NIO——Channel接口关系
Channel代表Java和一个IO设备之间交换数据的通道,而Buffer代表装载这些数据的器具。
Channel类有很复杂的接口关系,这篇文章主要介绍Channel类的接口关系。
AutoCloseable和Closeable
这两个接口和NIO没关系,它们只是代表可关闭的对象。
java.lang.AutoCloseable代表可以被try-with-resource语句自动关闭的对象,它不仅可以是与IO相关的资源,而是可以是各种资源,所以它的close方法抛出Exception。
public interface AutoCloseable {
void close() throws Exception;
}
java.io.Closeable是AutoCloseable的子接口,它代表一个可关闭的IO资源,所以它的close方法抛出IOException。
public interface Closeable extends AutoCloseable {
public void close() throws IOException;
}
很显然,Channel作为一种与IO操作相关的连接,它实现了Closeable。
Channel
/**
* 一个Channel代表一个打开的,与如一个硬件设备、一个文件、
* 一个网络套接字或一个具有执行一个或多个指定IO操作的能
* 力的程序组件的实体的连接。
*
* 一个Channel可以是打开的或者关闭的,它一经创建就是打开
* 的,当它被关闭后就变成关闭状态。一旦一个Channel关闭,
* 任何尝试对其调用的IO操作都会收到一个ClosedChannelException
*/
public interface Channel extends Closeable {
public boolean isOpen();
/*
* 调用一个已经关闭的channel的close不会有任何效果
* 当一个线程的close调用未完成,另一个线程也调用close
* 另一个线程需要阻塞等待之前的线程退出close,并且
* 第二个线程的调用不会产生任何效果
*/
public void close() throws IOException;
}
AsynchronousChannel
这里我只是根据官方文档来解释,因为我也还没学过这个Channel,所以理解上可能有偏差,欢迎指出~
一种支持异步IO操作的通道,它实现了Channel,所以准确的说,它是一种异步可关闭的通道,Channel的所有子类都是可关闭的。
如果一个IO操作正在进行,并且有人调用了AsynchronousChannel的close方法,这个IO操作就会失败并抛出AsynchronousCloseException。
AsynchronousChannel是多线程并发安全的,一些Channel实现可能支持并发读写,但是不允许一个以上read或一个以上write操作同时发生。(即一个read未完成不允许进行另一个read)
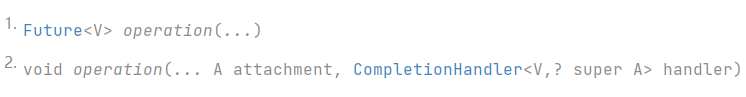
通常,它支持下面两种形式的IO操作(基于Future和基于回调):
取消
Future接口的cancel方法用来取消任务的执行,这将导致所有等待该IO操作结果的线程抛出java.util.concurrent.CancellationException,但一个任务具体可以取消是依赖于特定的高层实现的,所以在该接口里并没有任何相关的指定。如果取消使通道或它所连接的实体处于不一致状态,则通道将进入特定于实现的错误状态,以防止进一步尝试启动类似于已取消操作的 IO 操作,比如一个读取操作被取消,但这时并不能保证尚未从通道中读取数据,此时Channel应该被转换到一个高层实现指定的错误状态,以防止稍后的类似读取操作发生。
当cancel方法被调用时参数mayInterruptIfRunning为true,那么可以通过关闭通道来打断IO操作,此时所有等待该IO操作结果的线程抛出CancellationException异常,任何其他外部IO操作以AsynchronousCloseException结束。
代码
