四分树——UVa 297、UVa 806
四分树(Quadtrees, UVa 297)
如图6-8所示,可以用四分树来表示一个黑白图像,方法是用根结点表示整幅图像,然后把行列各分成两等分,按照图中的方式编号,从左到右对应4个子结点。如果某子结点对应的区域全黑或者全白,则直接用一个黑结点或者白结点表示;如果既有黑又有白,则用一个灰结点表示,并且为这个区域递归建树。

给出两棵四分树的先序遍历,求二者合并之后(黑色部分合并)黑色像素的个数。p表示中间结点,f表示黑色(full),e表示白色(empty)。
输入输出
Sample Input
3
ppeeefpffeefe
pefepeefe
peeef
peefe
peeef
peepefefe
Sample Output
There are 640 black pixels.
There are 512 black pixels.
There are 384 black pixels.
思路
题目不是那种看了之后一点思路都没有的,恶心的在于得把两个四分树合并,我之前没读完题目就去做了输入包括建树的处理,然后发现像我那样建树的话很难合并。
如下的代码是创建一个真正的四分树,但是我没做题目中要求的合并操作,我做的是把两棵树各自的黑块大小相加。
#include "iostream"
#include "cstdio"
#include "cstring"
#define LEN 32
#define MAXN 1034
#define NOT_INIT 0
#define P 1
#define E 2
#define F 3
using namespace std;
char s[MAXN];
int tree[MAXN];
// 获取第一个子节点
int fchild(int cur) {
return cur * 4 + 1;
}
// 获取父节点
int parent(int cur) {
return (cur-1) / 4;
}
// 递归创建四分树
void build(int cur,int i) {
char c = s[i];
if (!c)return;
if (c == 'p') {
tree[cur] = P;
// 递归子节点
build(fchild(cur), i + 1);
}
else {
tree[cur] = c == 'e' ? E : F;
if (cur % 4 == 0) // 回到父节点
cur = parent(cur);
build(cur + 1, i + 1);
}
}
int sum; // 递归计算面积
void sumit(int level,int cur,int i) {
int idx = cur + i;
if (tree[idx] == NOT_INIT||tree[idx] == E||idx > MAXN)return;
if (tree[idx] == P) {
for(int j=0;j<4;j++)
sumit(level + 1, fchild(idx),j);
}
else {
int l = 32 / (int)pow(2, level);
sum += l * l;
}
}
int main() {
int n;
while (scanf("%d", &n) != EOF) {
memset(tree, NOT_INIT, sizeof(tree));
sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
scanf("%s", s);
build(0,0);
}
sumit(0,0,0);
printf("%d\n",sum);
}
return 0;
}
这个代码啰嗦且难用。
刘汝佳大佬给的方法是创建一个二维的buf,真正的把这个图形存起来,这样的话合并操作就很简单了,而且其实不会浪费多少空间。因为最多也就是32*32的矩阵。
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
const int len = 32;
const int maxn = 1024 + 10;
char s[maxn];
int buf[len][len], cnt;
/*
* p: 当前读到了输入字符串的哪个字符
* r: 当前行
* c: 当前列
* w: 当前正方形的边长
*/
void draw(const char* s, int& p, int r, int c, int w) {
char ch = s[p++];
// p代表该分割当前的正方形了
if (ch == 'p') {
// 分成四个小的,这是第一个(右上)
draw(s, p, r, c + w / 2, w / 2);
// 第二个(左上)
draw(s, p, r, c, w / 2);
// 第三个(左下)
draw(s, p, r + w / 2, c, w / 2);
// 第四个(右下)
draw(s, p, r + w / 2, c + w / 2, w / 2);
}
else if (ch == 'f') { //画黑像素(白像素不画)
for (int i = r; i < r + w; i++)
for (int j = c; j < c + w; j++)
// 这里直接判断这个位置是不是还没画过,这样就做到了并集
if (buf[i][j] == 0) { buf[i][j] = 1; cnt++; }
}
}
int main() {
int T;
scanf("%d", &T);
while (T--) {
memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf));
cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
scanf("%s", s);
int p = 0;
draw(s, p, 0, 0, len);
}
printf("There are %d black pixels.\n", cnt);
}
return 0;
}
空间结构(Spatial Structures, ACM/ICPC World Finals 1998, UVa806)
黑白图像有两种表示法:点阵表示和路径表示。路径表示法首先需要把图像转化为四分树,然后记录所有黑结点到根的路径。例如,对于如图6-25所示的图像。
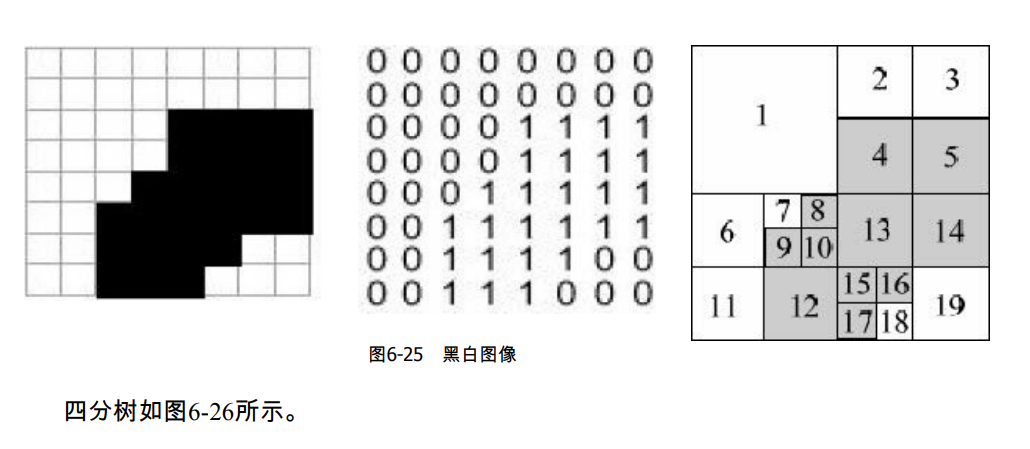

NW、NE、SW、SE分别用1、2、3、4表示。最后把得到的数字串看成是五进制的,转化为十进制后排序。例如上面的树在转化、排序后的结果是:9 14 17 22 23 44 63 69 88 94
