软工作业3:结对项目——基于python实现小学四则运算
| 软件工程 | 计科21级12班-广东工业大学计算机学院 |
|---|---|
| 这个作业要求在哪里 | 结对项目 |
| 这个作业的目标 | 体验结对编程;实现小学四则运算命令行程序 |
参与人员
| 姓名 | 学号 |
|---|---|
| 魏晓琪 | 3221004897 |
| 朱乐言 | 3221004899 |
GitHub项目地址
一、PSP表格
| Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
|---|---|---|
| Planning(计划) | 20 | 20 |
| Estimate(估计时间) | 10 | 12 |
| Development(开发) | 530 | 500 |
| Analysis(需求分析(包括学习新技术)) | 100 | 60 |
| Design Spec(生成设计文档) | 60 | 10 |
| Design Review(设计复审) | 30 | 40 |
| Coding Standard(代码规范 ) | 30 | 20 |
| Design(具体设计) | 70 | 70 |
| Coding(具体编码) | 180 | 240 |
| Code Review(代码复审) | 60 | 30 |
| Test(测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改)) | 120 | 170 |
| Test Report(测试报告) | 60 | 120 |
| Size Measurement(计算工作量) | 30 | 20 |
| Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan(事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划) | 30 | 30 |
| Total(合计) | 1330 | 1342 |
二、设计要求
-
使用 -n 参数控制生成题目的个数
-
使用 -r 参数控制题目中数值(自然数、真分数和真分数分母)的范围
-
生成的题目中计算过程不能产生负数,也就是说算术表达式中如果存在形如e1− e2的子表达式,那么e1≥ e2。
-
生成的题目中如果存在形如e1÷ e2的子表达式,那么其结果应是真分数。
-
每道题目中出现的运算符个数不超过3个。
-
程序一次运行生成的题目不能重复,即任何两道题目不能通过有限次交换+和×左右的算术表达式变换为同一道题目。
-
生成的题目存入执行程序的当前目录下的Exercises.txt文件
-
在生成题目的同时,计算出所有题目的答案,并存入执行程序的当前目录下的Answers.txt文件
-
程序应能支持一万道题目的生成。
-
程序支持对给定的题目文件和答案文件,判定答案中的对错并进行数量统计,统计结果输出到文件Grade.txt
三、效能分析
1. 程序总耗时分析
-
生成十道题目所花费时间
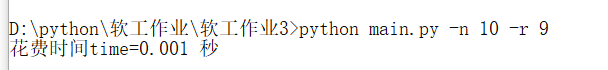
-
检测十道题目所花费时间

-
生成一万道题目所花费时间
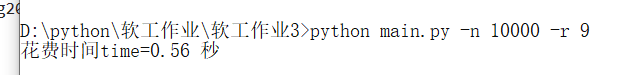
-
检测一万道题目所花费时间

分析:可以看出生成一万道题目用时不到1s,程序的运行效能还不错
2. 内存占用检测
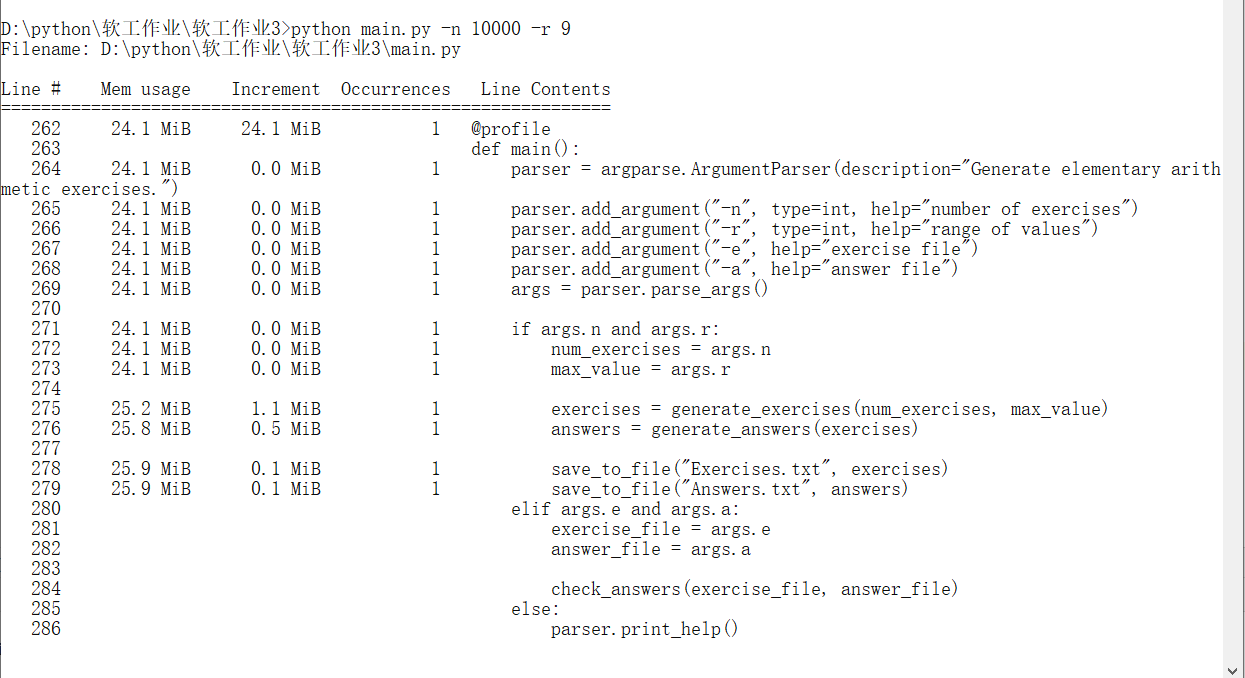
分析:可以看见,在生成一万道题目的过程中,generate_exercises占用了1.1MiB的内存,即生成四则运算时占用内存最多
3. 代码覆盖率

分析:可以看见当生成的题目数越多代码的覆盖率越高,当生成一万道题目时代码覆盖率也仅达到了82%,仍有改进空间
