基于tensorflow的花卉识别
一、思路
二、进程
三、参考
1.denny的学习专栏
这位大佬的博客里有关于tensorflow的很多内容,并且有花卉识别项目的源代码和介绍,很有参考价值。为了内容丢失,已装在到博客里。
2.Plain and Simple Estimators
这个小视频https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/30722498简单介绍了该项目,并简单讲解了代码,github已follow.
四、成功案列
(1)
前言
本文为一个利用卷积神经网络实现花卉分类的项目,因此不会过多介绍卷积神经网络的基本知识。此项目建立在了解卷积神经网络进行图像分类的原理上进行的。
项目简介
本项目为一个图像识别项目,基于tensorflow,利用CNN网络实现识别四种花的种类。
使用tensorflow进行一个完整的图像识别。项目包括对数据集的处理,从硬盘读取数据,CNN网络的定义,训练过程以及利用实际测试数据对训练好的模型结果进行测试功能。
准备训练数据。
训练数据存放路径为: ‘D:/ML/flower/input_data’
训练模型存储路径为:'D:/ML/flower/save/‘
测试样本路径及文件名为:'D:/ML/flower/flower_photos/roses/**.jpg‘
测试用图片文件从训练数据中任意拷贝一张即可。
训练数据如图
以roses种类的训练数据为例,文件夹内部均为该种类花的图像文件

模块组成
示例代码主要由四个模块组成:
input_data.py——图像特征提取模块,模块生成四种花的品类图片路径及对应标签的List
model.py——模型模块,构建完整的CNN模型
train.py——训练模块,训练模型,并保存训练模型结果
test.py——测试模块,测试模型对图片识别的准确度
项目模块执行顺序
- 运行train.py开始训练。
- 训练完成后- 运行test.py,查看实际测试结果
input_data.py——图像特征提取模块,模块生成四种花的品类图片路径及对应标签的List
import os import math import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # -----------------生成图片路径和标签的List------------------------------------ train_dir = 'D:/ML/flower/input_data' roses = [] label_roses = [] tulips = [] label_tulips = [] dandelion = [] label_dandelion = [] sunflowers = [] label_sunflowers = []
定义函数get_files,获取图片列表及标签列表
# step1:获取所有的图片路径名,存放到 # 对应的列表中,同时贴上标签,存放到label列表中。 def get_files(file_dir, ratio): for file in os.listdir(file_dir + '/roses'): roses.append(file_dir + '/roses' + '/' + file) label_roses.append(0) for file in os.listdir(file_dir + '/tulips'): tulips.append(file_dir + '/tulips' + '/' + file) label_tulips.append(1) for file in os.listdir(file_dir + '/dandelion'): dandelion.append(file_dir + '/dandelion' + '/' + file) label_dandelion.append(2) for file in os.listdir(file_dir + '/sunflowers'): sunflowers.append(file_dir + '/sunflowers' + '/' + file) label_sunflowers.append(3) # step2:对生成的图片路径和标签List做打乱处理 image_list = np.hstack((roses, tulips, dandelion, sunflowers)) label_list = np.hstack((label_roses, label_tulips, label_dandelion, label_sunflowers)) # 利用shuffle打乱顺序 temp = np.array([image_list, label_list]) temp = temp.transpose() np.random.shuffle(temp) # 将所有的img和lab转换成list all_image_list = list(temp[:, 0]) all_label_list = list(temp[:, 1]) # 将所得List分为两部分,一部分用来训练tra,一部分用来测试val # ratio是测试集的比例 n_sample = len(all_label_list) n_val = int(math.ceil(n_sample * ratio)) # 测试样本数 n_train = n_sample - n_val # 训练样本数 tra_images = all_image_list[0:n_train] tra_labels = all_label_list[0:n_train] tra_labels = [int(float(i)) for i in tra_labels] val_images = all_image_list[n_train:-1] val_labels = all_label_list[n_train:-1] val_labels = [int(float(i)) for i in val_labels] return tra_images, tra_labels, val_images, val_labels
定义函数get_batch,生成训练批次数据
# --------------------生成Batch---------------------------------------------- # step1:将上面生成的List传入get_batch() ,转换类型,产生一个输入队列queue,因为img和lab # 是分开的,所以使用tf.train.slice_input_producer(),然后用tf.read_file()从队列中读取图像 # image_W, image_H, :设置好固定的图像高度和宽度 # 设置batch_size:每个batch要放多少张图片 # capacity:一个队列最大多少 定义函数get_batch,生成训练批次数据 def get_batch(image, label, image_W, image_H, batch_size, capacity): # 转换类型 image = tf.cast(image, tf.string) label = tf.cast(label, tf.int32) # make an input queue input_queue = tf.train.slice_input_producer([image, label]) label = input_queue[1] image_contents = tf.read_file(input_queue[0]) # read img from a queue # step2:将图像解码,不同类型的图像不能混在一起,要么只用jpeg,要么只用png等。 image = tf.image.decode_jpeg(image_contents, channels=3) # step3:数据预处理,对图像进行旋转、缩放、裁剪、归一化等操作,让计算出的模型更健壮。 