java集合框架之ArrayList
参考http://how2j.cn/k/collection/collection-arraylist/363.html
使用数组的局限性
一个长度是10的数据:Hero[] heroArr=new Hero[10];
如果用数组存放数据,那么超过10的数据就放不下了
如果数据不足10个,那么数组空间就浪费了
package collection; import charactor.Hero; public class TestCollection { public static void main(String[] args) { //数组的局限性 Hero heros[] = new Hero[10]; //声明长度是10的数组 //不用的数组就浪费了 //超过10的个数,又放不下 heros[0] = new Hero("盖伦"); //放不下要报错 heros[20] = new Hero("提莫"); } }
ArrayList存放对象
ArrayList实现了接口List
常见的写法会把引用声明为接口List类型
注意:是java.util.List,而不是java.awt.List
List heros = new ArrayList();
为了解决数组的局限性,引入容器类的概念。 最常见的容器类就是
ArrayList
容器的容量"capacity"会随着对象的增加,自动增长
只需要不断往容器里增加英雄即可,不用担心会出现数组的边界问题。
package collection; import java.util.ArrayList; import charactor.Hero; public class TestCollection { @SuppressWarnings("rawtypes") public static void main(String[] args) { //容器类ArrayList,用于存放对象 ArrayList heros = new ArrayList(); heros.add( new Hero("盖伦")); System.out.println(heros.size()); //容器的容量"capacity"会随着对象的增加,自动增长 //只需要不断往容器里增加英雄即可,不用担心会出现数组的边界问题。 heros.add( new Hero("提莫")); System.out.println(heros.size()); } }
增加
add 有两种用法 第一种是直接add对象,把对象加在最后面 heros.add(new Hero("hero " + i)); 第二种是在指定位置加对象 heros.add(3, specialHero);
获取指定位置的对象
通过get获取指定位置的对象,如果输入的下标越界,一样会报错
package collection; import java.util.ArrayList; import charactor.Hero; public class TestCollection { public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayList heros = new ArrayList(); // 初始化5个对象 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { heros.add(new Hero("hero " + i)); } Hero specialHero = new Hero("special hero"); heros.add(specialHero); //获取指定位置的对象 System.out.println(heros.get(5)); //如果超出了范围,依然会报错 System.out.println(heros.get(6)); } }
获取对象所处的位置
indexOf用于判断一个对象在ArrayList中所处的位置
与contains一样,判断标准是对象是否相同,而非对象的name值是否相等
package collection; import java.util.ArrayList; import charactor.Hero; public class TestCollection { public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayList heros = new ArrayList(); // 初始化5个对象 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { heros.add(new Hero("hero " + i)); } Hero specialHero = new Hero("special hero"); heros.add(specialHero); System.out.println(heros); System.out.println("specialHero所处的位置:"+heros.indexOf(specialHero)); System.out.println("新的英雄,但是名字是\"hero 1\"所处的位置:"+heros.indexOf(new Hero("hero 1"))); } }
删除
remove用于把对象从ArrayList中删除
remove可以根据下标删除ArrayList的元素 heros.remove(2); 也可以根据对象删除 heros.remove(specialHero);
替换
set用于替换指定位置的元素
package collection; import java.util.ArrayList; import charactor.Hero; public class TestCollection { public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayList heros = new ArrayList(); // 初始化5个对象 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { heros.add(new Hero("hero " + i)); } Hero specialHero = new Hero("special hero"); heros.add(specialHero); System.out.println(heros); System.out.println("把下标是5的元素,替换为\"hero 5\""); heros.set(5, new Hero("hero 5")); System.out.println(heros); } }
获取大小
size 用于获取ArrayList的大小
转换为数组
toArray可以把一个ArrayList对象转换为数组。
需要注意的是,如果要转换为一个Hero数组,那么需要传递一个Hero数组类型的对象给toArray(),这样toArray方法才知道,你希望转换为哪种类型的数组,否则只能转换为Object数组
Hero hs[] = (Hero[])heros.toArray(new Hero[]{});
package collection; import java.util.ArrayList; import charactor.Hero; public class TestCollection { public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayList heros = new ArrayList(); // 初始化5个对象 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { heros.add(new Hero("hero " + i)); } Hero specialHero = new Hero("special hero"); heros.add(specialHero); System.out.println(heros); Hero hs[] = (Hero[])heros.toArray(new Hero[]{}); System.out.println("数组:" +hs); } }
把另一个容器所有对象都加进来
