filebeat输出结果到elasticsearch的多个索引
基本环境:
filebeat版本:6.5.4 (Linux,x86-64)
elasticsearch版本:6.54
(一)需求说明
在一台服务器上有多个日志需要使用filebeat日志收集到elasticsearch中,以便于查看。对于收集方法,主要有2种:
- 将同一台服务器上的日志收集到elasticsearch的同一个索引中,这种方式存在一个较大的问题,如果服务器上有多个业务在运行,产生了多个日志,那么将会被收集到elasticsearch的同一个索引中,如图1。
- 将同一台服务器上的日志收集到elasticsearch的不同索引中,每个索引都存放相关业务的日志,如图2。
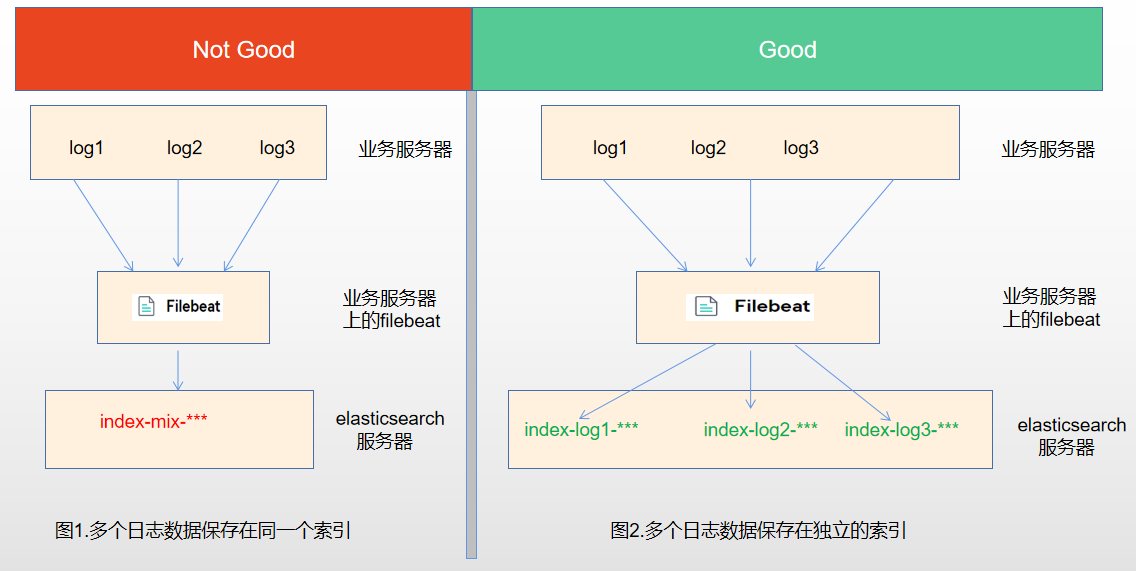
很明显,图2的日志输出是我们想要的,因为它将不同的日志放到了不同的索引中。
(二)解决方案
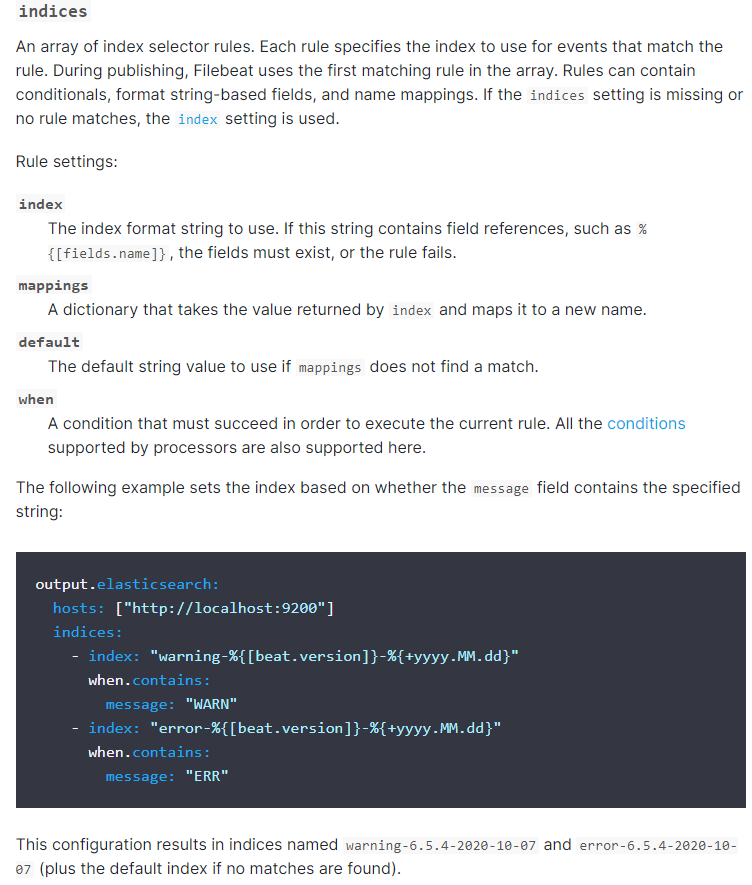
在使用filbeat收集日志输出到elasticsearch数据库时,可以使用indices参数来配置不同的日志输出到不同的索引中,官方文档及其配置例子如下:
(三)实际测试
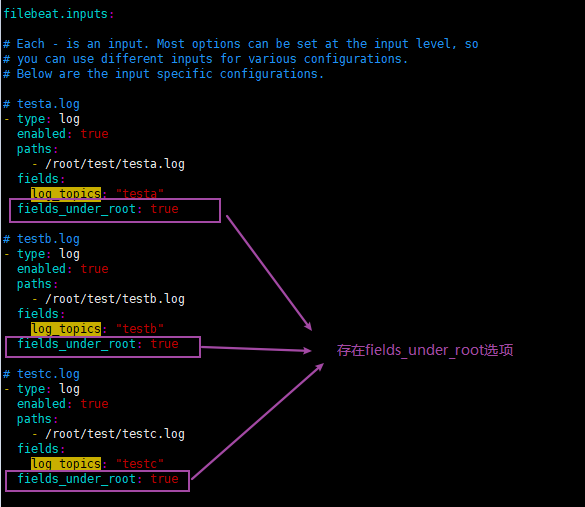
(3.1)输入存在fields_under_root: true选项
使用filebeat对3个日志testa.log、testb.log、testc.log进行数据抓取,要求:
- testa.log日志的数据存放到testa-log索引中
- testb.log日志的数据存放到testb-log索引中
- 其它(非testa.log和testb.log)的日志数据存放到test-other-log索引中
filebeat输入配置如下:
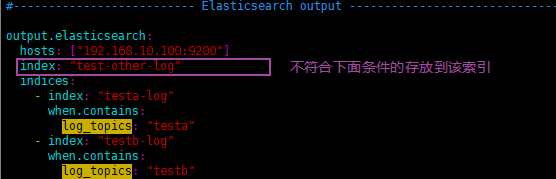
输出配置如下:
最终测试成功。
这里附一份完整的filebeat配置文件:

###################### Filebeat Configuration Example ######################### # This file is an example configuration file highlighting only the most common # options. The filebeat.reference.yml file from the same directory contains all the # supported options with more comments. You can use it as a reference. # # You can find the full configuration reference here: # https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/beats/filebeat/index.html # For more available modules and options, please see the filebeat.reference.yml sample # configuration file. #=========================== Filebeat inputs ============================= filebeat.inputs: # Each - is an input. Most options can be set at the input level, so # you can use different inputs for various configurations. # Below are the input specific configurations. # testa.log - type: log enabled: true paths: - /root/test/testa.log fields: log_topics: "testa" fields_under_root: true # testb.log - type: log enabled: true paths: - /root/test/testb.log fields: log_topics: "testb" fields_under_root: true # testc.log - type: log enabled: true paths: - /root/test/testc.log fields: log_topics: "testc" fields_under_root: true # Exclude lines. A list of regular expressions to match. It drops the lines that are # matching any regular expression from the list. #exclude_lines: ['^DBG'] # Include