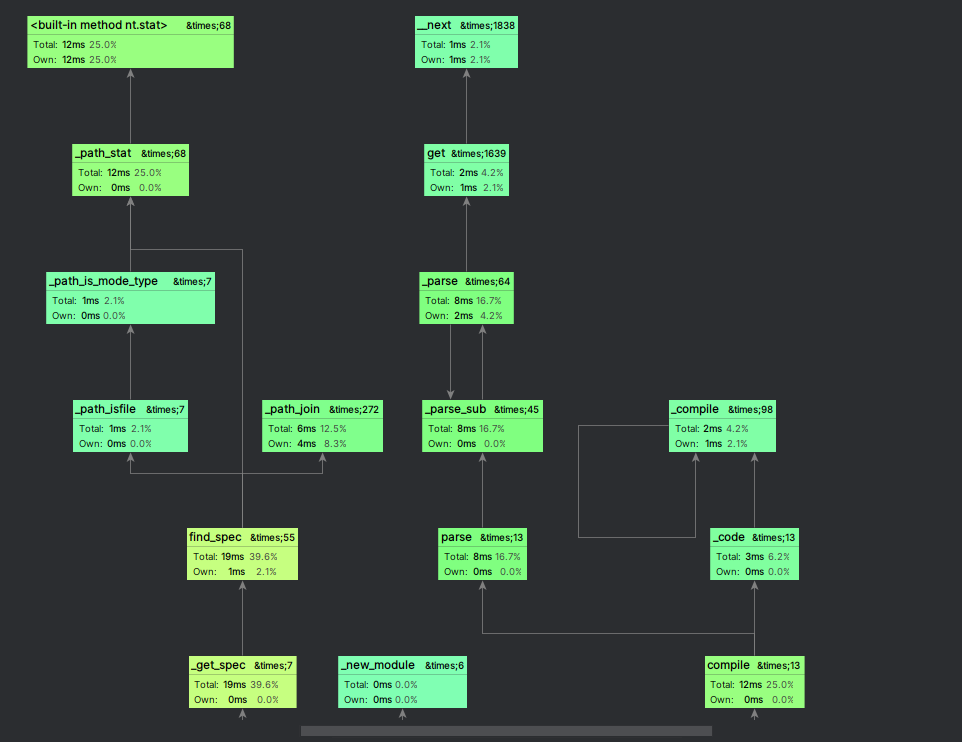
4. 利用pycharm自带工具Profile进行测试
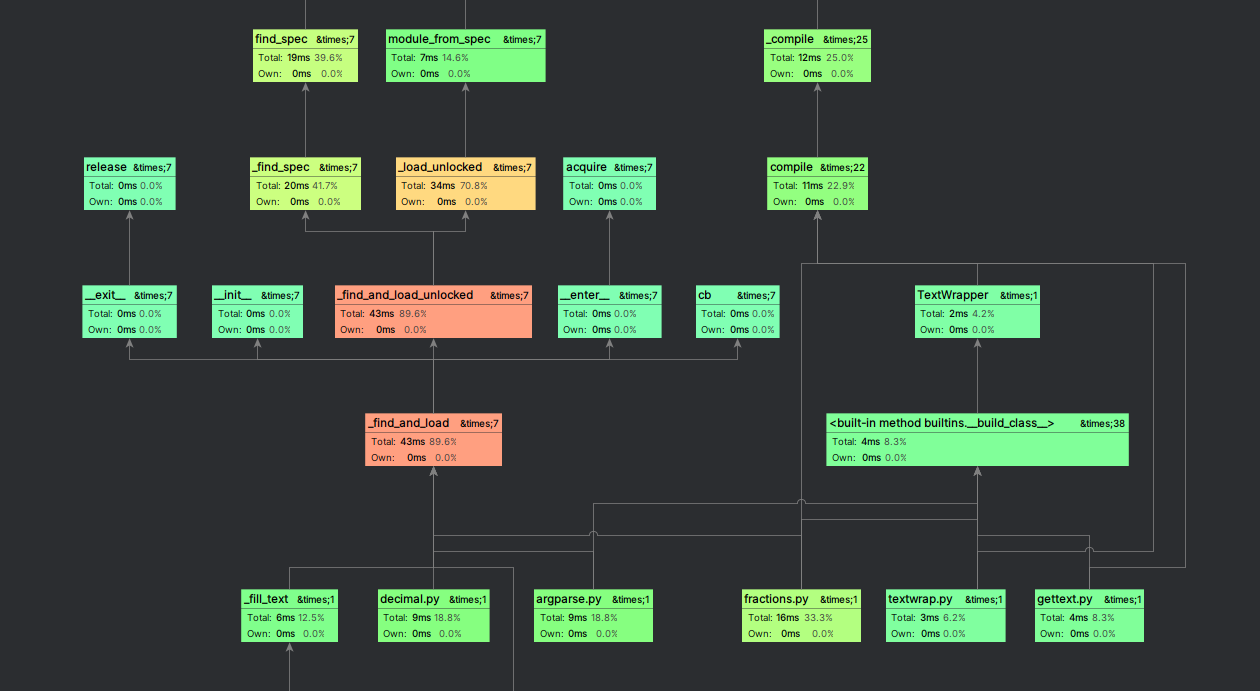

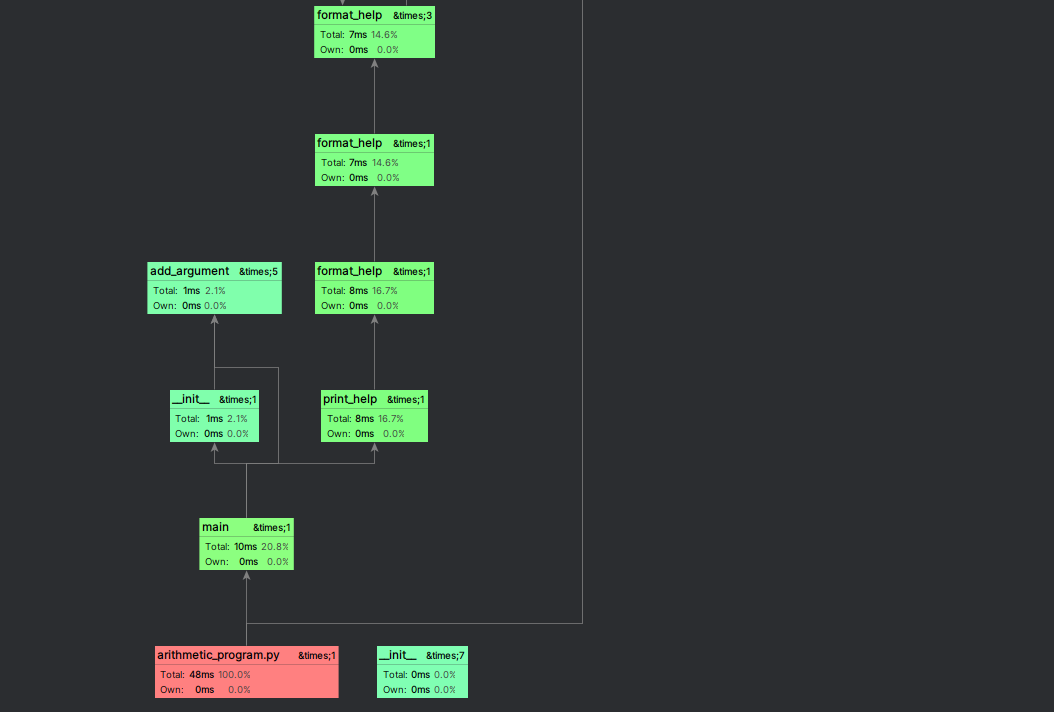
四、代码设计
1.各函数的功能介绍
| 函数名 | 传递变量 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|
| generate_expression | (max_value) 数值的范围,不包括该值 | 生成一个随机的算术表达式 |
| generate_operand | (max_value) 数值的范围,不包括该值 | 生成一个随机的操作数(自然数或真分数) |
| generate_exercises | (num_exercises, max_value) num_exercises: 题目数量 | 生成指定数量的四则运算题目 |
| calculate_answer | (expression) 生成的随机算术表达式 | 进行计算 |
| generate_answers | (exercises) 生成的题目 | 生成题目对应的答案列表 |
| save_to_file | (filename, data) | 将数据(data)保存到文件(filename)中 |
| load_from_file | (filename) | 从文件中读取数据 |
| check_answers | (exercise_file, answer_file) | 检查答案文件中的对错并进行数量统计 |
| main | NULL | 主函数 |
2. 命令行使用说明
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-n N number of exercises
-r R range of values
-e E exercise file
-a A answer file
例如:生成10以内的10道四则运算式
python arithmetic_program.py -n 10 -r 10
3.关键函数
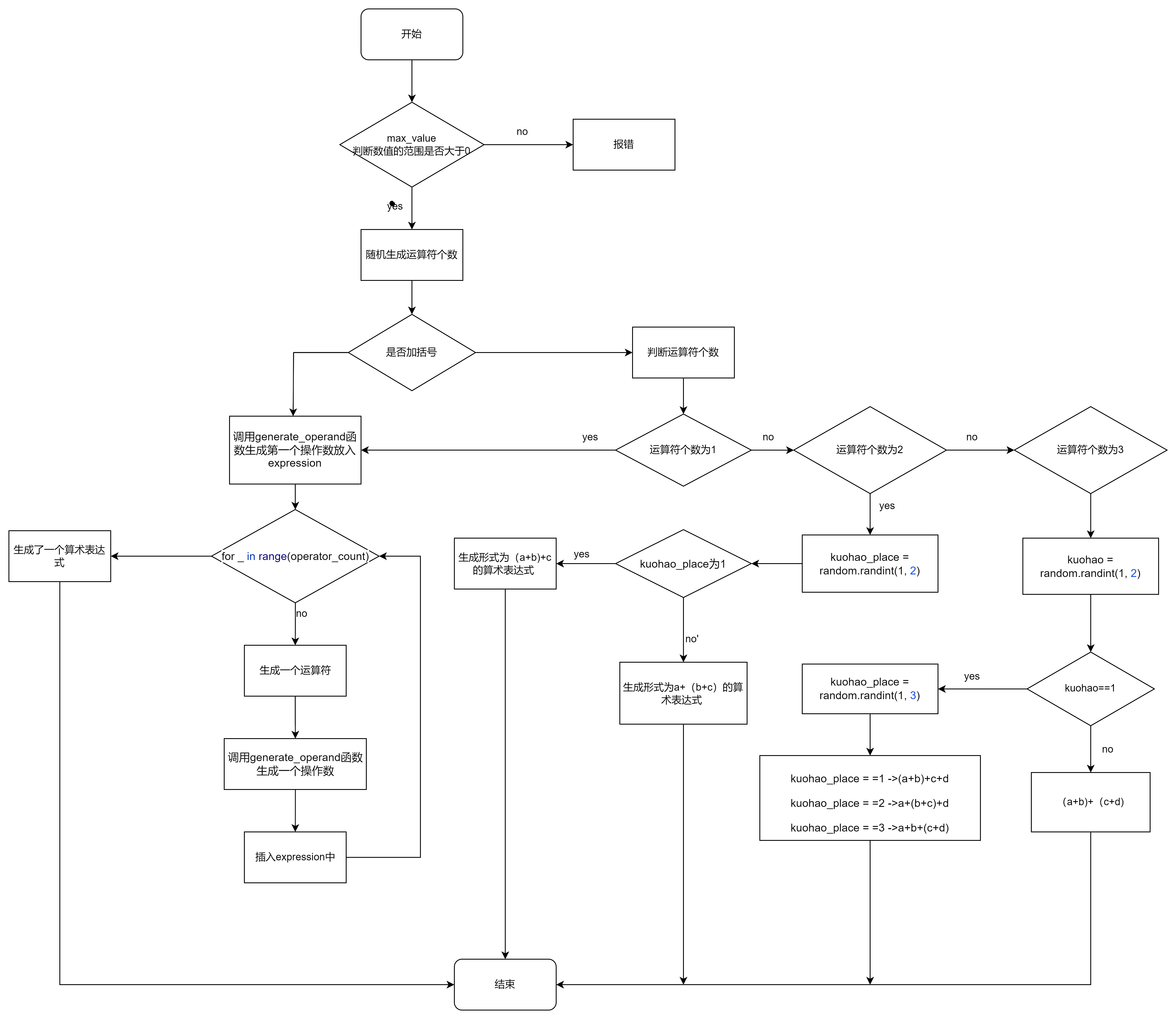
1. generate_expression——生成一个随机的算术表达式
- 流程图
点击查看代码
def generate_expression(max_value):
"""
生成一个随机的算术表达式
:param max_value: 数值的范围,不包括该值
:return: 算术表达式
"""
if max_value <= 0:
raise ValueError("max_value must be greater than 0")
# 运算符个数不超过3个
operator_count = random.randint(1, 3)
# 是否加括号
roll = random.randint(0, 1)
# 不加括号
if roll == 0:
expression = generate_operand(max_value)
for _ in range(operator_count):
operator = random.choice(OPERATORS)
# 生成一个随机的操作数(operand)
operand = generate_operand(max_value)
# 将'÷'替换成'/'
expression += f" {operator} {operand.replace('÷', '/')}"
# 加括号
else:
# 只有一个运算符。有没有括号都一样
if operator_count == 1:
expression = generate_operand(max_value)
