JDBC之Statement
Statement
Statement
Statement概述
接口的实现在数据库驱动中. 用来操作sql语句(增删改查),并返回相应结果对象
JDBC利用Statement把将要执行的SQL发送给MySQL服务端进行操作。
JDBC利用Statement把将要执行的SQL发送给MySQL服务端进行操作。
JDBC利用Statement把将要执行的SQL发送给MySQL服务端进行操作。
JDBC想要利用SQL完成对数据库的增删改查,只需要通过Statement这个对象向数据库发送增删改查对应的SQL语句即可。
要执行的SQL分为两类
查询
Statement.executeQuery方法用于向数据库发送查询语句,executeQuery方法返回代表查询结果的ResultSet对象。
增删改
Statement对象的executeUpdate方法,用于向数据库发送增、删、改的sql语句,executeUpdate执行完后,将会返回一个整数(即增删改对应的SQL语句导致了数据库有几行数据发生了变化)。
Statement继承体系
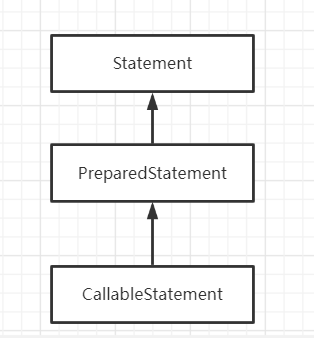
其中 CallableStatement 继承自 PreparedStatement, 而 PreparedStatement 又继承自 Statement。
他们的区别是:
| 名称 | Statement | PreparedStatement | CallableStatement |
|---|---|---|---|
| 说明 | Statement 提供基本的 SQL 操作. 适合静态SQL语句, 且传入的 SQL 语句无法接受参数. | PreparedStatement 可以在 SQL 中传递参数, 适合多次使用的 SQL 语句. | CallableStatement 可以调用 PL/SQL 存储过程. |
| 使用 | select * from account | select * from account where id = ? | |
| 额外说明 | 静态SQL,因为没有动态参数 | 动态SQL 可以防止SQL注入 SQL给会编译一次,而不会编译多次 |
不做了解,因为阿里巴巴规范中强制要求不要使用存储过程 |
SQL注入问题
下面先看下SQL注入出现的原因,代码如下:
public class SqlInjectTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mysql_index_test?useSSL=true";
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.setProperty("user","root");
properties.setProperty("password","root");
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, properties);
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
// 后面的参数1假如是用户传递的
String paremeter = "1";
String sql = "select * from film where id = " + paremeter;
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);
while (resultSet.next()){
int id = resultSet.getInt("id");
String name = resultSet.getString("name");
System.out.println(String.format("id是:%s,name是:%s",id,name));
}
resultSet.close();
statement.close();
connection.close();
}
}
查询结果如下:
id是:1,name是:film1
但是如果被有些别出心裁的人知道了SQL语句是这样子拼接的时候,那么可以伪造SQL,如下所示:
public class SqlInjectTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mysql_index_test?useSSL=true";
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.setProperty("user","root");
properties.setProperty("password","root");
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, properties);
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
// 后面的参数1假如是用户传递的
String paremeter = "1 or 1=1";
String sql = "select * from film where id = " + paremeter;
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);
while (resultSet.next()){
int id = resultSet.getInt("id");
String name = resultSet.getString("name");
System.out.println(String.format("id是:%s,name是:%s",id,name));
}
resultSet.close();
statement.close();
connection.close();
}
}
对应的结果如下所示:
id是:3,name是:film0
id是:1,name是:film1
id是:2,name是:film2
SQL注入问题解决
本质原因是因为上面使用的Statement是原生的,那么我们需要使用预编译的PreparedStatement解决问题
代码如下所示:
public class SqlInjectTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mysql_index_test?useSSL=true";
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.setProperty("user","root");
properties.setProperty("password","root");
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, properties);
// 后面的参数1假如是用户传递的
String paremeter = "film0";
String sql = "select * from film where name = ?" ;
PreparedStatement statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
// 设置第1个?的值是paremeter
statement.setString(1,paremeter);
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery();
while (resultSet.next()){
int id = resultSet.getInt("id");
String name = resultSet.getString("name");
System.out.println(String.format("id是:%s,name是:%s",id,name));
}
resultSet.close();
statement.close();
connection.close();
}
}
那么再看一下另外一种情况
public class SqlInjectTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mysql_index_test?useSSL=true";
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.setProperty("user","root");
properties.setProperty("password","root");
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, properties);
// 后面的参数1假如是用户传递的
String paremeter = "film0 or 1=1";
String sql = "select * from film where name = ?" ;
PreparedStatement statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
// 设置第1个?的值是paremeter【根据对应的数据类型来进行设置】
statement.setString(1,paremeter);
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery();
while (resultSet.next()){
int id = resultSet.getInt("id");
String name = resultSet.getString("name");
System.out.println(String.format("id是:%s,name是:%s",id,name));
}
resultSet.close();
statement.close();
connection.close();
}
}
没有结果!!!