public interface AsynchronousChannel
extends Channel
{
/**
* 关闭Channel
* 任何外部的异步操作以AsynchronousCloseException结束
* 当Channel关闭后,类似的IO操作尝试将立即由于ClosedChannelException而结束
*
*/
@Override
void close() throws IOException;
}
AsynchronousByteChannel
支持异步IO操作的,以字节为单位的通道,由于指定了存储,所以提供了具体的read和write方法。
public interface AsynchronousByteChannel
extends AsynchronousChannel
{
<A> void read(ByteBuffer dst,
A attachment,
CompletionHandler<Integer,? super A> handler);
Future<Integer> read(ByteBuffer dst);
<A> void write(ByteBuffer src,
A attachment,
CompletionHandler<Integer,? super A> handler);
Future<Integer> write(ByteBuffer src);
}
若一个read之前有一个未完成的read,则抛出ReadPendingException,write也一样,抛出WritePendingException。
ReadableByteChannel
该通道允许将数据读入到字节缓冲中
public interface ReadableByteChannel extends Channel {
public int read(ByteBuffer dst) throws IOException;
}
如果一个线程正在一个通道上执行read操作,那么其他线程对该通道的read操作都将阻塞。
ScatteringByteChannel
这种通道可以将数据读入到多个字节缓冲区中
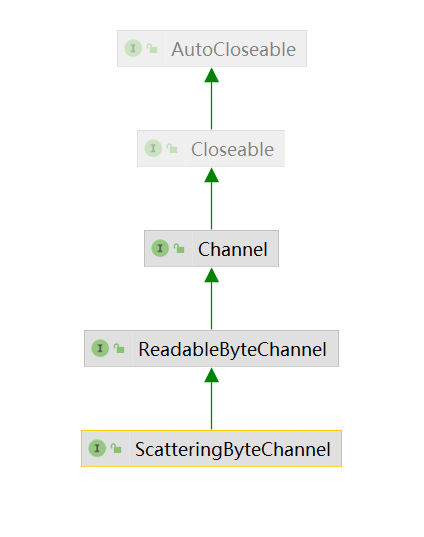
public interface ScatteringByteChannel
extends ReadableByteChannel
{
public long read(ByteBuffer[] dsts, int offset, int length)
throws IOException;
public long read(ByteBuffer[] dsts) throws IOException;
}
WritableByteChannel
这种通道可以将来自字节缓冲的数据写入到通道中
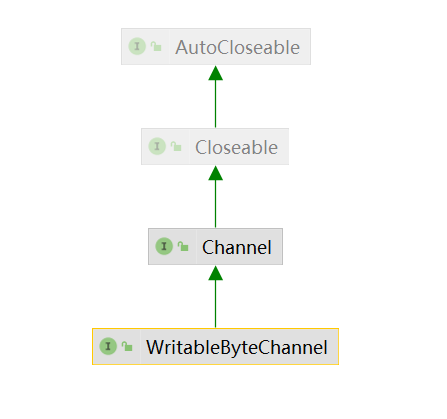
public interface WritableByteChannel
extends Channel
{
public int write(ByteBuffer src) throws IOException;
}
如果一个线程正在一个通道上执行write操作,那么其他线程对该通道的write操作都将阻塞。
GatheringByteChannel
这种通道可以将来自多个字节缓冲的数据写入到通道中
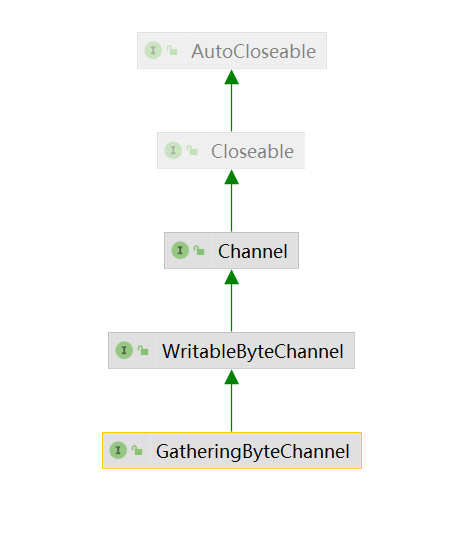
public interface GatheringByteChannel
extends WritableByteChannel
{
public long write(ByteBuffer[] srcs, int offset, int length)
throws IOException;
public long write(ByteBuffer[] srcs) throws IOException;
}
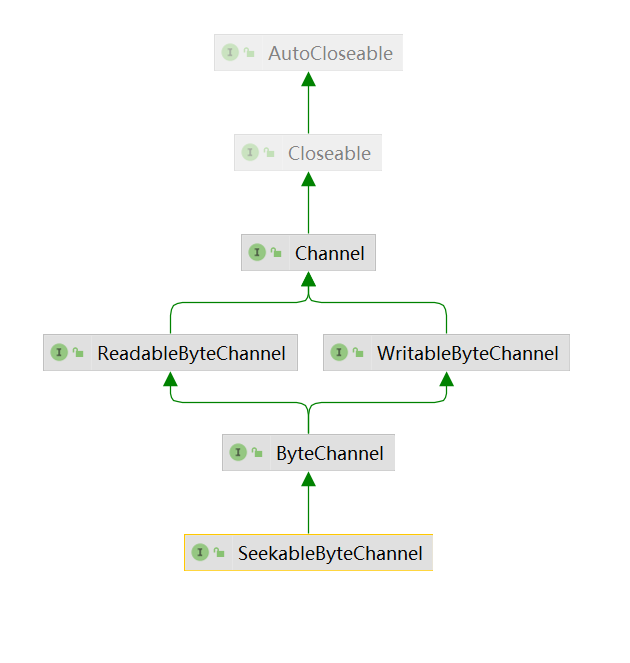
ByteChannel
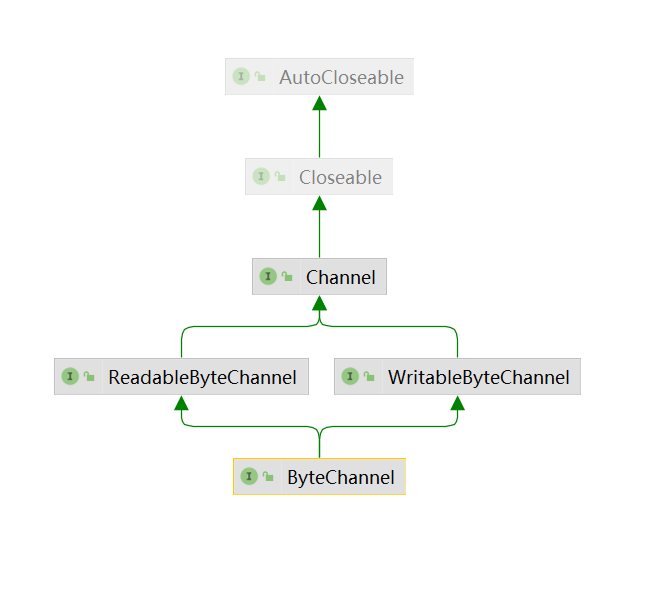