for _ in range(operator_count):
operator = random.choice(OPERATORS)
# 生成一个随机的操作数(operand)
operand = generate_operand(max_value)
# 将'÷'替换成'/'
expression += f" {operator} {operand.replace('÷', '/')}"
# 两个运算符 括号最多一对
if operator_count == 2:
kuohao_place = random.randint(1, 2)
# (a+b)+c
if kuohao_place == 1:
operand = generate_operand(max_value)
expression = f"{'('} {operand} "
operator = random.choice(OPERATORS)
operand = generate_operand(max_value)
expression += f" {operator} {operand.replace('÷', '/')}"
operator = random.choice(OPERATORS)
operand = generate_operand(max_value)
expression += f"{')'} {operator} {operand.replace('÷', '/')}"
# a+(b+c)
else:
expression = generate_operand(max_value)
operator = random.choice(OPERATORS)
operand = generate_operand(max_value)
expression += f" {operator}{'('}{operand.replace('÷', '/')}"
operator = random.choice(OPERATORS)
operand = generate_operand(max_value)
expression += f"{operator} {operand.replace('÷', '/')}{')'} "
# 三个运算符,括号最多两对
if operator_count == 3:
kuohao = random.randint(1, 2)
# 只有一对括号
if kuohao == 1:
kuohao_place = random.randint(1, 3)
# (a+b)+c+d
if kuohao_place == 1:
operand = generate_operand(max_value)
expression = f"{'('} {operand} "
operator = random.choice(OPERATORS)
operand = generate_operand(max_value)
expression += f" {operator} {operand.replace('÷', '/')}{')'}"
operator = random.choice(OPERATORS)
operand = generate_operand(max_value)
expression += f" {operator} {operand.replace('÷', '/')}"
operator = random.choice(OPERATORS)
operand = generate_operand(max_value)
expression += f" {operator} {operand.replace('÷', '/')}"
# a+(b+c)+d
if kuohao_place == 2:
expression = generate_operand(max_value)
