(this.properties.shouldForce(Type.REQUEST)); filter.setForceResponseEncoding(this.properties.shouldForce(Type.RESPONSE)); return filter; }
根据当前不同的条件判断,决定这个配置类是否生效? 一但这个配置类生效;这个配置类就会给容器中添加各种组件;
这些组件的属性是从对应的properties类中获取 的,这些类里面的每一个属性又是和配置文件绑定的;
5)、所有在配置文件中能配置的属性都是在xxxxProperties类中封装者‘;
配置文件能配置什么就可以参照某个功 能对应的这个属性类
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.http.encoding") //从配置文件中获取指定的值和bean的属 性进行绑定 public class HttpEncodingProperties { public static final Charset DEFAULT_CHARSET = Charset.forName("UTF‐8");
精髓:
1)、SpringBoot启动会加载大量的自动配置类
2)、我们看我们需要的功能有没有SpringBoot默认写好的自动配置类;
3)、我们再来看这个自动配置类中到底配置了哪些组件;(只要我们要用的组件有,我们就不需要再来配置了)
4)、给容器中自动配置类添加组件的时候,会从properties类中获取某些属性。我们就可以在配置文件中指定这 些属性的值;
xxxxAutoConfigurartion:
给容器中添加组件
xxxxProperties:封装配置文件中相关属性;



