tomcat阅读第十五篇(tomcat Wrapper)
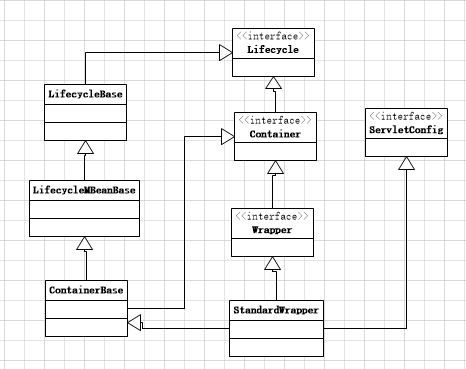
这篇分析另一个人容器Wrapper,这个跟之前分析的Server、Service、Host、Engine 和Context不同,前面分析的容器可以直接在Server.xml配置,Context可以配置也可不配置,但是Wrapper是在容器初始化过程中创建的。主要是在第十三章中分析WebConfig方法的第九步configureContext里面创建的,下图是Wrapper的继承关系
下面是创建Wrapper的代码片段
private void configureContext(WebXml webxml) { ………………………. for (ServletDef servlet : webxml.getServlets().values()) { //调用StandardContext对象createWrapper方法创建StandardWrapper对象,给对象添加LifecyecleListener和ContainerListener Wrapper wrapper = context.createWrapper(); //下面一系列的set都是将servlet的配置设置给Wrapper,由此可见Wrapper就是对Servelt的一个包装(decorator设计模式) if (servlet.getLoadOnStartup() != null) { wrapper.setLoadOnStartup(servlet.getLoadOnStartup().intValue()); } if (servlet.getEnabled() != null) { wrapper.setEnabled(servlet.getEnabled().booleanValue()); } wrapper.setName(servlet.getServletName()); Map<String,String> params = servlet.getParameterMap(); for (Entry<String, String> entry : params.entrySet()) { wrapper.addInitParameter(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue()); } wrapper.setRunAs(servlet.getRunAs()); Set<SecurityRoleRef> roleRefs = servlet.getSecurityRoleRefs(); for (SecurityRoleRef roleRef : roleRefs) { wrapper.addSecurityReference( roleRef.getName(), roleRef.getLink()); } wrapper.setServletClass(servlet.getServletClass()); MultipartDef multipartdef = servlet.getMultipartDef(); if (multipartdef != null) { if (multipartdef.getMaxFileSize() != null && multipartdef.getMaxRequestSize()!= null && multipartdef.getFileSizeThreshold() != null) { wrapper.setMultipartConfigElement(new MultipartConfigElement( multipartdef.getLocation(), Long.parseLong(multipartdef.getMaxFileSize()), Long.parseLong(multipartdef.getMaxRequestSize()), Integer.parseInt( multipartdef.getFileSizeThreshold()))); } else { wrapper.setMultipartConfigElement(new MultipartConfigElement( multipartdef.getLocation())); } } if (servlet.getAsyncSupported() != null) { wrapper.setAsyncSupported( servlet.getAsyncSupported().booleanValue()); } wrapper.setOverridable(servlet.isOverridable()); //add的同时会start Wrapper context.addChild(wrapper); } for (Entry<String, String> entry : webxml.getServletMappings().entrySet()) { //StandardContext添加与Servlet对应的ServletMapping context.addServletMappingDecoded(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue()); } …………………………….. }
现在来看StandardWrapper类,首先是它的构造方法,创建Valve,处理http请求的时候起作用,后面分析
public StandardWrapper() { super(); swValve=new StandardWrapperValve(); pipeline.setBasic(swValve); broadcaster = new NotificationBroadcasterSupport(); }
还有几个重要的方法,allocate、load、unload
先看下load方法的调用链
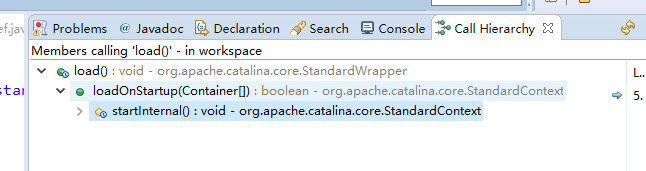
StandardContext startInternal方法触发ContextConfig的Config_Start(Wrapper是在webConfig方法step9创建)方法后,调用loadOnStartup 从而调用到Wrapper的load方法,下面是StartInternal的代码片段
fireLifecycleEvent(Lifecycle.CONFIGURE_START_EVENT, null); …………………. if (ok) { if (!loadOnStartup(findChildren())){ log.error(sm.getString("standardContext.servletFail")); ok = false; } }
Load方法代码
public synchronized void load() throws ServletException { //goto 分析loadServlet方法 instance = loadServlet(); if (!instanceInitialized) { //没有实例化这个servlet就调用initServlet //goto分析initServlet方法 initServlet(instance); } if (isJspServlet) { //如果是jspservlet,则把这个servlet作为MBean StringBuilder oname = new StringBuilder(getDomain()); oname.append(":type=JspMonitor"); oname.append(getWebModuleKeyProperties()); oname.append(",name="); oname.append(getName()); oname.append(getJ2EEKeyProperties()); try { jspMonitorON = new ObjectName(oname.toString()); Registry.getRegistry(null, null) .registerComponent(instance, jspMonitorON, null); } catch( Exception ex ) { log.info("Error registering JSP monitoring with jmx " + instance); } } }