operator = random.choice(OPERATORS)
operand = generate_operand(max_value)
expression += f" {operator}{'('}{operand.replace('÷', '/')}"
operator = random.choice(OPERATORS)
operand = generate_operand(max_value)
expression += f"{operator} {operand.replace('÷', '/')}{')'} "
operator = random.choice(OPERATORS)
operand = generate_operand(max_value)
expression += f" {operator} {operand.replace('÷', '/')}"
# a+b+(c+d)
if kuohao_place == 3:
expression = generate_operand(max_value)
operator = random.choice(OPERATORS)
operand = generate_operand(max_value)
expression += f" {operator} {operand.replace('÷', '/')}"
operator = random.choice(OPERATORS)
operand = generate_operand(max_value)
expression += f" {operator}{'('} {operand.replace('÷', '/')}"
operator = random.choice(OPERATORS)
operand = generate_operand(max_value)
expression += f" {operator}{operand.replace('÷', '/')}{')'}"
# 两对括号-----(a+b)+(c+d)
if kuohao == 2:
operand = generate_operand(max_value)
expression = f"{'('} {operand} "
operator = random.choice(OPERATORS)
operand = generate_operand(max_value)
expression += f" {operator} {operand.replace('÷', '/')}{')'}"
operator = random.choice(OPERATORS)
operand = generate_operand(max_value)
expression += f" {operator}{'('} {operand.replace('÷', '/')}"
operator = random.choice(OPERATORS)
operand = generate_operand(max_value)
expression += f" {operator} {operand.replace('÷', '/')}{')'}"
return expression
- 算法设计思路
该函数用于生成一个随机的算术表达式,其中包含随机的运算符和操作数。函数的参数 max_value 指定了操作数的范围(不包括该值)。
1.检查 max_value 是否大于 0,如果小于等于 0,则抛出异常。
2.随机生成一个运算符个数 operator_count,范围在 1 到 3 之间。
3.随机生成一个是否加括号的标志 roll,范围在 0 和 1 之间。
4.如果 roll 的值为 0,表示不加括号,则生成一个随机操作数作为表达式的起始部分,并通过循环生成 operator_count 个随机运算符和操作数,并将它们添加到表达式中。