因为对应的SQL已经被修改了,变成了
select * from film where name = 'film0 or 1=1'
而不是我们想象的
select * from film where name = 'film0' or 1=1
所以上面的查询是没有结果的,因为在数据库中根本就没有找到这样的name
获取得到主键自增的ID
通常我们在应用中对mysql执行了insert操作后,需要获取插入记录的自增主键,这时候通常用getGeneratedKeys()方法获取主键
使用JDBC 3.0提供的 getGeneratedKeys。推荐使用
java.sql.Statement#getGeneratedKeys
/** Retrieves any auto-generated keys created as a result of executing this Statement object. If this Statement object did not
* generate any keys, an empty ResultSet object is returned.
*/
ResultSet getGeneratedKeys() throws SQLException;
步骤:
1. 获得数据库返回的主键:insert into book values(null,'lig',45);
2. 获得主键的步骤:
conn.prepareStatement(sql,autoGeneratedKeys)
// autoGeneratedKeys是一个int值 ,1代表返回生成的主键,2代表不返回生成的主键;为了方便记忆,使用
// Statement中的属性
// Statement.Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS,Statement.NO_GENERATED_KEYS
3.利用prepareStatement设置参数,然后执行insert语句之后,返回修改的行数;
4.获得得到结果集,拿到生成的主键
ResultSet rs=ps.getGeneratedKesy();
rs.next();
int userno= rs.getInt(1);
实例:
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
stmt = conn.createStatement(java.sql.ResultSet.TYPE_FORWARD_ONLY,
java.sql.ResultSet.CONCUR_UPDATABLE);
// ...
// 省略若干行(如上例般创建demo表)
// ...
stmt.executeUpdate(
"INSERT INTO autoIncTutorial (dataField) "
+ "values ('Can I Get the Auto Increment Field?')",
Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS); // 向驱动指明需要自动获取generatedKeys!
int autoIncKeyFromApi = -1;
rs = stmt.getGeneratedKeys(); // 获取自增主键!