image = tf.image.resize_image_with_crop_or_pad(image, image_W, image_H) image = tf.image.per_image_standardization(image) # step4:生成batch # image_batch: 4D tensor [batch_size, width, height, 3],dtype=tf.float32 # label_batch: 1D tensor [batch_size], dtype=tf.int32 image_batch, label_batch = tf.train.batch([image, label], batch_size=batch_size, num_threads=32, capacity=capacity) # 重新排列label,行数为[batch_size] label_batch = tf.reshape(label_batch, [batch_size]) image_batch = tf.cast(image_batch, tf.float32) return image_batch, label_batch
model.py——CN模型构建
import tensorflow as tf #定义函数infence,定义CNN网络结构 #卷积神经网络,卷积加池化*2,全连接*2,softmax分类 #卷积层1 def inference(images, batch_size, n_classes): with tf.variable_scope('conv1') as scope: weights = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(shape=[3,3,3,64],stddev=1.0,dtype=tf.float32), name = 'weights',dtype=tf.float32) biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(value=0.1, dtype=tf.float32, shape=[64]), name='biases', dtype=tf.float32) conv = tf.nn.conv2d(images, weights, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME') pre_activation = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases) conv1 = tf.nn.relu(pre_activation, name=scope.name) # 池化层1 # 3x3最大池化,步长strides为2,池化后执行lrn()操作,局部响应归一化,对训练有利。 with tf.variable_scope('pooling1_lrn') as scope: pool1 = tf.nn.max_pool(conv1, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME', name='pooling1') norm1 = tf.nn.lrn(pool1, depth_radius=4, bias=1.0, alpha=0.001 / 9.0, beta=0.75, name='norm1') # 卷积层2 # 16个3x3的卷积核(16通道),padding=’SAME’,表示padding后卷积的图与原图尺寸一致,激活函数relu() with tf.variable_scope('conv2') as scope: weights = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(shape=[3, 3, 64, 16], stddev=0.1, dtype=tf.float32), name='weights', dtype=tf.float32) biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(value=0.1, dtype=tf.float32, shape=[16]), name='biases', dtype=tf.float32) conv = tf.nn.conv2d(norm1, weights, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME') pre_activation = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases) conv2 = tf.nn.relu(pre_activation, name='conv2') # 池化层2 # 3x3最大池化,步长strides为2,池化后执行lrn()操作, # pool2 and norm2 with tf.variable_scope('pooling2_lrn') as scope: norm2 = tf.nn.lrn(conv2, depth_radius=4, bias=1.0, alpha=0.001 / 9.0, beta=0.75, name='norm2') pool2 = tf.nn.max_pool(norm2, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 1], strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME', name='pooling2') # 全连接层3 # 128个神经元,将之前pool层的输出reshape成一行,激活函数relu() with tf.variable_scope('local3') as scope: reshape = tf.reshape(pool2, shape=[batch_size, -1]) dim = reshape.get_shape()[1].value weights = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(shape=[dim, 128], stddev=0.005, dtype=tf.float32), name='weights', dtype=tf.float32) biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(value=0.1, dtype=tf.float32, shape=[128]), name='biases', dtype=tf.float32) local3 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(reshape, weights) + biases, name=scope.name) # 全连接层4 # 128个神经元,激活函数relu() with tf.variable_scope('local4') as scope: weights = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(shape=[128, 128], stddev=0.005, dtype=tf.float32), name='weights', dtype=tf.float32) biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(value=0.1, dtype=tf.float32, shape=[128]), name='biases', dtype=tf.float32) local4 