5.如果 roll 的值为 1,表示加括号,根据 operator_count 的值选择不同的括号组合方式,并生成相应的表达式。最后返回生成的算术表达式
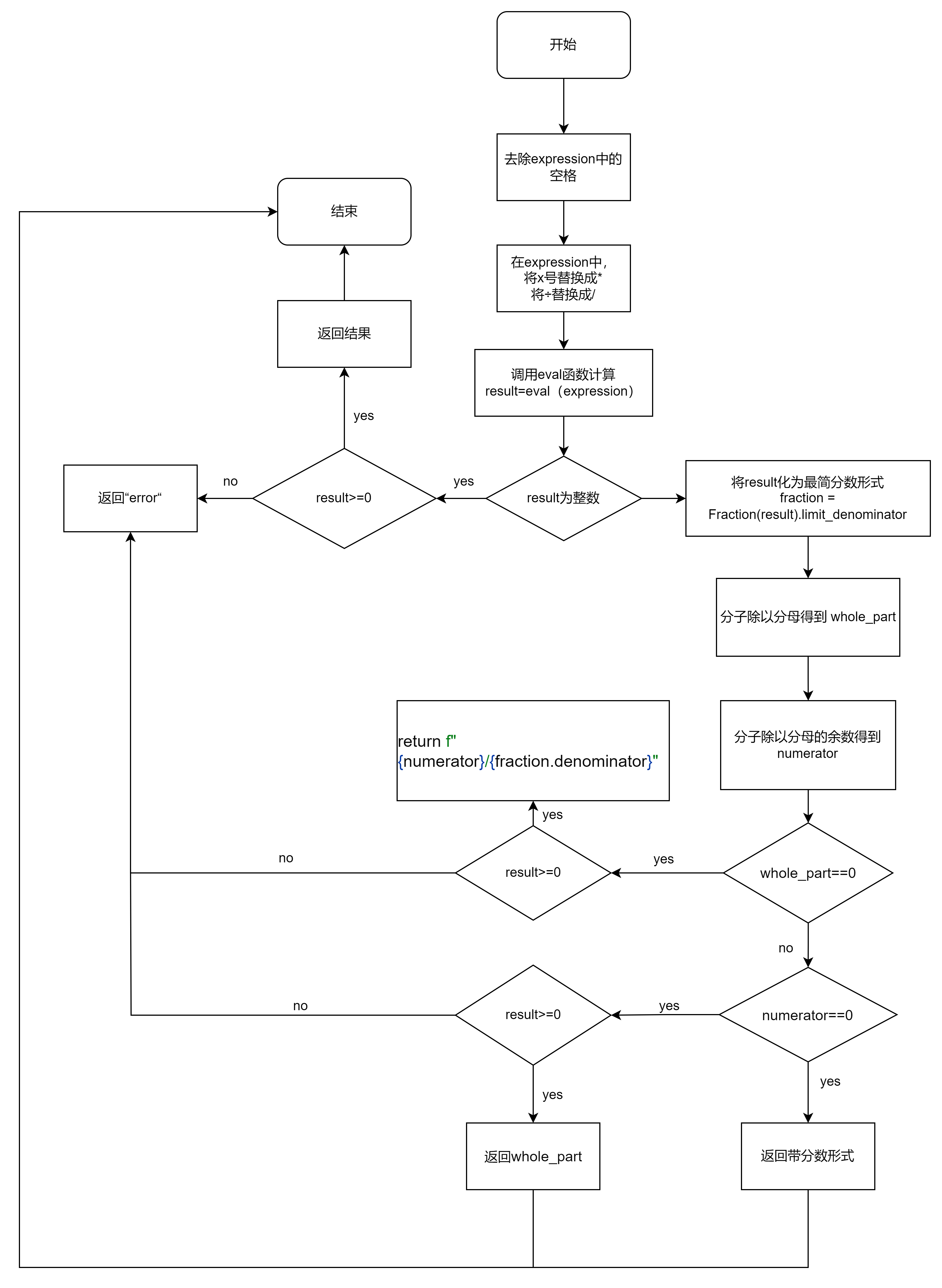
2. calculate_answer——计算
- 流程图
点击查看代码
def calculate_answer(expression):
expression = expression.replace(' ', '') # 去除空格
expression = expression.replace('×', '*').replace('÷', '/')
try:
result = eval(expression)
if isinstance(result, int):
return str(result) if result >= 0 else "Error"
else:
fraction = Fraction(result).limit_denominator()
whole_part = fraction.numerator // fraction.denominator
numerator = fraction.numerator % fraction.denominator
if whole_part == 0:
return f"{numerator}/{fraction.denominator}" if result >= 0 else "Error"
elif numerator == 0:
return str(whole_part) if result >= 0 else "Error"
else:
return f"{whole_part}'{numerator}/{fraction.denominator}" if result >= 0 else "Error"
except ZeroDivisionError:
return "Error: Division by zero"
except Exception:
return "Error: Invalid expression"
- 算法设计思路
该函数用于计算给定算术表达式的结果并返回一个字符串表示。
1.通过替换操作将表达式中的空格、乘号(×)和除号(÷)转换为对应的 Python 运算符(* 和 /)。
2.使用 eval() 函数对修改后的表达式进行求值,得到结果。
3.如果结果是一个整数,判断其是否大于等于 0。如果大于等于 0,则将结果转换为字符串并返回;否则返回字符串 "Error"。
4.如果结果不是整数,将其转换为分数形式,并使用 Fraction 类对分数进行处理。然后,根据分数的情况进行判断:
5.如果分数的整数部分为 0,则返回分数的字符串表示形式(例如 "1/2"),如果结果大于等于 0;否则返回字符串 "Error"。
6.如果分数的分子为 0,则返回整数部分的字符串表示形式(例如 "2"),如果结果大于等于 0;否则返回字符串 "Error"。
7.如果分数既有整数部分又有分数部分,则返回带有整数部分的带分数形式的字符串表示(例如 "1'1/2"),如果结果大于等于 0;否则返回字符串 "Error"。
异常处理:
1.如果在求值过程中遇到除以零的错误(ZeroDivisionError),则返回字符串 "Error: Division by zero"。
2.如果在求值过程中遇到其他异常(Exception),则返回字符串 "Error: Invalid expression",表示表达式无效。
3. check_answers——检查答案文件中的对错并进行数量统计
- 流程图
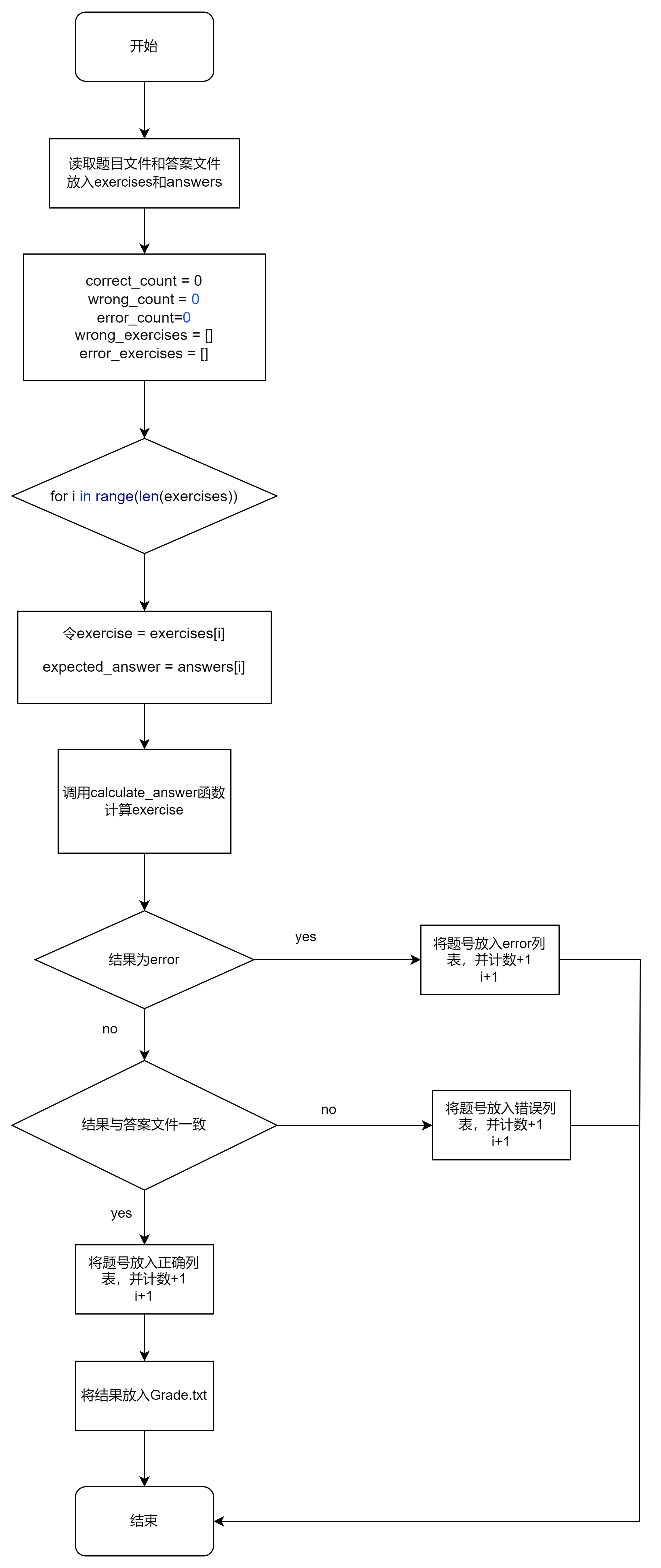
点击查看代码
def check_answers(exercise_file, answer_file):