if (rs.next()) {
autoIncKeyFromApi = rs.getInt(1);
} else {
// throw an exception from here
}
rs.close();
rs = null;
System.out.println("Key returned from getGeneratedKeys():"
+ autoIncKeyFromApi);
} finally { ... }
自己也来写一行代码,代码展示如下所示:
public class MyJDBCGetAutogenerateKeyTestOne {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbc", "root", "root");
String sql = "insert into account (name,money) values (?,?)";
// 预编译
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql,Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS);
preparedStatement.setString(1, "lig");
preparedStatement.setDouble(2,200L);
// 获取得到更新的行数
int i = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
System.out.println("更改的行数为:"+i);
// 利用preparedStatement
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.getGeneratedKeys();
// 游标移动到下一行中来
resultSet.next();
int id = resultSet.getInt(1);
resultSet.close();
preparedStatement.close();
connection.close();
System.out.println("获取得到新增的id的值是:"+id);
}
}
首先要把增删改的代码执行掉,然后从结果集中获取得到执行的结果,这样子做不会分两次去执行SQL,就是在一次结果中产生的。
因为这里的执行和查询结果集中的信息是不一致的,所以导致了获取得到的信息也不同。
但是解决是不会执行两次SQL
批量提交
批量SQL针对的是增删改,在批量更新SQL操作的时候建议使用addBatch,这样效率是高些,数据量越大越能体现出来
Statement接口里有两个方法:
| 方法名称 | void addBatch(String sql) | int[] executeBatch() |
|---|---|---|
| 方法解释 | 将给定的 SQL 命令添加到此 Statement 对象的当前命令列表中。 通过调用方法 executeBatch 可以批量执行此列表中的命令。 |
将一批命令提交给数据库来执行,如果全部命令执行成功, 则返回更新计数组成的数组。 |
| 额外说明 | 包含当前一批中每个命令的一个元素的更新计数所组成的数组(数组中的每个元素为:成功处理了命令后,执行命令所影响数据库中行数的更新计数)。数组的元素根据将命令添加到批中的顺序排序。 | |
PreparedStatement接口里:重写了addBatch()的方法,executeBatch()并没有重写。
注意:PreparedStatement的addBatch( )没有参数的。
方法作用:将一组参数添加到此 PreparedStatement 对象的批处理命令中。
| 方法 | addBatch() | executeUpdate() |
|---|---|---|
| 说明 | 把若干sql语句装载到一起,然后一次送到数据库执行,执行需要很短的时间 | 一条一条发往数据库执行的 时间都消耗在数据库连接的传输上面 |
我这有一台超大功率的面粉加工机,前者相当于 把所有农户袋装的麦子收集起来用卡车一次送往加工厂 后者相当于农户排好队用同样的卡车一人一人的往加工厂送麦子 麦子加工5分钟完成,但是每个人到工厂就得3小时,我数据库执行效率再高也没用,时间都耗在传输的路上了!!
问题
我的当前MySQL驱动为8.0.27.
对于批量操作来说,最常见的错误对应的SQL过大,查看MySQL服务端最多能够接收SQL的大小:
mysql> show global variables like 'max_allowed_packet';
+--------------------+---------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+--------------------+---------+
| max_allowed_packet | 4194304 |
+--------------------+---------+
默认是4M。SQL语句长度大于1M,而服务器机器上的MySQL是默认设置,也就是说mysql通讯的数据包大小设置是1M,这就造成sql语句执行失败。
解决方法是:可以把把mysql的配置文件(my.ini)中的max_allowed_packet变大,问题就解决了。
适用环境 mysql 5.7
修改配置文件即可
[mysqld]
pid-file = /var/run/mysqld/mysqld.pid
socket = /var/run/mysqld/mysqld.sock
datadir = /var/lib/mysql
#log-error = /var/log/mysql/error.log
# By default we only accept connections from localhost
#bind-address = 127.0.0.1
# Disabling symbolic-links is recommended to prevent assorted security risks
symbolic-links=0
innodb_log_file_size = 512M
innodb_strict_mode = 0
lower-case-table-names=1
#设置最大sql值
max_allowed_packet = 100M
如果批量提交的SQL大于了这个体积,那么就会出现下面的错误:
Could not execute JDBC batch xxxx
但是一般来说,我们在客户端这边,不会发送大量的SQL过去。
如果有时候我们也不知道SQL有多大,但是我们可以知道对应的SQL条数,所以我们可以通过条数目来进行控制。
public class BatchTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbc?rewriteBatchedStatements=true";
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, "root", "root");
// 预编译SQL,只会编译一次。效率相对来说搞
String sql = "insert into account (name,money) values (?,?)";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
long beginTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
preparedStatement.setString(1,String.valueOf(i+10000));
preparedStatement.setDouble(2,Double.valueOf(i+200));
// 可以理解成存储到缓存区中,达到了临界区批量刷新到MySQL服务端
preparedStatement.addBatch();
}
int[] ints = preparedStatement.executeBatch();
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 不添加:13418ms
// 添加了 rewriteBatchedStatements=true 之后,发现执行时间为163ms,差不多一百个数量级
System.out.println("当前插入耗时:"+(endTime-beginTime));
int length = ints.length;
System.out.println("当前插入的SQL语句有:"+length);
preparedStatement.close();
connection.close();
}
}
为什么rewriteBatchedStatements可以大幅度提供性能?