lines. A list of regular expressions to match. It exports the lines that are # matching any regular expression from the list. #include_lines: ['^ERR', '^WARN'] # Exclude files. A list of regular expressions to match. Filebeat drops the files that # are matching any regular expression from the list. By default, no files are dropped. #exclude_files: ['.gz$'] # Optional additional fields. These fields can be freely picked # to add additional information to the crawled log files for filtering #fields: # level: debug # review: 1 ### Multiline options # Multiline can be used for log messages spanning multiple lines. This is common # for Java Stack Traces or C-Line Continuation # The regexp Pattern that has to be matched. The example pattern matches all lines starting with [ #multiline.pattern: ^\[ # Defines if the pattern set under pattern should be negated or not. Default is false. #multiline.negate: false # Match can be set to "after" or "before". It is used to define if lines should be append to a pattern # that was (not) matched before or after or as long as a pattern is not matched based on negate. # Note: After is the equivalent to previous and before is the equivalent to to next in Logstash #multiline.match: after #============================= Filebeat modules =============================== filebeat.config.modules: # Glob pattern for configuration loading path: ${path.config}/modules.d/*.yml # Set to true to enable config reloading reload.enabled: true # Period on which files under path should be checked for changes #reload.period: 10s #==================== Elasticsearch template setting ========================== setup.template.settings: index.number_of_shards: 1 #index.codec: best_compression #_source.enabled: false setup.template.name: "prod-file*" setup.template.pattern: "prod-file*" setup.ilm.enabled: false #================================ General ===================================== # The name of the shipper that publishes the network data. It can be used to group # all the transactions sent by a single shipper in the web interface. #name: # The tags of the shipper are included in their own field with each # transaction published. #tags: ["service-X", "web-tier"] # Optional fields that you can specify