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(local3, weights) + biases, name='local4') # dropout层 # with tf.variable_scope('dropout') as scope: # drop_out = tf.nn.dropout(local4, 0.8) # Softmax回归层 # 将前面的FC层输出,做一个线性回归,计算出每一类的得分 with tf.variable_scope('softmax_linear') as scope: weights = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(shape=[128, n_classes], stddev=0.005, dtype=tf.float32), name='softmax_linear', dtype=tf.float32) biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(value=0.1, dtype=tf.float32, shape=[n_classes]), name='biases', dtype=tf.float32) softmax_linear = tf.add(tf.matmul(local4, weights), biases, name='softmax_linear') return softmax_linear # ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- # loss计算 # 传入参数:logits,网络计算输出值。labels,真实值,在这里是0或者1 # 返回参数:loss,损失值 def losses(logits, labels): with tf.variable_scope('loss') as scope: cross_entropy = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits, labels=labels, name='xentropy_per_example') loss = tf.reduce_mean(cross_entropy, name='loss') tf.summary.scalar(scope.name + '/loss', loss) return loss # -------------------------------------------------------------------------- # loss损失值优化 # 输入参数:loss。learning_rate,学习速率。 # 返回参数:train_op,训练op,这个参数要输入sess.run中让模型去训练。 def trainning(loss, learning_rate): with tf.name_scope('optimizer'): optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=learning_rate) global_step = tf.Variable(0, name='global_step', trainable=False) train_op = optimizer.minimize(loss, global_step=global_step) return train_op # ----------------------------------------------------------------------- # 评价/准确率计算 # 输入参数:logits,网络计算值。labels,标签,也就是真实值,在这里是0或者1。 # 返回参数:accuracy,当前step的平均准确率,也就是在这些batch中多少张图片被正确分类了。 def evaluation(logits, labels): with tf.variable_scope('accuracy') as scope: correct = tf.nn.in_top_k(logits, labels, 1) correct = tf.cast(correct, tf.float16) accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(correct) tf.summary.scalar(scope.name + '/accuracy', accuracy) return accuracy
train.py——利用D:/ML/flower/input_data/路径下的训练数据,对CNN模型进行训练
import input_data import model # 变量声明 N_CLASSES = 4 # 四种花类型 IMG_W = 64 # resize图像,太大的话训练时间久 IMG_H = 64 BATCH_SIZE = 20 CAPACITY = 200 MAX_STEP = 2000 # 一般大于10K learning_rate = 0.0001 # 一般小于0.0001 # 获取批次batch train_dir = 'F:/input_data' # 训练样本的读入路径 logs_train_dir = 'F:/save' # logs存储路径 # train, train_label = input_data.get_files(train_dir) train, train_label, val, val_label = input_data.get_files(train_dir, 0.3) # 训练数据及标签 train_batch, train_label_batch = input_data.get_batch(train, train_label, IMG_W, IMG_H, BATCH_SIZE, CAPACITY) # 测试数据及标签 val_batch, val_label_batch = input_data.get_batch(val, val_label, IMG_W, IMG_H, BATCH_SIZE, CAPACITY) # 训练操作定义 train_logits = model.inference(train_batch, BATCH_SIZE, N_CLASSES) train_loss = model.losses(train_logits, train_label_batch) train_op = model.trainning(train_loss, learning_rate) train_acc = model.evaluation(train_logits, train_label_batch) # 测试操作定义 test_logits = model.inference(val_batch, BATCH_SIZE, N_CLASSES) test_loss = model.losses(test_logits, val_label_batch) test_acc = model.evaluation(test_logits, val_label_batch) # 这个是log汇总记录 summary_op = tf.summary.merge_all() # 产生一个会话 sess = tf.Session() # 产生一个writer来写log文件 train_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(logs_train_dir, sess.graph) # val_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(logs_test_dir, sess.graph) # 产生一个saver来存储训练好的模型 saver = tf.train.Saver() # 所有节点初始化 sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) # 队列监控 coord = tf.train.Coordinator() threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess, coord=coord) # 进行batch的训练 try: # 执行MAX_STEP步的训练,一步一个batch for step in np.arange(MAX_STEP): if coord.should_stop(): break _, tra_loss, tra_acc = sess.run([train_op, train_loss, train_acc]) # 每隔50步打印一次当前的loss以及acc,同时记录log,写入writer if step % 10 == 0: print('Step %d, train loss = %.2f, train accuracy = %.2f%%' % (step, tra_loss, tra_acc * 100.0)) summary_str = sess.run(summary_op) train_writer.add_summary(summary_str, step) # 每隔100步,保存一次训练好的模型 if (step + 1) == MAX_STEP: checkpoint_path = os.path.join(logs_train_dir, 'model.ckpt') saver.save(sess, checkpoint_path, global_step=step) except tf.errors.OutOfRangeError: print('Done training -- epoch limit reached') finally: coord.request_stop()
test.py——利用D:/ML/flower/flower_photos/roses路径下的测试数据,查看识别效果
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import model from input_data import get_files # 获取一张图片 def get_one_image(train): # 输入参数:train,训练图片的路径 # 返回参数:image,从训练图片中随机抽取一张图片 n = len(train) ind = np.random.randint(0, n) img_dir = train[ind] # 随机选择测试的图片 img = Image.open(img_dir) plt.imshow(img) plt.show() image = np.array(img) return image # 测试图片 def evaluate_one_image(image_array): with tf.Graph().as_default(): BATCH_SIZE = 1 N_CLASSES = 4 image = tf.cast(image_array, tf.float32) image = tf.image.per_image_standardization(image) image = tf.reshape(image, [1, 64, 64, 3]) logit = model.inference(image, BATCH_SIZE, N_CLASSES) logit = tf.nn.softmax(logit) x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[64, 64, 3]) # you need to change the directories to yours. logs_train_dir = 'F:/save/' saver = tf.train.Saver() with tf.Session() as sess: print("Reading checkpoints...") ckpt = tf.train.get_checkpoint_state(logs_train_dir) if ckpt and ckpt.model_checkpoint_path: global_step = ckpt.model_checkpoint_path.split('/')[-1].split('-')[-1] saver.restore(sess, ckpt.model_checkpoint_path) print('Loading success, global_step is %s' % global_step) else: print('No checkpoint file found') prediction = sess.run(logit, feed_dict={x: image_array}) max_index = np.argmax(prediction) if max_index == 0: result = ('这是玫瑰花的可能性为: %.6f' % prediction[:, 0]) elif max_index == 1: result = ('这是郁金香的可能性为: %.6f' % prediction[:, 1]) elif max_index == 2: result = ('这是蒲公英的可能性为: %.6f' % prediction[:, 2]) else: result = ('这是这是向日葵的可能性为: %.6f' % prediction[:, 3]) return result # ------------------------------------------------------------------------ if __name__ == '__main__': img = Image.open('F:/input_data/dandelion/1451samples2.jpg') plt.imshow(img) plt.show() imag = img.resize([64, 64]) image = np.array(imag) print(evaluate_one_image(image))
项目执行结果:
1.执行train模块,结果如下:

同时,训练结束后,在电脑指定的训练模型存储路径可看到保存的训练好的模型数据。

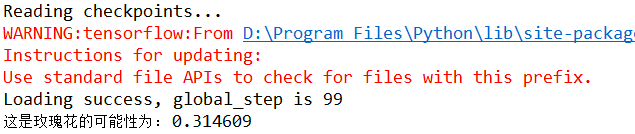
2.执行test模块,结果如下:
显示一张测试用的图片

关闭显示的测试图片后,console查看测试结果如下:
至此我们对整个项目流程做一个总结:
图片预处理模块:对获得的花卉图片训练数据,进行预处理,构造训练用数据结构
训练模块:利用Tensorflow实现CNN(神经网络算法)模型,经过两层卷积-池化处理,并使用梯度下降算法作为优化器、Softmax算法作为分类器、平方损失函数(最小二乘法, Ordinary Least Squares)作为优化器,构建训练模型,利用训练数据对模型进行训练,最终得到训练后的模型数据,并以文件形式存储至本机。
分类准确度验证模块:利用Tensorflow的reduce_mean方法作为评估模型,对构建的花卉分类模型分类准确性进行验证。
模型测试模块:使用测试集数据,对构建并训练后的分类模型进行测试,验证实际数据的测试准确度。
具体代码以及附件可在我的个人GitHub上下载
我的githubworkspace
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/CrimsonK/article/details/100190807
二、https://www.cnblogs.com/lijitao/protected/articles/12173520.html