"""
检查答案文件中的对错并进行数量统计
:param exercise_file: 题目文件
:param answer_file: 答案文件
"""
exercises = load_from_file(exercise_file)
answers = load_from_file(answer_file)
correct_count = 0
wrong_count = 0
error_count=0
wrong_exercises = []
error_exercises = []
for i in range(len(exercises)):
exercise = exercises[i]
expected_answer = answers[i]
actual_answer = calculate_answer(exercise)
if expected_answer != 'Error':
if expected_answer == actual_answer:
correct_count += 1
else:
wrong_count += 1
wrong_exercises.append(i + 1)
else:
error_count += 1
error_exercises.append(i + 1)
#正确题目
result = f"Correct: {correct_count} ({', '.join(map(str, range(1, correct_count + 1)))})\n"
#错误题目
result += f"Wrong: {wrong_count} ({', '.join(map(str, wrong_exercises))})\n"
#结果为负数的题目
result += f"Error: {error_count} ({', '.join(map(str, error_exercises))})\n"
save_to_file("Grade.txt", [result])
- 算法设计思路
该函数用于检查答案文件中的答案是否正确,并进行数量统计。
1.调用 load_from_file() 函数从题目文件和答案文件中加载题目和答案,将它们分别存储在 exercises 和 answers 列表中。
2.定义变量 correct_count、wrong_count 和 error_count,分别用于统计正确答案的数量、错误答案的数量和无效表达式的数量。
3.定义空列表 wrong_exercises 和 error_exercises,用于存储答错的题目编号和无效表达式的题目编号。
4.使用循环遍历题目列表 exercises,获取当前题目 exercise、期望答案 expected_answer 和实际答案 actual_answer。如果期望答案不是 "Error",则判断实际答案是否与期望答案相同。如果相同,则将 correct_count 增加 1;否则,将 wrong_count 增加 1,并将当前题目的编号(i+1)添加到 wrong_exercises 列表中。如果期望答案是 "Error",则将 error_count 增加 1,并将当前题目的编号(i+1)添加到 error_exercises 列表中。
5.构建结果字符串 result,其中包括正确题目的数量和编号、错误题目的数量和编号,以及结果为负数的题目的数量和编号。
6.调用 save_to_file() 函数,将结果字符串保存到名为 "Grade.txt" 的文件中。
4. main——主函数
- 流程图
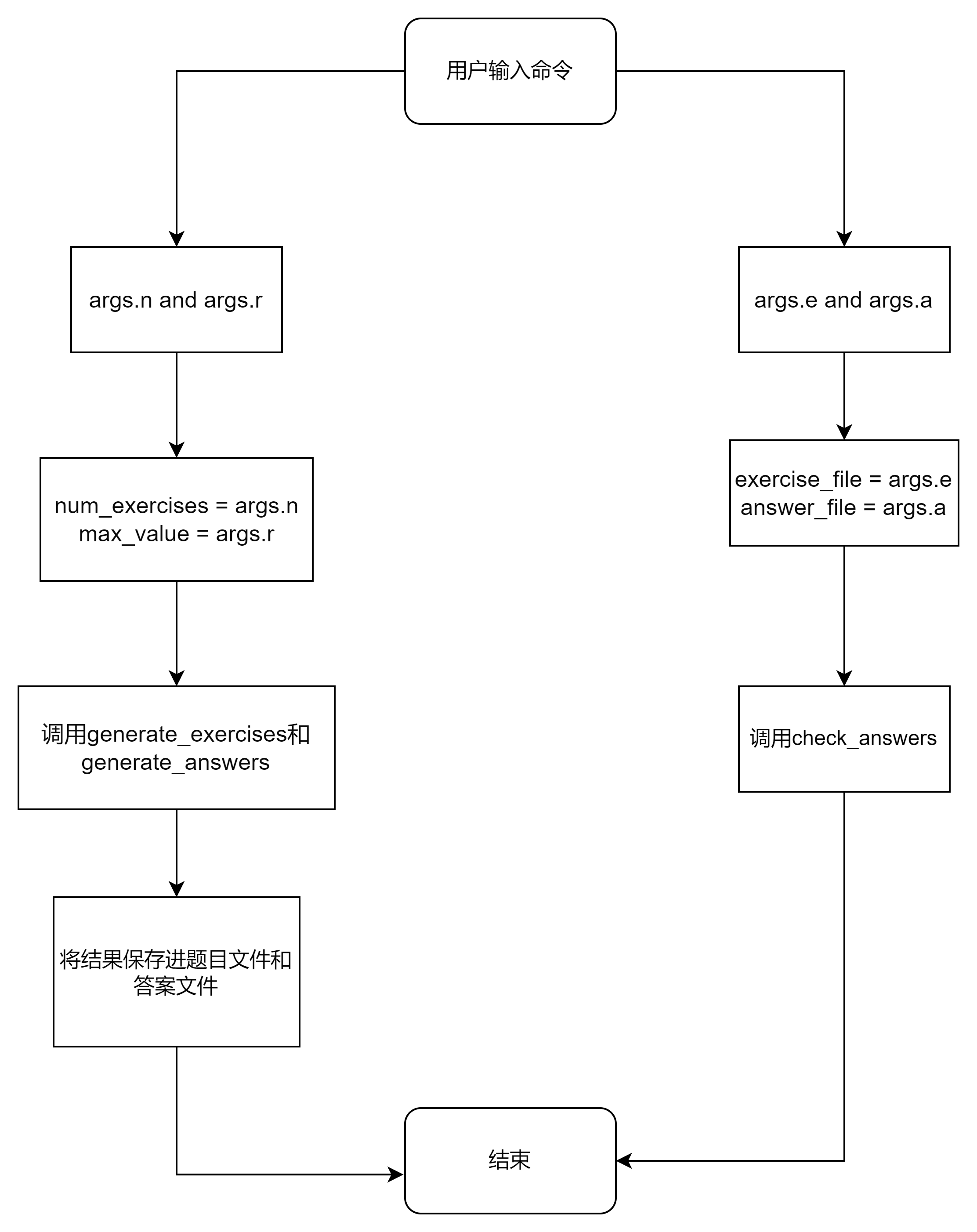
点击查看代码
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Generate elementary arithmetic exercises.")