分析loadServlet方法:
public synchronized Servlet loadServlet() throws ServletException { if (!singleThreadModel && (instance != null)) return instance; PrintStream out = System.out; if (swallowOutput) { SystemLogHandler.startCapture(); } Servlet servlet; try { long t1=System.currentTimeMillis(); if (servletClass == null) { unavailable(null); throw new ServletException (sm.getString("standardWrapper.notClass", getName())); } // InstanceManager默认是DefaultInstanceManager,StandardContext创建DefaultInstanceManager后,会用Webapploader的classloader binding InstanceManager instanceManager = ((StandardContext)getParent()).getInstanceManager(); try { //用instanceManager实例化Servlet,每个StandardContext都会创建InstanceManager,每个instanceManager会合每个webapploader的classloader绑定
//不同的Context的servlet会用不同的classloader加载 servlet = (Servlet) instanceManager.newInstance(servletClass); } catch (ClassCastException e) { unavailable(null); throw new ServletException (sm.getString("standardWrapper.notServlet", servletClass), e); } catch (Throwable e) { e = ExceptionUtils.unwrapInvocationTargetException(e); ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(e); unavailable(null); // Added extra log statement for Bugzilla 36630: // http://bz.apache.org/bugzilla/show_bug.cgi?id=36630 if(log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug(sm.getString("standardWrapper.instantiate", servletClass), e); } // Restore the context ClassLoader throw new ServletException (sm.getString("standardWrapper.instantiate", servletClass), e); } if (multipartConfigElement == null) { //实例化MultipartConfigElement,解析MultipartConfig注解,跟文件上传有关 MultipartConfig annotation = servlet.getClass().getAnnotation(MultipartConfig.class); if (annotation != null) { multipartConfigElement = new MultipartConfigElement(annotation); } } //处理ServletSecurity 注解,调用Context addServletSecurity processServletSecurityAnnotation(servlet.getClass()); //判断这个servlet是不是 ContainerServlet(类全名有org.apache.catalina.或者继承ContainerServlet) if ((servlet instanceof ContainerServlet) && (isContainerProvidedServlet(servletClass) ||((Context) getParent()).getPrivileged() )) { ((ContainerServlet)servlet).setWrapper(this); } classLoadTime=(int) (System.currentTimeMillis() -t1); if (servlet instanceof SingleThreadModel) { if (instancePool == null) { //实例化instancePool instancePool = new Stack<>(); } singleThreadModel = true; } //调用Servlet的init方法,参数是ServletConfig initServlet(servlet); fireContainerEvent("load", this); loadTime=System.currentTimeMillis() -t1; } finally { if (swallowOutput) { String log = SystemLogHandler.stopCapture(); if (log != null && log.length() > 0) { if (getServletContext() != null) { getServletContext().log(log); } else { out.println(log); } } } } return servlet; }
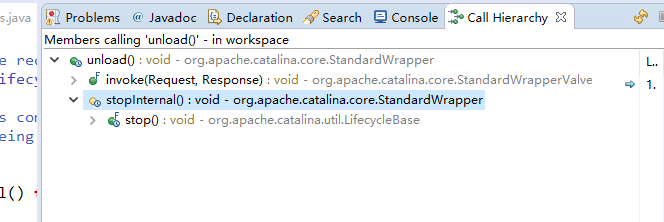
Unload方法:主要逻辑调用servlet的destroy方法
下图是unload方法的调用链
Allocate方法:这个跟请求处理相关,后面分析,现在只看下调用链

本來打算用的新的一篇讲StandardContext的XXXInternal方法,但是浏览源码发现都是对Context所用类(比如Manager等)的创建和释放,主要跟程序相关的配置逻辑还是
在ContextConfig中,Context使用的那些类主要是在处理请求的时候起作用,到时候再分析。
下篇开始,就要分析跟处理请求相关的逻辑了,涉及到tomcat的另一大部分Connector,从Service那里,先分析的Engine这条线(tomcat内部逻辑),现在要分析Connector相关,
因为他跟请求处理相关,还有各个容器的相对应的Valve类,也是跟请求处理相关,下篇开始我们分析Connector相关内容。


