java基础教程-线程(六)
六、线程
6.1单线程(cpu在固定的时间点上一定是在单线程工作)

Java中的线程是通过java.lang.Thread类实现的,VM启动时会有一个由主方法(public static void main(){})所决定的线程,可以通过创建Thread的实例来创建新的线程。每个线程都是通过某个特定的Thread对象对应的run()来完成其操作,run()中写什么语句,就执行什么语句,调用start()方法,(start是启动一个与main并行运行的线程,而run是调用函数)。

方法1 建立线程比较好
Thread实际上就实现了Runnable接口
两种方法实现多线程。
public class TestThread1 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Runner1 r = new Runner1();
r.start();
//r.run();
//Thread t = new Thread(r);
//t.start();
for(int i=0; i<100; i++) {
System.out.println("Main Thread:------" + i);
}
}
}
//class Runner1 implements Runnable {
class Runner1 extends Thread {
public void run() {
for(int i=0; i<100; i++) {
System.out.println("Runner1 :" + i);
}
}
}

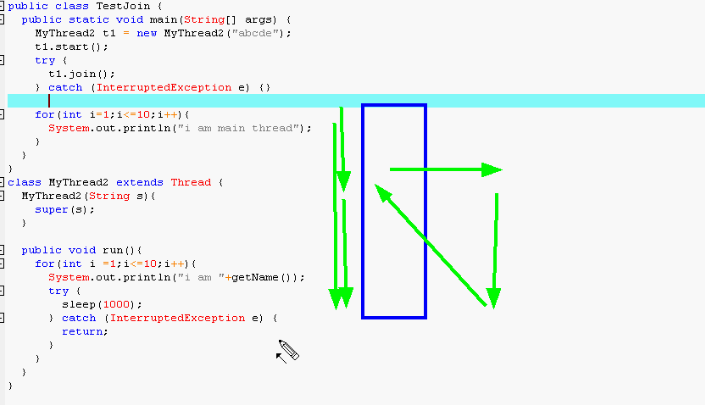
t1.join的作用相当于调用,合并后,等t1执行完以后,主程序才继续执行。

t1.setPriority(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY +3)// Thread.NORM_PRIORITY指正常的优先级,设置以后,t1的优先级提升3,执行t1很久以后才会执行t2
线程同步(很重要)
public class TestSync implements Runnable {
Timer timer = new Timer();
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestSync test = new TestSync();
Thread t1 = new Thread(test);
Thread t2 = new Thread(test);
t1.setName("t1");
t2.setName("t2");
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
public void run(){
timer.add(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
class Timer{
private static int num = 0;
public synchronized void add(String name){ //简便方法这么写,执行该方法过程中,当前对象被锁定
synchronized (this) {//锁定当前执行对象,执行该对象过程中,不会被其他线程所打断
num ++;
try {Thread.sleep(1);}
catch (InterruptedException e) {}
System.out.println(name+", 你是第"+num+"个使用timer的线程");
}
}
}

6.2锁定(当两个都锁定时,只有一个执行完,另一个才能执行,因为另一个锁不住了,只能等着那把锁)

wait()必须与notify()在一块用,

6.3wait和sleep区别:
wait是object类的方法;sleep是Thread的方法:
sleep执行过程中,锁定后不准其他人访问,而wait()时,别人可以访问对象
6.4线程和进程:
线程,一个程序里不同的执行路径;进程,一个class文件,静态概念