113。你的任务是在这两种表示法之间进行转换。在点阵表示法中,1表示黑色,0表示白色。图像总是正方形的,且长度n为2的整数幂,并满足n≤64。输入输出细节请参见原题。
输入输出
Sample Input
-8
9 14 17 22 23 44 63 69 88 94 113 -1
8
00000000
00000000
00001111
00001111
00011111
00111111
00111100
00111000
Sample Output
Image 1
........
........
....****
....****
...*****
..******
..****..
..***...
Image 2
Total number of black nodes = 11
9 14 17 22 23 44 63 69 88 94 113
思路
总的来说和上一题差不多,只不过是双向的转换。题目中要求的格式贼他妈狗,对着UDebug调了半天。
#include "iostream"
#include "cstdio"
#include "vector"
#include "queue"
#include "cmath"
#include "cstring"
#include <algorithm>
#include "cstdlib"
#define LEN 64
using namespace std;
int mt[LEN][LEN];
int img_cnt = 0;
queue<int> to_five_b(int num){
queue<int> fb;
while (num != 0) {
fb.push(num % 5);
num /= 5;
}
return fb;
}
int dx[] = { 0,0,1,0,1};
int dy[] = { 0,0,0,1,1 };
vector<int> ans;
// 行 列 深度 第几个
bool is_full_of_black(int r, int c, int w) {
for (int i = r; i < r + w; i++) {
for (int j = c; j < c + w; j++) {
if (!mt[i][j]) {
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
void _build_mt(int n,int r, int c, int depth,int num_five_b) {
int w = n / (int) pow(2, depth);
if (w == 0)return;
if (is_full_of_black(r,c,w)) {
//printf("%d %d %d %d\n", r, c, depth,w);
int sum_10b = 0,power=0;
while (num_five_b) {
int r = num_five_b % 10;
sum_10b += r*(int)pow(5, power++);
num_five_b /= 10;
}
ans.push_back(sum_10b);
}
else {
// 递归四个子块
int k = (int)pow(10, depth);
_build_mt(n, r, c, depth + 1,1*k+num_five_b);
_build_mt(n, r, c + w / 2, depth + 1,2*k+num_five_b);
_build_mt(n, r+w/2, c, depth + 1,3*k+num_five_b);
_build_mt(n, r+w/2, c + w / 2, depth + 1,4*k+num_five_b);
}
}
void build_mt(int n) {
getchar();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
char c; scanf("%c", &c);
mt[i][j] = c - '0';
}
getchar();
}
_build_mt(n, 0, 0,0,0);
sort(ans.begin(),ans.end());
// 糟糕的输出处理
printf("Image %d\n", ++img_cnt);
for (int i = 0; i < ans.size(); i++) {
int answer = ans[i];
printf("%d", answer);
if ((i+1) % 12 == 0)printf("\n"); else if (i != ans.size() - 1)printf(" ");
}
if (ans.size()%12!=0)printf("\n");
printf("Total number of black nodes = %d\n", ans.size());
}
void build_num(int n){
int in;
while (true) {
scanf("%d", &in);
if (in == -1)break;
queue<int> fb = to_five_b(in);
int w = n;
int x = 0, y = 0;
while (!fb.empty()) {
w /= 2;
int pos = fb.front(); fb.pop();
x += dx[pos] * w;
y += dy[pos] * w;
}
for (int i = x; i < x+w; i++)
for (int j = y; j < y + w; j++) {
mt[j][i] = 1;
}
}
printf("Image %d\n", ++img_cnt);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
printf("%c", mt[i][j]?'*':'.');
}
printf("\n");
}
}
int main() {
int n;
bool first = true;
while (scanf("%d", &n) != EOF) {
if (!first && n!=0) {
printf("\n");
}
first = false;
ans.clear();
memset(mt, 0, sizeof(mt));
if (n > 0) build_mt(n);
else if (n < 0) build_num(-n);
else break;
}
return 0;
}

