linux-2.6.18源码分析笔记---中断
![]() 一、中断初始化
一、中断初始化
中断的一些硬件机制不做过多的描述,只介绍一些和linux实现比较贴近的机制,便于理解代码。
1.1 关于intel和linux几种门的简介
intel提供了4种门:系统门,中断门,陷阱门,调用门。
调用门:不同特权级之间实现受控的程序控制转移,它是放在GDT或LDT之中。使用调用门需要为CALL或JMP指令的操作数提供一个远指针,该指针中的段选择符用于指定调用门,指向的是GDT或LDT中的一个段,在低特权级代码切换到高特权级代码是会发生代码段的转移。(linux没有使用这种门,感觉这是intel用来给操作系统实现系统调用的机制,但是linux没有使用,linux使用陷阱门来实现系统调用,原因是软件实现更加灵活,有优化空间,而且可以用来检查一些硬件无法检查的段寄存器数据的正确性)
任务门:用来处理中断和异常。可以放在GDT、LDT、IDT中,任务门描述符中TSS选择符字段指向GDT的一个TSS段描述符,在跳转时必须跳转到TSS选择符指向的段,(linux在GDT中只定义了一个TSS,即每个CPU一个TSS),这也是linux中唯一使用调用门来处理的异常,其他异常都使用陷阱门来处理。
中断门:处理中断。放在IDT中,清空IF标志,屏蔽将到来的中断。linux在intel的基础上将其中断门分为如下两类:
- 中断门:用户态进程不能访问,所有的中断处理程序都通过中断门激活,限制在内核态
- 系统中断门:能被用户态程序访问,与向量3相关的异常处理程序由系统中断门来激活,在用户态可以使用int3指令,该指令表示断点,用来调试。
陷阱门:与中断门类似,只是不修改IF标志位。
- 陷阱门:用户态进程不能访问,大部分的linux异常都由陷阱门激活。
- 系统门:能被用户态程序访问,用户态程序可以发布into、bound、int 0x80指令,其中int 0x80是系统中断
门能否被用户态访问是有一套优先级判断机制,这里不做描述了。
1.2 几种异常的初始化
arch\i386\kernel\trap.s中的trap_init函数

void __init trap_init(void) { #ifdef CONFIG_EISA void __iomem *p = ioremap(0x0FFFD9, 4); if (readl(p) == 'E'+('I'<<8)+('S'<<16)+('A'<<24)) { EISA_bus = 1; } iounmap(p); #endif #ifdef CONFIG_X86_LOCAL_APIC init_apic_mappings(); #endif set_trap_gate(0,÷_error); set_intr_gate(1,&debug); set_intr_gate(2,&nmi); set_system_intr_gate(3, &int3); /* int3/4 can be called from all */ set_system_gate(4,&overflow); set_trap_gate(5,&bounds); set_trap_gate(6,&invalid_op); set_trap_gate(7,&device_not_available); set_task_gate(8,GDT_ENTRY_DOUBLEFAULT_TSS); set_trap_gate(9,&coprocessor_segment_overrun); set_trap_gate(10,&invalid_TSS); set_trap_gate(11,&segment_not_present); set_trap_gate(12,&stack_segment); set_trap_gate(13,&general_protection); set_intr_gate(14,&page_fault); set_trap_gate(15,&spurious_interrupt_bug); set_trap_gate(16,&coprocessor_error); set_trap_gate(17,&alignment_check); #ifdef CONFIG_X86_MCE set_trap_gate(18,&machine_check); #endif set_trap_gate(19,&simd_coprocessor_error); if (cpu_has_fxsr) { /* * Verify that the FXSAVE/FXRSTOR data will be 16-byte aligned. * Generates a compile-time "error: zero width for bit-field" if * the alignment is wrong. */ struct fxsrAlignAssert { int _:!(offsetof(struct task_struct, thread.i387.fxsave) & 15); }; printk(KERN_INFO "Enabling fast FPU save and restore... "); set_in_cr4(X86_CR4_OSFXSR); printk("done.\n"); } if (cpu_has_xmm) { printk(KERN_INFO "Enabling unmasked SIMD FPU exception " "support... "); set_in_cr4(X86_CR4_OSXMMEXCPT); printk("done.\n"); } set_system_gate(SYSCALL_VECTOR,&system_call); /* * Should be a barrier for any external CPU state. */ cpu_init(); trap_init_hook(); }
根据前面对各种门的描述,可以知道如下函数的含义(门的含义参考linux划分而不是intel划分):
set_trap_gate(n,addr):在IDT的n项插入一个陷阱门
set_intr_gate(n,addr):在IDT的n项插入一个中断门
set_system_intr_gate(n,addr):在IDT的n项插入一个系统中断门
set_system_gate(n,addr):在IDT的n项插入一个系统门
set_task_gate(n,addr):在IDT的n项插入一个任务
可以看到先注册了19个中断向量的处理函数,函数具体实现在arch\i386\kernel\entry.S
SYSCALL_VECTOR是定义在include\asm-i386\mach-default\irq_vector.h中的宏,为0x80,可知注册的系统调用处理函数为system_call,在entry.S中。
1.3 中断和异常的硬件处理
假设所有的初始化已经结束,在发出一个中断或是异常时,硬件会做一些工作,然后才会跳转到IDT中的处理函数,为了理解处理函数的最开始一部分,我们有必要了解硬件做了什么。
下面的步骤假设门是中断门或是陷阱门,并且只关注特权级切换的情况,了解在linux系统中的用户态栈切换到内核栈的过程(linux只使用了两种特权级,0和3,3表示用户态,0表示内核态)
a、根据tr寄存器找到TSS,然后根据TSS中的ESP0字段找到内核栈的位置。
b、依次向内核栈中保存ss、esp、eflags、cs、eip这几个寄存器的值
c、如果产生了一个硬件出错码,则将它保存在栈中
d、然后根据中断向量找到中断或是异常处理程序,执行异常处理程序。
1.4 异常处理程序的一般流程
可以观察entry.S中的几个异常处理程序,它们都有一个比较通用的流程
先是调用了RING0_INT_FRAME或是RING0_EC_FRAME宏,该宏定义在entry.S头部,看看实现