parser.add_argument("-n", type=int, help="number of exercises")
parser.add_argument("-r", type=int, help="range of values")
parser.add_argument("-e", help="exercise file")
parser.add_argument("-a", help="answer file")
args = parser.parse_args()
if args.n and args.r:
num_exercises = args.n
max_value = args.r
exercises = generate_exercises(num_exercises, max_value)
answers = generate_answers(exercises)
save_to_file("Exercises.txt", exercises)
save_to_file("Answers.txt", answers)
elif args.e and args.a:
exercise_file = args.e
answer_file = args.a
check_answers(exercise_file, answer_file)
else:
parser.print_help()
- 算法设计思路
1.创建一个 argparse.ArgumentParser 对象,用于解析命令行参数并提供程序的描述信息。
2.添加命令行参数 -n(题目数量)、-r(数值范围)、-e(题目文件)和 -a(答案文件)。
3.使用 parser.parse_args() 解析命令行参数,并将结果存储在 args 变量中。
4.如果同时提供了 -n 和 -r 参数,表示要生成练习题和答案文件:从 args 中获取题目数量 num_exercises 和数值范围 max_value。调用 generate_exercises(num_exercises, max_value) 生成题目列表 exercises。调用 generate_answers(exercises) 生成答案列表 answers。使用 save_to_file() 将题目列表 exercises 保存到名为 "Exercises.txt" 的文件中。使用 save_to_file() 将答案列表 answers 保存到名为 "Answers.txt" 的文件中。
5.如果同时提供了 -e 和 -a 参数,表示要检查答案文件:从 args 中获取题目文件名 exercise_file 和答案文件名 answer_file。调用 check_answers(exercise_file, answer_file) 检查答案文件中的答案,如果没有提供正确的参数组合,调用 parser.print_help() 打印帮助信息。
6.打印花费的时间差。
五、测试部分
1. 单元测试
- 测试文件:
点击查看代码
import unittest
import random
from 软工作业3.main import calculate_answer, generate_answers, generate_operand, OPERATORS
class MyTestCase(unittest.TestCase):
def test_calculate_answer(self):
excise='1+2+3'
result=calculate_answer(excise)
self.assertEqual(result, '6') # add assertion here
def test_generate_answers(self):
answers = []
excise=['1','2','3']
excises='123'
answers=generate_answers(excises)
self.assertEqual(answers,excise )
def test_generate_expression(self, max_value=9):
# 运算符个数不超过3个
operator_count= 1
# 是否加括号
roll = 0
# 不加括号
if roll == 0:
expression = '2'
for _ in range(operator_count):
operator = '+'
# 生成一个随机的操作数(operand)
operand = '2'
# 将'÷'替换成'/'
expression += f" {operator} {operand.replace('÷', '/')}"
# 加括号
else:
# 只有一个运算符。有没有括号都一样
if operator_count == 1:
expression = generate_operand(max_value)
for _ in range(operator_count):
operator = random.choice(OPERATORS)
# 生成一个随机的操作数(operand)
operand = generate_operand(max_value)
# 将'÷'替换成'/'
expression += f" {operator} {operand.replace('÷', '/')}"
# 两个运算符 括号最多一对
if operator_count == 2:
kuohao_place = random.randint(1, 2)
# (a+b)+c
if kuohao_place == 1:
operand = generate_operand(max_value)
expression = f"{'('} {operand} "
operator = random.choice(OPERATORS)
operand = generate_operand(max_value)
expression += f" {operator} {operand.replace('÷', '/')}"
operator = random.choice(OPERATORS)
operand = generate_operand(max_value)
expression += f"{')'} {operator} {operand.replace('÷', '/')}"
# a+(b+c)
else:
expression = generate_operand(max_value)
operator = random.choice(OPERATORS)
operand = generate_operand(max_value)
expression += f" {operator}{'('}{operand.replace('÷', '/')}"
operator = random.choice(OPERATORS)
operand = generate_operand(max_value)
expression += f"{operator} {operand.replace('÷', '/')}{')'} "
# 三个运算符,括号最多两对
if operator_count == 3:
kuohao = random.randint(1, 2)
# 只有一对括号
if kuohao == 1:
kuohao_place = random.randint(1, 3)
# (a+b)+c+d
if kuohao_place == 1:
operand = generate_operand(max_value)
expression = f"{'('} {operand} "
operator = random.choice(OPERATORS)
operand = generate_operand(max_value)
expression += f" {operator} {operand.replace('÷', '/')}{')'}"
operator = random.choice(OPERATORS)
operand = generate_operand(max_value)
expression += f" {operator} {operand.replace('÷', '/')}"
operator = random.choice(OPERATORS)
operand = generate_operand(max_value)
