字符设备驱动之LED驱动
实现
①编写驱动框架
②编写硬件实现代码
(在Linux系统下操作硬件,需要操作虚拟地址,因此需要先把物理地址转换为虚拟地址 ioremap())
如何实现单个灯的操作:
实现方法之一——操作次设备号
主设备号:用于查找对应的文件操作结构体;
次设备号:用于区分同类型设备下的不同设备;
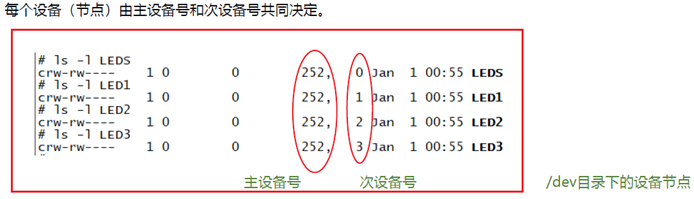
实例
driver.c
1 #include <linux/module.h>
2 #include <linux/kernel.h>
3 #include <linux/fs.h>
4 #include <linux/init.h>
5 #include <linux/delay.h>
6 #include <asm/uaccess.h>
7 #include <asm/irq.h>
8 #include <asm/io.h>
9 #include <asm/arch/regs-gpio.h>
10 #include <asm/hardware.h>
11
12 static int major;
13
14 static struct class *myLED_class;
15 static struct class_device *myLED_class_dev[4];
16
17 volatile unsigned long *gpfcon;
18 volatile unsigned long *gpfdat;
19
20 static int myLED_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file);
21 static ssize_t myLED_write(struct file *file, const char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *ppos);
22
23 static struct file_operations myLED_fops = {
24 .open = myLED_open,
25 .write = myLED_write,
26 .owner = THIS_MODULE,
27 };
28
29 static int myLED_open(struct
inode *inode, struct file *file)
30 {
31 /* 初始化LED硬件 —— GPF4、GPF5、GPF6设置为输出 */
32 *gpfcon &= ~((0x3<<(4*2)) | (0x3<<(5*2)) | (0x3<<(6*2)));
33 *gpfcon |= (0x1<<(4*2)) | (0x1<<(5*2)) | (0x1<<(6*2));
34 return 0;
35 }
36
37
38 static ssize_t myLED_write(struct file *file, const char __user *buf,
39
size_t count, loff_t *ppos)
40 {
41 int val;
42 int minor = MINOR(file->f_dentry->d_inode->i_rdev); //获取被操作设备的次设备号
43
44 copy_from_user(&val, buf, count);
45 switch (minor)
46 {
47 case 1:
48 if (1 == val)
49 {
50 *gpfdat &= ~(1<<4);
51 }
52 else {
53 *gpfdat |= 1<<4;
54 }
55 break;
56
57 case 2:
58 if (1 == val)
59 {
60 *gpfdat &= ~(1<<5);
61 }
62 else {
63 *gpfdat |= 1<<5;
64 }
65 break;
66
67 case 3:
68 if (1 == val)
69 {
70 *gpfdat &= ~(1<<6);
71 }
72 else {
73 *gpfdat |= 1<<6;
74 }
75 break;
76
77 default:
78 if (1 == val)
79 {
80 *gpfdat &= ~((1<<4) | (1<<5) | (1<<6));
81 }
82 else {
83 *gpfdat |= (1<<4) | (1<<5) | (1<<6);
84 }
85 break;
86
87 }
88 return 0;
89 }
90
91 static int __init myLED_init(void)
92 {
93 int minor;
94
95 /* 物理地址映射成虚拟地址 */
96 gpfcon = (volatile unsigned long*)ioremap(0x56000050, 16);
97 gpfdat = gpfcon + 1;
98
99 major = register_chrdev(0, "myLED", &myLED_fops);
100 myLED_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "myLEDclass");
101
102 /* 创建有主设备号和次设备号的设备节点系统信息 */
103 myLED_class_dev[0] = class_device_create(myLED_class, NULL, MKDEV(major, 0), NULL, "LEDS");
104
105 for (minor=1; minor<4; minor++)
106 {
107 myLED_class_dev[minor] = class_device_create(myLED_class, NULL, MKDEV(major, minor), NULL, "LED%d", minor);
108 }
109 return 0;
110 }
111
112 static void __exit myLED_exit(void)
113 {
114 int minor;
115
116 /* 释放虚拟地址映射 */
117 iounmap(0x56000050);
118
119 unregister_chrdev(major, "myLED");
120
121 class_device_unregister(myLED_class_dev[0]);
122 for (minor=1; minor<4; minor++)
123 {
124 myLED_class_dev[minor] = class_device_unregister(myLED_class_dev[minor]);
125 }
126 class_destroy(myLED_class);
127 return;
128 }
129
130 module_init(myLED_init);
131 module_exit(myLED_exit);
app.c
1 #include <sys/types.h>
2 #include <sys/stat.h>
3 #include <fcntl.h>
4 #include <stdio.h>
5
6 int main (int argc, char **argv)
7 {
8 int fd;
9 int val = 1;
10 char *filename;
11
12 printf("test app!\n");
13 if (argc != 3)
14 {
15 printf("Usage: LEDx <on|off>\n");
16 return -1;
17 }
18
19 filename = argv[1];
20
21 fd = open(filename, O_RDWR);
22 if(fd < 0)
23 {
24 printf("open failed!---%d---\n", fd);
25 return -1;
26 }
27
28 if (!strcmp("on", argv[2]))
29 {
30 val = 1;
31 write(fd, &val, 4);
32 }
33 else if(!strcmp("off", argv[2]))
34 {
35 val = 0;
36 write(fd, &val, 4);
37 }
38 return 0;
39 }
Makefile
1 KERN_DIR = /work/system/linux-2.6.22.6
2
3 all:
4 make -C $(KERN_DIR) M=`pwd` modules
5
6 clean:
7 make -C $(KERN_DIR) M=`pwd`
modules clean
8 rm -rf modules.order
9
10 obj-m
+= myLED.o



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号