(AE 2018 Forecast)Impact of chemical lateral boundary conditions in a regional air quality forecast model on surface ozone predictions during stratospheric intrusions
可参考的表达方式:
However, there is an additional benefit from the correct characterization of the location of the tropopause along the western lateral boundary such that the model can correctly simulate stratospheric intrusions and their associated exchange of ozone from stratosphere to troposphere.
然而,沿西侧界对流层顶位置的正确描述还有一个额外的好处,即该模型可以正确地模拟平流层侵入及其相关的臭氧从平流层到对流层的交换。
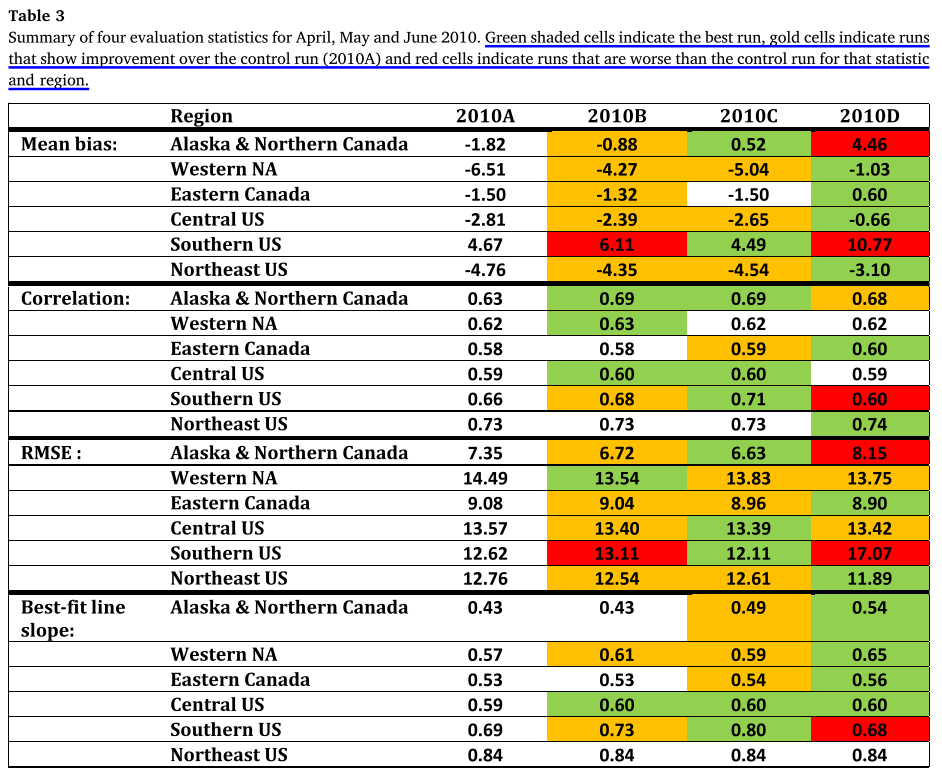
Over a three-month period in spring 2010, the mean bias was seen to improve by as much as 5 ppbv and the correlation by 0.1 depending on location, and on the form of the chemical lateral boundary condition.
在2010年春季的三个月时间里,平均偏差被提高了多达5 ppbv,相关性提高了0.1,这取决于所在位置和化学侧边界条件的形式。
The improvement is two-fold: first, the time-dependent ozone on the lateral boundaries at or near the surface allows the ozone field to have a more realistic evolution (e.g., in Texas and Florida in both years, Alaska in 2010), including long-range transport and a diurnal cycle, and second the representation of the ozone field in the UTLS region such that the gradient in ozone across the tropopause better matches the meteorology.
这一改进体现在两方面:首先,地表侧面边界上或附近的臭氧随时间变化,使臭氧场有更现实的演变(例如,德克萨斯州和佛罗里达州在这两年,阿拉斯加在2010年),包括远距离运输和日周期,其次,UTLS区域臭氧场的表现,使得横过对流层顶的臭氧梯度更符合气象学。
The DynOzone method is the simplest to implement and the least computationally expensive.
DynOzone方法最容易实现,计算成本也最低。
注意作者在表3的表述方式,他将最好的结果标注为绿色,变好的结果标注为黄色,变差的结果标注为红色。