expression += f" {operator} {operand.replace('÷', '/')}"
# a+(b+c)+d
if kuohao_place == 2:
expression = generate_operand(max_value)
operator = random.choice(OPERATORS)
operand = generate_operand(max_value)
expression += f" {operator}{'('}{operand.replace('÷', '/')}"
operator = random.choice(OPERATORS)
operand = generate_operand(max_value)
expression += f"{operator} {operand.replace('÷', '/')}{')'} "
operator = random.choice(OPERATORS)
operand = generate_operand(max_value)
expression += f" {operator} {operand.replace('÷', '/')}"
# a+b+(c+d)
if kuohao_place == 3:
expression = generate_operand(max_value)
operator = random.choice(OPERATORS)
operand = generate_operand(max_value)
expression += f" {operator} {operand.replace('÷', '/')}"
operator = random.choice(OPERATORS)
operand = generate_operand(max_value)
expression += f" {operator}{'('} {operand.replace('÷', '/')}"
operator = random.choice(OPERATORS)
operand = generate_operand(max_value)
expression += f" {operator}{operand.replace('÷', '/')}{')'}"
# 两对括号-----(a+b)+(c+d)
if kuohao == 2:
operand = generate_operand(max_value)
expression = f"{'('} {operand} "
operator = random.choice(OPERATORS)
operand = generate_operand(max_value)
expression += f" {operator} {operand.replace('÷', '/')}{')'}"
operator = random.choice(OPERATORS)
operand = generate_operand(max_value)
expression += f" {operator}{'('} {operand.replace('÷', '/')}"
operator = random.choice(OPERATORS)
operand = generate_operand(max_value)
expression += f" {operator} {operand.replace('÷', '/')}{')'}"
self.assertEqual(expression, '2 + 2')
if __name__ == '__main__':
unittest.main()
- 运行结果:

分析:对generate_expression函数,generate_answers函数以及calculate_answer函数进行了测试,并且都通过了测试,故我们认为我们的代码是可行的
2. 测试用例
篇幅有限仅展示其中一个测试用例
1. 操作数范围1~9,生成25道题目
- 生成的Exercises.txt文件
(7/8) × (3/5)
( (1/2) ÷ (3/4)) + 8 ÷ (1/4)
( 8 - 5) + (2/3)
(1/7) ÷ 9
9 ÷ 8 ÷ (1/7) ÷ 8
(7/8) ÷ (5/9) × (5/9) - (3/4)
8 - 9
(1/2) × (3/4) × (1/2) + (1/3)
(2/3) + 4 + (5/9) ÷ (3/7)
9 ÷ 5 - (1/2)
(1/2) - (3/5) + (3/8) - (5/6)
9 ÷ (3/4) - (1/9)
9 × 9
( 5 ÷ 9) × (2/3)
9 - 1 + 3
(1/2) × (3/4) ÷ 1
(3/7) ÷ 2
(2/3) - (7/8) + 2
7 × (1/2)
(7/8) +((2/9)- (3/7)) × 9
9 ÷ (1/3) ÷ (7/9) ÷ (1/2)
(3/4) - (1/6)
( (1/2) ÷ (7/9)) ÷ (8/9)
( 9 - 8) +( 5 + (5/8))
(3/4) ÷ 8 + (7/8) - 9
- 生成的Answers.txt文件
21/40
32'2/3
3'2/3
1/63
63/64
1/8
Error
25/48
5'26/27
1'3/10
Error
11'8/9
81
10/27
11
3/8
3/14
1'19/24
3'1/2
Error
69'3/7
7/12
81/112
6'5/8
Error
说明:结果为负数就输出为Error,经过手动计算并逐条进行检查可以说明计算结果正确率很高,说明该程序的设计是可行的
- 将Exercises.txt和Answers.txt进行比较
- 比较未修改的文件
Correct: 21 (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21)
Wrong: 0 ()
Error: 4 (7, 11, 20, 25)
- 将答案文件中的第10,11,5,7,9题修改成错误的答案
21/40
32'2/3
3'2/3
1/63
1 #
1/8
2 #
25/48
3 #
1 #
1 #
11'8/9
81
10/27
11
3/8
3/14
1'19/24
3'1/2
Error
69'3/7
7/12
81/112
6'5/8
Error
- 比较修改后的文件
Correct: 18 (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18)
Wrong: 5 (5, 7, 9, 10, 11)
Error: 2 (20, 25)
六、项目小结
- 朱乐言:
- 在本次项目中,我们体验了结对编程,在交流与沟通以及分工中以较高的效率完成了本次任务,认识到了结对编程的好处,结对编程比起一个人编程可以更容易找到一些隐藏的代码问题,两个人思想的碰撞、集思广益,为项目的顺利完成贡献了巨大的作用,对提高任务的效率起到了非常大的帮助。同时,也明白了结对编程中需要时时沟通与交流,不然只会事倍功半。
- 而在完成本次项目的过程中,我对python更加熟悉了,同时也掌握了一些新的方法,对程序的性能分析、测试的掌握也有了进步。
- 在编程中也遇到了许多问题,比如分数的计算,在算术表达式中插入括号等,在解决的过程中我们也学会了新的知识。
- 当然,本次的程序还有不小的提升空间,但由于时间比较紧张和个人水平限制,最后一些优化的想法没有得到实现,也是本次项目中的遗憾。
- 最后再次感谢我的搭档。
- 魏晓琪:
- 在本次结对作业中,我们一起商量对于本次项目的想法和思路,通过查阅很多资料然后确定了我们的代码设计
- 我们分工很明确,代码的主体架构由我负责编写,但在实现生成四则运算式的过程中遇到了括号如何进行添加以及在处理计算部分的代码时也遇到了除法计算容易产生错误的问题,而这个时候就由我的搭档提出想法并且成功解决了代码中所遇到的问题,这体现出了团队合作的重要性,集思广益才能够实现效率的最大化
- 接下来的测试部分以及流程图的绘画以及博客的大体由我的搭档进行完成,而我则进行算法思路的介绍以及博客的完善
- 通过这次作业,让我们对于python编程以及如何进行代码测试和性能分析都有了进一步的了解,也知道了团队合作中如何与搭档进行有效沟通,督促彼此,不推脱责任。
- 最后,再次感谢我的搭档的帮助与配合