网上很多文章,都说MySQL驱动并没有实现"真正的"batchUpdate,执行的时候还是一条一条按顺序将SQL发送到MySQL服务器,其实这是错误的。
那么从上面的executeBatch方法来追踪一下
在底层执行时,最主要的区别是方法 ClientPreparedStatement#executeBatchInternal
protected long[] executeBatchInternal() throws SQLException {
synchronized (checkClosed().getConnectionMutex()) {
// ...省略代码
try {
// ...省略代码
// 关键性代码
if (!this.batchHasPlainStatements && this.rewriteBatchedStatements.getValue()) {
if (getParseInfo().canRewriteAsMultiValueInsertAtSqlLevel()) {
return executeBatchedInserts(batchTimeout);
}
if (!this.batchHasPlainStatements && this.query.getBatchedArgs() != null
&& this.query.getBatchedArgs().size() > 3 /* cost of option setting rt-wise */) {
return executePreparedBatchAsMultiStatement(batchTimeout);
}
}
// 不走if的时候走这里
return executeBatchSerially(batchTimeout);
} finally {
this.query.getStatementExecuting().set(false);
clearBatch();
}
}
}
这里不得不来说明两个参数:
| 参数 | batchHasPlainStatements | rewriteBatchedStatements |
|---|---|---|
| javaDoc | Does the batch (if any) contain "plain" statements added by Statement.addBatch(String)? | 无 |
| 说明 | 如果是用statement.addBatch(sql),那么就不能重新编写它以使用多值或多查询 | 重写批量的statemtent |
| 默认值 | false | false |
那么从上面可以看到,Statement.addBatch(SQL)和上面的batchHasPlainStatements区别在哪里呢?
从源码注释中可以看到,如果是batchHasPlainStatements=true,那么就不能够以多值的形式。
那么看一下Statement.addBatch
/**
* Adds the given SQL command to the current list of commands for this
* <code>Statement</code> object. The commands in this list can be
* executed as a batch by calling the method <code>executeBatch</code>.
* <P>
*<strong>Note:</strong>This method cannot be called on a
* <code>PreparedStatement</code> or <code>CallableStatement</code>.
* @param sql typically this is a SQL <code>INSERT</code> or
* <code>UPDATE</code> statement
* @exception SQLException if a database access error occurs,
* this method is called on a closed <code>Statement</code>, the
* driver does not support batch updates, the method is called on a
* <code>PreparedStatement</code> or <code>CallableStatement</code>
* @see #executeBatch
* @see DatabaseMetaData#supportsBatchUpdates
* @since 1.2
*/
void addBatch( String sql ) throws SQLException;
1、只能够用于Statement,不能够用于PreparedStatement或者CallableStatement;
2、只能够适用于INSERT、UPDATE
但是这种情况很明显是不适用的,因为大多数我们的SQL不是静态的,而是动态的!!!所以我们只能够放弃使用这种Statement
rewriteBatchedStatements.getValue()==false
为FALSE的时候,会进入到com.mysql.cj.jdbc.ClientPreparedStatement#executeBatchSerially
在这个方法注释上写着
Executes the current batch of statements by executing them one-by-one.