#define RING0_INT_FRAME \ CFI_STARTPROC simple;\ CFI_DEF_CFA esp, 3*4;\ /*CFI_OFFSET cs, -2*4;*/\ CFI_OFFSET eip, -3*4
而以CFI开头的宏定义在include\asm-i386\dwarf2.h中,发现其实这段宏好像也并不涉及到实际的汇编代码

#ifdef CONFIG_UNWIND_INFO #define CFI_STARTPROC .cfi_startproc #define CFI_ENDPROC .cfi_endproc #define CFI_DEF_CFA .cfi_def_cfa #define CFI_DEF_CFA_REGISTER .cfi_def_cfa_register #define CFI_DEF_CFA_OFFSET .cfi_def_cfa_offset #define CFI_ADJUST_CFA_OFFSET .cfi_adjust_cfa_offset #define CFI_OFFSET .cfi_offset #define CFI_REL_OFFSET .cfi_rel_offset #define CFI_REGISTER .cfi_register #define CFI_RESTORE .cfi_restore #define CFI_REMEMBER_STATE .cfi_remember_state #define CFI_RESTORE_STATE .cfi_restore_state #else /* Due to the structure of pre-exisiting code, don't use assembler line comment character # to ignore the arguments. Instead, use a dummy macro. */ .macro ignore a=0, b=0, c=0, d=0 .endm #define CFI_STARTPROC ignore #define CFI_ENDPROC ignore #define CFI_DEF_CFA ignore #define CFI_DEF_CFA_REGISTER ignore #define CFI_DEF_CFA_OFFSET ignore #define CFI_ADJUST_CFA_OFFSET ignore #define CFI_OFFSET ignore #define CFI_REL_OFFSET ignore #define CFI_REGISTER ignore #define CFI_RESTORE ignore #define CFI_REMEMBER_STATE ignore #define CFI_RESTORE_STATE ignore #endif #endif
查看了《深入理解linux内核》、《linux内核源代码情景分析》,他们在讲述这段代码时都没有涉及到相关宏的含义,而且逻辑也是完整的,这里就以这种宏没有实质代码来分析,不知道他是处于什么考虑才设计的这段代码。
参考《深入理解linux内核》分析异常处理的通用流程,假设handler_name代表一个通用的异常处理程序的名字:

ENTRY(handler_name) pushl $0 /*只有有些异常处理程序有*/ pushl $do_handler_name jmp error_code
1、如果控制单元没有把一个硬件出错码插入到栈中,相应的汇编程序语言会包含一条push $0指令。可以查看entry.S中的几种异常处理程序,如果没有push $0指令,则代表该异常发生时,硬件向栈中push了一个出错码。
2、push一个c语言函数,代表异常处理程序,以do_开头,后面加异常处理的名称
3、跳转到一段称为error_code的代码

error_code: pushl %ds CFI_ADJUST_CFA_OFFSET 4 /*CFI_REL_OFFSET ds, 0*/ pushl %eax CFI_ADJUST_CFA_OFFSET 4 CFI_REL_OFFSET eax, 0 xorl %eax, %eax pushl %ebp CFI_ADJUST_CFA_OFFSET 4 CFI_REL_OFFSET ebp, 0 pushl %edi CFI_ADJUST_CFA_OFFSET 4 CFI_REL_OFFSET edi, 0 pushl %esi CFI_ADJUST_CFA_OFFSET 4 CFI_REL_OFFSET esi, 0 pushl %edx CFI_ADJUST_CFA_OFFSET 4 CFI_REL_OFFSET edx, 0 decl %eax # eax = -1 pushl %ecx CFI_ADJUST_CFA_OFFSET 4 CFI_REL_OFFSET ecx, 0 pushl %ebx CFI_ADJUST_CFA_OFFSET 4 CFI_REL_OFFSET ebx, 0 cld pushl %es CFI_ADJUST_CFA_OFFSET 4 /*CFI_REL_OFFSET es, 0*/ UNWIND_ESPFIX_STACK popl %ecx CFI_ADJUST_CFA_OFFSET -4 /*CFI_REGISTER es, ecx*/ movl ES(%esp), %edi # get the function address movl ORIG_EAX(%esp), %edx # get the error code movl %eax, ORIG_EAX(%esp) movl %ecx, ES(%esp) /*CFI_REL_OFFSET es, ES*/ movl $(__USER_DS), %ecx movl %ecx, %ds movl %ecx, %es movl %esp,%eax # pt_regs pointer call *%edi jmp ret_from_exception CFI_ENDPROC
error_code执行如下流程:
a、将ds、eax、edi、esi、edx、ecx、ebx保存到栈中,执行cld,清除方向标志。
b、将es寄存器的值保存到ecx,将esp+0x20的值赋给edi(在栈中的寄存器还有ds-ebx,共28个字节,由于esp指向第一个空位,所以esp+0x20指向ds之前的4个字节,是异常处理通用流程的第二步push到栈中的c语言函数地址),将esp+0x24赋值给edx(esp+0x24为出错码),在原出错码的地址填上-1(用来隔开0x80异常)。c函数地址处填入es的值。将栈指针赋值给eax,然后调用异常处理通用流程的第二步push到栈中的c语言函数地址,该函数是通过寄存器eax、edx来传递参数而不是通过栈。
c、等到c语言的中断异常处理函数执行完之后就跳转到ret_from_exception,就像它的函数名字一样,从异常中返回
二、中断处理
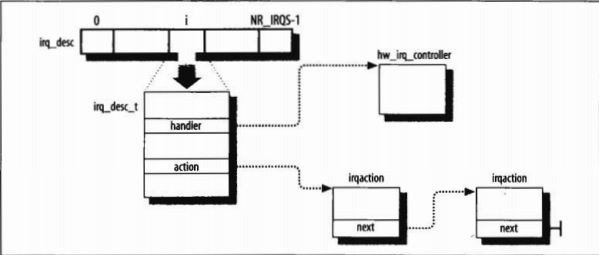
在include\linux\irq.h中,定义了struct irq_desc,中断描述符,status的状态也在该文件中。

