左子右兄弟表示法
题目RootedTree#
《挑战程序设计竞赛2 算法和数据结构》中8.2章中有这样一道题。
请编写一个程序,输出给定有根树T中各节点u的信息,信息内容如下。
- u的节点编号
- u的节点种类(根、内部节点、叶)
- u的父节点编号
- u的字节点列表
- u的深度
输入#
第一行输入结点的个数n,接下来n行按照下述格式输入各个节点的信息,每个节点占一行。
id k c1 c2 ... ck
id为节点编号,k为该节点的度,也就是有几个子节点,c1~ck就是它的子节点。
输出#
node id: parent = p, depth = d,type, [c1,...,ck]
示例#
输入
13
0 3 1 4 10
1 2 2 3
2 0
3 0
4 3 5 6 7
5 0
6 0
7 2 8 9
8 0
9 0
10 2 11 12
11 0
12 0
输出
node 0: parent = -1, depth = 0, root,[1,4,10]
node 1: parent = 0, depth = 1, internal node,[2,3]
node 2: parent = 1, depth = 2, leaf,[]
node 3: parent = 1, depth = 2, leaf,[]
node 4: parent = 0, depth = 1, internal node,[5,6,7]
node 5: parent = 4, depth = 2, leaf,[]
node 6: parent = 4, depth = 2, leaf,[]
node 7: parent = 4, depth = 2, internal node,[8,9]
node 8: parent = 7, depth = 3, leaf,[]
node 9: parent = 7, depth = 3, leaf,[]
node 10: parent = 0, depth = 1, internal node,[11,12]
node 11: parent = 10, depth = 2, leaf,[]
node 12: parent = 10, depth = 2, leaf,[]
左子右兄弟表示法#
书里给的算法是一个使用左子右兄弟表示法表示的树。我没看懂书中写的代码,我自己理解了一下,不知道说的对不对,反正结果是正确的。
和名字一样,这棵树的每个节点有两个附属节点,左面的附属节点是当前节点的子节点,右面的附属节点是当前节点的兄弟节点。左子右兄弟可以把任意形状的有根树转换成二叉树。
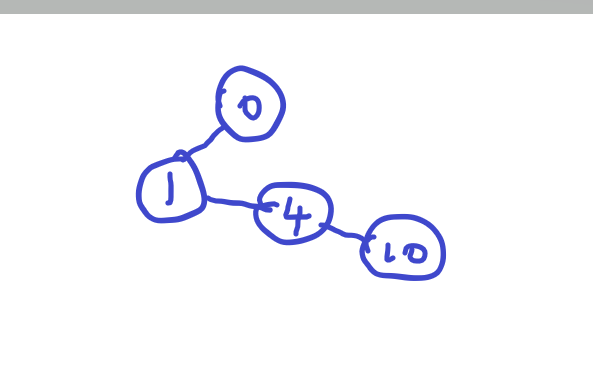
我们先手绘它给的数据。
首先知道0是根节点它的子节点有1,4和10。那根据左子右兄弟树的定义,我们可以这样画。
因为1,4,10都是0的子节点,但是0只有左面一个指向子节点的附属节点,不能同时指向三个,但是1,4是兄弟关系,我们可以把4接到1的右附属兄弟节点上,然后10和4又是兄弟关系,我们又可以把10接到4的右节点上。
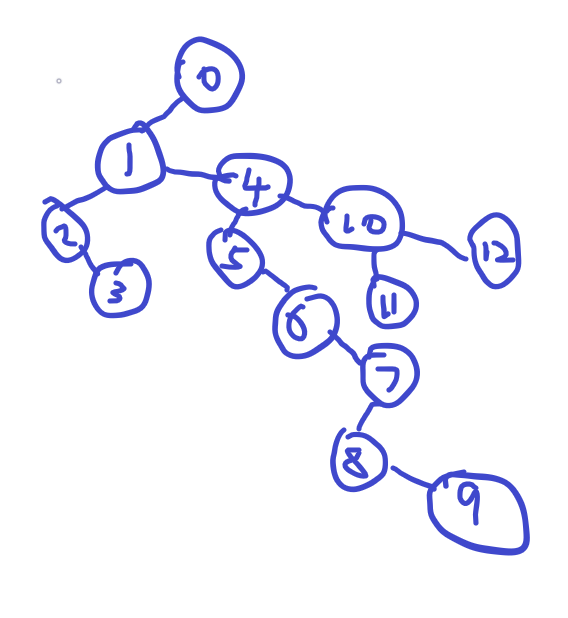
也就是说在一棵左子右兄弟表示的树中,当前节点c的左节点是实际树关系中该节点的直接子节点,并且左子节点的所有右侧节点构成的链表(如图中的1,4,10)在实际的树关系中是平级的,都是c的直接子节点。
所以给定数据的左子右兄弟表示完整版本是这样的
写代码#
并不是按照题目中要求的输入写的,只是把示例数据给写死了。写的也是稍微有些乱。
#include "iostream"
#include "string"
#define N 13
#define RIGHT_CHILD 0
#define LEFT_CHILD 1
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int parent, left, right;
};
struct Node nodeList[N];
int treeData[][N] = {
{0,3,1,4,10},
{1,2,2,3},
{2,0},
{3,0},
{4,3,5,6,7},
{5,0},
{6,0},
{7,2,8,9},
{8,0},
{9,0},
{10,2,11,12},
{11,0},
{12,0}
};
void bindChild(int leftAndRight, int childIdx, int parentIdx) {
if (leftAndRight == LEFT_CHILD)
nodeList[parentIdx].left = childIdx;
else
nodeList[parentIdx].right = childIdx;
nodeList[childIdx].parent = parentIdx;
}
void createTree() {
nodeList[0].parent = -1;
nodeList[0].right = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
int curNodeChildCount = treeData[i][1];
if (curNodeChildCount == 0) {
nodeList[i].left = -1;
continue;
}
int curChildIdx = treeData[i][2];
bindChild(LEFT_CHILD, curChildIdx, i);
for (int j = 3; j < curNodeChildCount + 2; j++) {
nodeList[curChildIdx].right = treeData[i][j];
nodeList[treeData[i][j]].parent = i;
curChildIdx = treeData[i][j];
}
nodeList[curChildIdx].right = -1;
}
}
int getDepth(int idx) {
struct Node curNode = nodeList[idx];
int depth = 0;
while (curNode.parent != -1) {
depth++;
curNode = nodeList[curNode.parent];
}
return depth;
}
string getType(int idx) {
struct Node node = nodeList[idx];
if (node.parent == -1)
return "root";
else if (node.left == -1)
return "leaf";
else
return "internal node";
}
void printChildsString(int idx){
cout << "[";
struct Node curNode = nodeList[idx];
if (curNode.left == -1) {
cout << "]";
return;
}
cout << curNode.left << ",";
curNode = nodeList[curNode.left];
while (curNode.right != -1) {
cout << curNode.right;
curNode = nodeList[curNode.right];
if (curNode.right != -1)cout << ",";
}
cout << "]";
}
void printNode(int idx){
cout << "node " << idx << ": parent = " << nodeList[idx].parent << ", depth = " << getDepth(idx)
<< ", " << getType(idx) << ",";
printChildsString(idx);
cout << endl;
}
int main() {
createTree();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
printNode(i);
return 0;
}
作者:Yudoge
出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/lilpig/p/13797458.html
版权:本作品采用「署名-非商业性使用-相同方式共享 4.0 国际」许可协议进行许可。
欢迎按协议规定转载,方便的话,发个站内信给我嗷~




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)