一行一行的去执行SQL语句
看一下这里的核心代码
for (this.batchCommandIndex = 0; this.batchCommandIndex < nbrCommands; this.batchCommandIndex++) {
Object arg = this.batchedArgs.get(this.batchCommandIndex);
try {
if (arg instanceof String) {
updateCounts[this.batchCommandIndex] = executeUpdateInternal((String) arg, true, this.retrieveGeneratedKeys);
// limit one generated key per OnDuplicateKey statement
getBatchedGeneratedKeys(this.results.getFirstCharOfQuery() == 'I' && containsOnDuplicateKeyInString((String) arg) ? 1 : 0);
} else {
BatchParams paramArg = (BatchParams) arg;
//核心代码,for循环执行每一条SQL
updateCounts[this.batchCommandIndex] = executeUpdateInternal(paramArg.parameterStrings, paramArg.parameterStreams,
paramArg.isStream, paramArg.streamLengths, paramArg.isNull, true);
// limit one generated key per OnDuplicateKey statement
getBatchedGeneratedKeys(containsOnDuplicateKeyUpdateInSQL() ? 1 : 0);
}
} catch (SQLException ex) {
updateCounts[this.batchCommandIndex] = EXECUTE_FAILED;
if (this.continueBatchOnError && !(ex instanceof MySQLTimeoutException) && !(ex instanceof MySQLStatementCancelledException)
&& !hasDeadlockOrTimeoutRolledBackTx(ex)) {
sqlEx = ex;
} else {
long[] newUpdateCounts = new long[this.batchCommandIndex];
System.arraycopy(updateCounts, 0, newUpdateCounts, 0, this.batchCommandIndex);
throw SQLError.createBatchUpdateException(ex, newUpdateCounts, getExceptionInterceptor());
}
}
}
通过代码分析,也确实是一条一条SQL执行,而不是把batch的SQL发送到服务器
rewriteBatchedStatements.getValue()==true
当rewriteBatchedStatements.getValue()==true的时候,可以看到进入到if中来
if (!this.batchHasPlainStatements && this.rewriteBatchedStatements.getValue()) {
// insert
if (getParseInfo().canRewriteAsMultiValueInsertAtSqlLevel()) {
return executeBatchedInserts(batchTimeout);
}
// update||delete 且对应的条数数量要大于3
if (!this.batchHasPlainStatements && this.query.getBatchedArgs() != null
&& this.query.getBatchedArgs().size() > 3 /* cost of option setting rt-wise */) {
return executePreparedBatchAsMultiStatement(batchTimeout);
}
}
return executeBatchSerially(batchTimeout);
如果是insert语句,满成条件情况下,会整合成形如:"insert into xxx_table values (xx),(yy),(zz)..."这样的语句
如果是update||delete语句,满成条件情况下,会整合成形如:"update t set … where id = 1; update t set … where id = 2; update t set … where id = 3 ..."这样的语句
然后分批次发送给MySQL(会有一次发送的package大小限制,所以需要拆分批次)
int maxAllowedPacket = this.connection.getMaxAllowedPacket();
在这里总结一下,如果想要达到MySQL真正batchUpdate效果,需要有以下几个条件:
- 需要在jdbcUrl后添加参数rewriteBatchedStatements=true
- this.batchHasPlainStatements 为false
- 如果是update \ delete 语句,还需要mysql版本>=4.1.0,并且batch的数量>3
因此,如果可能的情况下,请在jdbcUrl后添加参数rewriteBatchedStatements=true,尽可能利用上MySQL给我们提供的便利,提高性能。
