SpringMVC文档、源码瞎读——DispatcherServlet处理请求流程
处理流程#
DispatcherServlet像下面这样处理请求:
WebApplicationContext被搜索并作为一个属性绑定到request对象中,以让处理过程中的其它元素可以使用到它。绑定时默认使用DispatcherServlet.WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE这个键。- Locale Resovler被绑定到请求中,以允许处理过程中的其它元素在处理请求时可以解析到区域信息。如果你不需要这个功能,就不需要Locale Resolver
- Theme Resovler被绑定到请求中,以允许处理过程中的其它类似视图的元素能决定使用什么主题。如果你不使用主题功能,忽略即可。
- 如果你定义了一个Multipart File Resolver,就会检查请求的Multipart部分。如果找到了这个部分,请求会被包装到一个
MultipartHttpServletRequest以被处理过程中的其它元素进一步的处理。 - 搜索一个合适的Handler。如果找到了,与这个Handler相关的执行链(Preprocessors、Postprocessors和Controllers)被运行以准备一个Model用于渲染。Alternatively, for annotated controllers, the response can be rendered (within the HandlerAdapter) instead of returning a view.
- 如果一个Model被返回了,视图就被渲染,否则(可能由于preprocessor或postprocessor拦截了请求,比如由于安全原因),没有视图被渲染,因为请求可能已经被满足了。
在WebApplicationContext中定义的HandlerExceptionResolverbean将被用于解析在请求处理过程中抛出的异常。可以通过这些异常解析器来定制异常处理的逻辑。
处理流程源码#
我们直接看DispatcherServlet的doService方法:
@Override
protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
// ...省略一些代码...
// 向handler和view暴露框架对象
request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext());
request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource());
if (this.flashMapManager != null) {
FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response);
if (inputFlashMap != null) {
request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap));
}
request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap());
request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager);
}
try {
// 分派请求
doDispatch(request, response);
}
finally {/*...*/}
}
就像官方文档说的,doService方法首先做了一些预处理,把框架中的一些组件(WebApplicationContext、LocalResovler等)通过设置请求属性的方式暴露给处理过程中的其它元素,然后,它调用了doDispatch来分派请求:
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
// 检测multipart
// 该方法首先检测是否配置了MultipartResolver,如果配置了,并且在请求中检测到multipart
// 那么返回的processedRequest应该是被包装后的MultipartHttpServletRequest
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// 获得该请求的Handler执行链(包含Handler和Interceptors)
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
// 如果没找到,调用`noHandlerFound`
// 这个方法会在`throwExceptionIfNoHandlerFound==true`时抛出一个`NoHandlerFoundException`
// 否则,向前端返回404
if (mappedHandler == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// 寻找能够适配Handler到框架中的HandlerAdapter
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// 检查LastModified,如果并未修改过代表前端的缓存还有效,那么不进行进一步的处理
// 这个需要Handler支持lastModified功能
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
// preprocessing,如果任何一个Interceptor返回false,代表该请求已经被Interceptor拦截并处理完毕,不进行进一步的处理
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// 实际处理请求,返回ModelAndView
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
// 如果mv中不包含视图,并且能根据请求找到一个默认视图名,就将默认视图名设置给mv
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
// postprocessing
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
// 捕获处理过程中发生的异常,记录到dispathException中
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,
// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
// 将处理结果、响应对象、handlerChain、ModelAndView以及异常统统传进去,处理Dispatch结果
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}
doDispatch方法中也和官方文档描述的差不多,检查Multipart,调用Handler实际处理请求,并在处理前后应用preprocessing、postprocessing。如果preprocessing没有拦截请求,那么Handler中返回了一个ModelAndView(HandlerAdapter返回的)。请求过程中抛出的任何异常(包括未找到Handler)都被记录到dispatchException中。