package collection; import java.util.ArrayList; import charactor.Hero; public class TestCollection { public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayList heros = new ArrayList(); // 初始化5个对象 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { heros.add(new Hero("hero " + i)); } System.out.println("ArrayList heros:\t" + heros); //把另一个容器里所有的元素,都加入到该容器里来 ArrayList anotherHeros = new ArrayList(); anotherHeros.add(new Hero("hero a")); anotherHeros.add(new Hero("hero b")); anotherHeros.add(new Hero("hero c")); System.out.println("anotherHeros heros:\t" + anotherHeros); heros.addAll(anotherHeros); System.out.println("把另一个ArrayList的元素都加入到当前ArrayList:"); System.out.println("ArrayList heros:\t" + heros); } }
清空
clear 清空一个ArrayList,heros.clear();
做一个一样的MyStringBuffer练习,但是不使用字符数组,而是使用ArrayList来实现
package Test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
/**
* @Auther: 李景然
* @Date: 2018/5/23 15:56
* @Description:做一个一样的MyStringBuffer练习,但是不使用字符数组,而是使用ArrayList来实现
*/
public class MyStringBufferTest{
ArrayList sb = new ArrayList();
public MyStringBufferTest() {
}
public MyStringBufferTest(String string) {
this.append(string);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyStringBufferTest sb = new MyStringBufferTest("there light");
System.out.println(sb);
sb.insert(0, "let ");
System.out.println(sb);
sb.insert(10, "be ");
System.out.println(sb);
sb.insert(0, "God Say:");
System.out.println(sb);
sb.append("!");
System.out.println(sb);
sb.append('?');
System.out.println(sb);
sb.reverse();
System.out.println(sb);
sb.reverse();
System.out.println(sb);
sb.delete(0, 4);
System.out.println(sb);
sb.delete(4);
System.out.println(sb);
}
public void append(String str) {
this.insert(sb.size(), str);
}
public void append(char c) {
this.insert(sb.size(), c);
}
public void insert(int pos, char b) {
sb.add(pos, String.valueOf(b));
}
public void insert(int pos, String b) {
if (pos < 0 || pos > sb.size()) throw new RuntimeException("角标越界");
if (b.equals("")) throw new IllegalArgumentException("请勿输入空字符串");
for (int i = pos; i < b.length(); i++) {
sb.add(i, b.charAt(i - pos));
}
}
public void delete(int start) {
this.delete(start, sb.size());
}
public void delete(int start, int end) {
for (int i = start; i < end; i++) {
sb.remove(i);
}
}
public void reverse() {
for (int i = 0; i <= sb.size() - i; i++) {
char c = (char) sb.indexOf(i);
sb.set(i, sb.indexOf(sb.size() - i));
sb.set(sb.size() - i, c);
}
}
public int length() {
return sb.size();
}
public String toString() {
return sb.toString();
}
}

泛型 Generic
不指定泛型的容器,可以存放任何类型的元素
指定了泛型的容器,只能存放指定类型的元素以及其子类
//对于不使用泛型的容器,可以往里面放英雄,也可以往里面放物品 List heros = new ArrayList(); heros.add(new Hero("盖伦")); //本来用于存放英雄的容器,现在也可以存放物品了 heros.add(new Item("冰杖"));
遍历
用for循环遍历
for (int i = 0; i < heros.size(); i++) { Hero h = heros.get(i); System.out.println(h); }
迭代器遍历
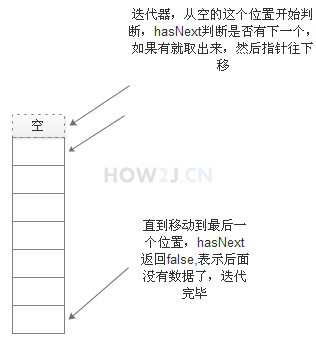
package collection; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.List; import charactor.Hero; public class TestCollection { public static void main(String[] args) { List<Hero> heros = new ArrayList<Hero>(); //放5个Hero进入容器 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { heros.add(new Hero("hero name " +i)); } //第二种遍历,使用迭代器 System.out.println("--------使用while的iterator-------"); Iterator<Hero> it= heros.iterator(); //从最开始的位置判断"下一个"位置是否有数据 //如果有就通过next取出来,并且把指针向下移动 //直达"下一个"位置没有数据 while(it.hasNext()){ Hero h = it.next(); System.out.println(h); } //迭代器的for写法 System.out.println("--------使用for的iterator-------"); for (Iterator<Hero> iterator = heros.iterator(); iterator.hasNext();) { Hero hero = (Hero) iterator.next(); System.out.println(hero); } } }
用增强型for循环
使用增强型for循环可以非常方便的遍历ArrayList中的元素,这是很多开发人员的首选。
不过增强型for循环也有不足:
无法用来进行ArrayList的初始化
无法得知当前是第几个元素了,当需要只打印单数元素的时候,就做不到了。 必须再自定下标变量。
for (Hero h : heros) { System.out.println(h); }
利用迭代器可以删除ArrayList中的元素
Iterator<Hero> i=hList.iterator(); while (i.hasNext()){ Hero h=i.next(); i.remove(); //这样会把ArrayList中的数据删除光 }
下一节LinkedList