public interface ByteChannel
extends ReadableByteChannel, WritableByteChannel
{
}
SeekableByteChannel
这种通道维护一个当前位置,并且允许改变位置。
public interface SeekableByteChannel
extends ByteChannel
{
@Override
int read(ByteBuffer dst) throws IOException;
@Override
int write(ByteBuffer src) throws IOException;
long position() throws IOException;
SeekableByteChannel position(long newPosition) throws IOException;
long size() throws IOException;
SeekableByteChannel truncate(long size) throws IOException;
}
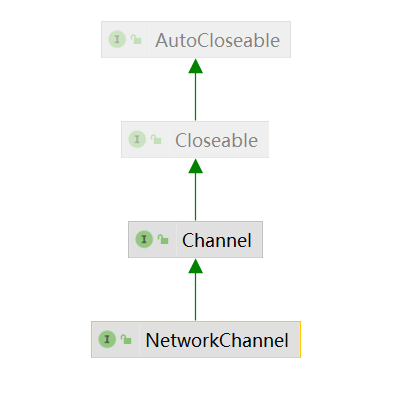
NetworkChannel
一个连接到网络socket的通道。
public interface NetworkChannel
extends Channel
{
NetworkChannel bind(SocketAddress local) throws IOException;
SocketAddress getLocalAddress() throws IOException;
<T> NetworkChannel setOption(SocketOption<T> name, T value) throws IOException;
<T> T getOption(SocketOption<T> name) throws IOException;
Set<SocketOption<?>> supportedOptions();
}
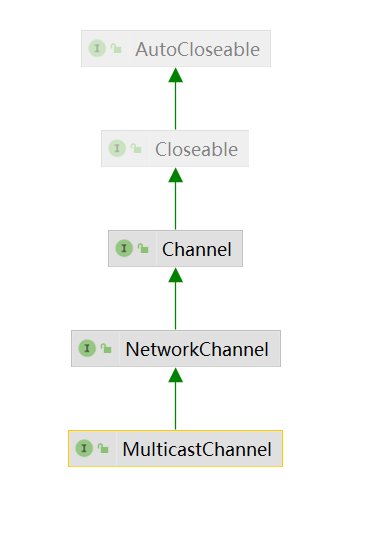
MulticastChannel
一种用于支持IP多播的通道。
public interface MulticastChannel
extends NetworkChannel
{
@Override void close() throws IOException;
MembershipKey join(InetAddress group, NetworkInterface interf)
throws IOException;
MembershipKey join(InetAddress group, NetworkInterface interf, InetAddress source)
throws IOException;
}
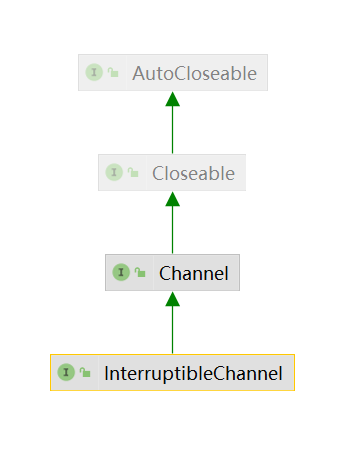
InterruptibleChannel
一种可以被异步关闭和中断的通道。
实现了该接口的Channel是异步的:如果一个线程阻塞在一个InterruptibleChannel的IO操作上,这时其他线程调用了该Channel的close方法,这个阻塞线程将收到AsynchronousCloseException。
实现了该接口的Channel是可中断的:如果一个线程阻塞在一个InterruptibleChannel的IO操作上,这时其他线程调用了该阻塞线程的interrupt方法,这将导致Channel关闭,阻塞线程将收到ClosedByInterruptException,并且阻塞线程的interrupt状态将被设置。
如果一个线程的interrupt状态已经设置,然后它调用了一个阻塞IO操作,那么这个通道将关闭,并且线程接收到一个ClosedByInterruptException,线程的interrupt状态保持。
public interface InterruptibleChannel
extends Channel
{
public void close() throws IOException;
}