/** * struct irq_desc - interrupt descriptor * * @handle_irq: highlevel irq-events handler [if NULL, __do_IRQ()] * @chip: low level interrupt hardware access * @handler_data: per-IRQ data for the irq_chip methods * @chip_data: platform-specific per-chip private data for the chip * methods, to allow shared chip implementations * @action: the irq action chain * @status: status information * @depth: disable-depth, for nested irq_disable() calls * @wake_depth: enable depth, for multiple set_irq_wake() callers * @irq_count: stats field to detect stalled irqs * @irqs_unhandled: stats field for spurious unhandled interrupts * @lock: locking for SMP * @affinity: IRQ affinity on SMP * @cpu: cpu index useful for balancing * @pending_mask: pending rebalanced interrupts * @move_irq: need to re-target IRQ destination * @dir: /proc/irq/ procfs entry * @affinity_entry: /proc/irq/smp_affinity procfs entry on SMP * * Pad this out to 32 bytes for cache and indexing reasons. */ struct irq_desc { void fastcall (*handle_irq)(unsigned int irq, struct irq_desc *desc, struct pt_regs *regs); struct irq_chip *chip; void *handler_data; void *chip_data; struct irqaction *action; /* IRQ action list */ unsigned int status; /* IRQ status */ unsigned int depth; /* nested irq disables */ unsigned int wake_depth; /* nested wake enables */ unsigned int irq_count; /* For detecting broken IRQs */ unsigned int irqs_unhandled; spinlock_t lock; #ifdef CONFIG_SMP cpumask_t affinity; unsigned int cpu; #endif #if defined(CONFIG_GENERIC_PENDING_IRQ) || defined(CONFIG_IRQBALANCE) cpumask_t pending_mask; unsigned int move_irq; /* need to re-target IRQ dest */ #endif #ifdef CONFIG_PROC_FS struct proc_dir_entry *dir; #endif } ____cacheline_aligned; extern struct irq_desc irq_desc[NR_IRQS];
注意上部分代码最后还创建了一个irq_desc数组,表示所有中断向量的处理方式。其中NR_IRQS定义在include\asm-i386\mach-default\irq_vectors_limits.h中,为224。
2.1 中断向量初始化
在arch\i386\kernel\i8259.c中定义了init_IRQ函数用来设置大量用于外设的通用中断门

void __init init_IRQ(void) { int i; /* all the set up before the call gates are initialised */ pre_intr_init_hook(); /* * Cover the whole vector space, no vector can escape * us. (some of these will be overridden and become * 'special' SMP interrupts) */ for (i = 0; i < (NR_VECTORS - FIRST_EXTERNAL_VECTOR); i++) { int vector = FIRST_EXTERNAL_VECTOR + i; if (i >= NR_IRQS) break; if (vector != SYSCALL_VECTOR) set_intr_gate(vector, interrupt[i]); } /* setup after call gates are initialised (usually add in * the architecture specific gates) */ intr_init_hook(); /* * Set the clock to HZ Hz, we already have a valid * vector now: */ setup_pit_timer(); /* * External FPU? Set up irq13 if so, for * original braindamaged IBM FERR coupling. */ if (boot_cpu_data.hard_math && !cpu_has_fpu) setup_irq(FPU_IRQ, &fpu_irq); irq_ctx_init(smp_processor_id()); }
在include\asm-i386\mach-default\irq_vectors.h中定义了一些宏,NR_VECTORS表示中断向量的最大数,i386有256个,FIRST_EXTERNAL_VECTOR表示第一个用于外部中断的中断号,前19个中断向量用于异常,20到31intel保留,所以第一个外部中断号为32.
interrupt数组定义在arch\i386\kernel\entry.S中,由几段汇编程序创建
2.2 IRQ共享和动态分配
IRQ共享表示一个IRQ线由多个设备共享,当一个IRQ线出现中断时,每个中断服务例程(ISA)都被执行。
IRQ动态分配指一条IRQ线只有到最后时刻才与一个设备驱动程序相关联。
前面描述的irq_desc数组代表了所有中断向量,既然一个IRQ线能被多个设备同时使用,那该向量应该以某种方式记录共享该线的设备,irq_desc结构中有action字段,该字段为irqaction结构,定义在include\linux\interrupt.h中

struct irqaction { irqreturn_t (*handler)(int, void *, struct pt_regs *); unsigned long flags; cpumask_t mask; const char *name; void *dev_id; struct irqaction *next; int irq; struct proc_dir_entry *dir; };
该结构中还定义了一个next指针,指向下一个irqaction结构。
所以最终的结构是这样:


 一、中断初始化
一、中断初始化

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号