在com.mysql.cj.jdbc.ClientPreparedStatement#executePreparedBatchAsMultiStatement方法中有几行代码
for (int i = 0; i < numberArgsToExecute; i++) {
// 如果循环中达到了最大值
if (i != 0 && i % numValuesPerBatch == 0) {
try {
// 那么直接直接刷新到数据库server端
batchedStatement.execute();
} catch (SQLException ex) {
sqlEx = handleExceptionForBatch(batchCounter, numValuesPerBatch, updateCounts, ex);
}
// 否则每次执行一下
updateCountCounter = processMultiCountsAndKeys((StatementImpl) batchedStatement, updateCountCounter, updateCounts);
batchedStatement.clearParameters();
batchedParamIndex = 1;
}
batchedParamIndex = setOneBatchedParameterSet(batchedStatement, batchedParamIndex, this.query.getBatchedArgs().get(batchCounter++));
}
try {
// 再次来进行刷新
batchedStatement.execute();
} catch (SQLException ex) {
sqlEx = handleExceptionForBatch(batchCounter - 1, numValuesPerBatch, updateCounts, ex);
}
当一个数据包的长度不超过maxAllowedPacket,会持续累加,直到超过最大长度时将数据包发送出去。
总结
Statement的选择-PreparedStatement
在日常开发中,普通Statement、预编译PreparedStatement和存储过程CallableStatement
| Statement | PreparedStatement | CallableStatement |
|---|---|---|
| 静态SQL | 支持动态SQL | 不考虑。阿里巴巴明确要求禁用存储过程 |
| 支持批处理 | 支持批处理,只不过是自己实现的 | |
| 不支持获取自增ID | 支持获取自增ID | |
| 存在防止SQL注入问题 | 防止SQL注入 | |
| 不需要预编译SQL | 预编译效率高SQL |
所以选择上面的优点,集中考虑于使用PreparedStatement
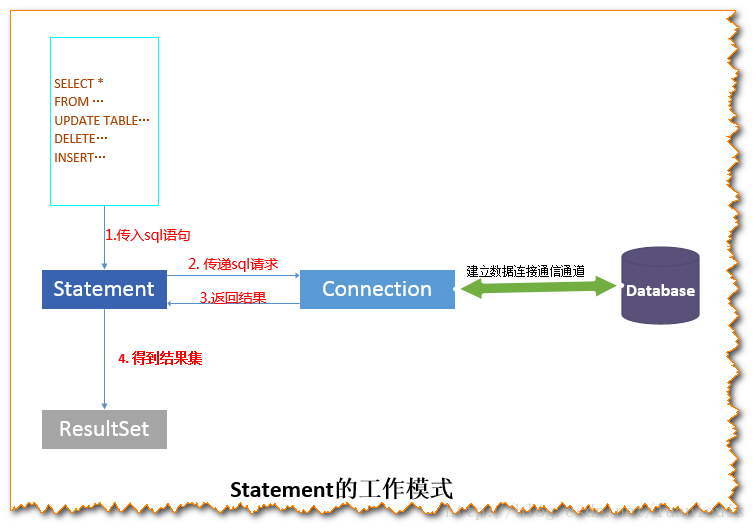
Statement的执行流程
Statement 的功能在于根据传入的sql语句,将传入sql经过整理组合成数据库能够识别的sql语句(对于静态的sql语句,不需要整理组合;而对于预编译sql语句和批量语句,则需要整理),然后传递sql请求,之后会得到返回的结果
批处理
如果是批处理,那么会按照批处理的大小,一次性通过connection刷新到数据库Server端;
也就是说,在Statement中会做一个缓冲,只有达到了,才会刷新过去;没有的话,那么就会继续积累到一定程度上刷新过去。
非批处理
一条一条的将SQL通过connection刷新到数据库服务端,所以效率较慢。
批处理
一定要注意当前驱动版本,我的是8.0.27,在使用增删改的时候,要想实现真正的批处理,那么需要保证在URL后面拼接
jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbc?rewriteBatchedStatements=true
1、preparedStatement.addBatch()
2、preparedStatement.executeBatch()
解释可以直接参考源码注释中的说明,代码在上面的测试类中。
但是看到网上说的有一个误区,我在这里需要指正一下,部分代码如下所示:
for (int i = 1; i <=count ; i++) {
statement.setInt(1,list.get(i).getId());
statement.setString(2,list.get(i).getUsername());
statement.setString(3,list.get(i).getGrep());
//批量操作打包
statement.addBatch();
if(i%100==0){
statement.executeQuery();
connection.commit();
//提交后,Batch清空。
statement.clearBatch();
}
那么看一下com.mysql.cj.jdbc.ClientPreparedStatement#executePreparedBatchAsMultiStatement中的for循环中的代码。
发现JDBC会自动的帮助帮我们在筛选,所以不需要来做上面的操作。
for (int i = 1; i <=count ; i++) {
statement.setInt(1,list.get(i).getId());
statement.setString(2,list.get(i).getUsername());
statement.setString(3,list.get(i).getGrep());
//批量操作打包
statement.addBatch();
}
//
statement.executeQuery();
这样子直接操作就可以了!!!