doDispatch阶段中产生的所有结果,比如ModelAndView、异常信息等都被传入到processDispatchResult中做进一步的处理。
private void processDispatchResult(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
@Nullable HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler, @Nullable ModelAndView mv,
@Nullable Exception exception) throws Exception {
boolean errorView = false;
// 如果异常对象不为空,证明请求处理过程中有异常发生,请求处理过程是失败的
if (exception != null) {
// 如果异常是一个`ModelAndViewDefiningException`
// 那代表这个异常中包含指导我们去向哪个异常展示页面的ModelAndView对象
// 直接用这个里面的ModelAndView替换mv
if (exception instanceof ModelAndViewDefiningException) {
logger.debug("ModelAndViewDefiningException encountered", exception);
mv = ((ModelAndViewDefiningException) exception).getModelAndView();
}
else {
// 否则,在所有注册的`HandlerExceptionResolver`中找到第一个可以处理该异常的
// 让它处理异常,并使用由它返回的ModelAndView替换mv
Object handler = (mappedHandler != null ? mappedHandler.getHandler() : null);
mv = processHandlerException(request, response, handler, exception);
errorView = (mv != null);
}
}
// 如果到了这里,mv不为空的话(有可能是正常处理返回的mv或异常发生后解析出的异常页面mv)
if (mv != null && !mv.wasCleared()) {
// 渲染
render(mv, request, response);
if (errorView) {
WebUtils.clearErrorRequestAttributes(request);
}
}
else {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No view rendering, null ModelAndView returned.");
}
}
if (WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Concurrent handling started during a forward
return;
}
if (mappedHandler != null) {
// Exception (if any) is already handled..
mappedHandler.triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null);
}
}
processDispatchResult方法中,判断是否有异常发生,如果有就尝试通过异常对象来解析出一个异常页面的ModelAndView(有可能是通过HandlerExceptionResolver),并替换原先的ModelAndView。稍后,对这个mv进行渲染操作。
这里有两个疑问:
- 如果Interceptor的postprocessing中抛出了一个异常,那么根据这个逻辑,结果将定位到异常页面,但Handler的处理已经发生。这会不会误导用户,认为他发起的操作未成功完成,但是实际上他发起的操作的作用已经产生
- 如果请求阶段抛出了一个异常,但没有通过异常解析到任何mv,那么按照这个逻辑,用户应该啥结果也接收不到?
关于两个疑问的实验#
第一个疑问,确实是这样的,自己写个代码就知道了:
Controller中打印内容:
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
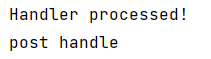
System.out.println("Handler processed!");
return "helloPage";
}
Interceptor的后处理中抛出异常:
public class HelloInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
System.out.println("post handle");
throw new RuntimeException("HelloInterceptor throws an exception");
}
}
执行结果,Handler的处理效果产生,系统被定位到异常页面:
第二个疑问,是因为我没细看processHandlerException的代码:
@Nullable
protected ModelAndView processHandlerException(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
@Nullable Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
request.removeAttribute(HandlerMapping.PRODUCIBLE_MEDIA_TYPES_ATTRIBUTE);
// 从HandlerExceptionResolver中解析mv
ModelAndView exMv = null;
if (this.handlerExceptionResolvers != null) {
for (HandlerExceptionResolver resolver : this.handlerExceptionResolvers) {
exMv = resolver.resolveException(request, response, handler, ex);
if (exMv != null) {
break;
}
}
}
// 如果解析到,返回这个mv
if (exMv != null) {
// ...
return exMv;
}
// 否则将异常抛出
throw ex;
}
也就是说这个异常最终会被抛出给Servlet容器来处理,所以我们能看到这种
作者:Yudoge
出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/lilpig/p/16510475.html
版权:本作品采用「署名-非商业性使用-相同方式共享 4.0 国际」许可协议进行许可。
欢迎按协议规定转载,方便的话,发个站内信给我嗷~




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
2021-07-23 你不知道的JavaScript——异步编程(上)传统回调模式