to add additional information to the # output. #fields: # env: staging #============================== Dashboards ===================================== # These settings control loading the sample dashboards to the Kibana index. Loading # the dashboards is disabled by default and can be enabled either by setting the # options here or by using the `setup` command. #setup.dashboards.enabled: false # The URL from where to download the dashboards archive. By default this URL # has a value which is computed based on the Beat name and version. For released # versions, this URL points to the dashboard archive on the artifacts.elastic.co # website. #setup.dashboards.url: #============================== Kibana ===================================== # Starting with Beats version 6.0.0, the dashboards are loaded via the Kibana API. # This requires a Kibana endpoint configuration. setup.kibana: # Kibana Host # Scheme and port can be left out and will be set to the default (http and 5601) # In case you specify and additional path, the scheme is required: http://localhost:5601/path # IPv6 addresses should always be defined as: https://[2001:db8::1]:5601 #host: "localhost:5601" # Kibana Space ID # ID of the Kibana Space into which the dashboards should be loaded. By default, # the Default Space will be used. #space.id: #============================= Elastic Cloud ================================== # These settings simplify using Filebeat with the Elastic Cloud (https://cloud.elastic.co/). # The cloud.id setting overwrites the `output.elasticsearch.hosts` and # `setup.kibana.host` options. # You can find the `cloud.id` in the Elastic Cloud web UI. #cloud.id: # The cloud.auth setting overwrites the `output.elasticsearch.username` and # `output.elasticsearch.password` settings. The format is `<user>:<pass>`. #cloud.auth: #================================ Outputs ===================================== # Configure what output to use when sending the data collected by the beat. #-------------------------- Elasticsearch output ------------------------------ #output.elasticsearch: # hosts: ["192.168.10.30:9200"] # index: "testlog-666" #output.elasticsearch: # hosts: ["192.168.10.30:9200"] # indices: # - index: "testa-log" # when.contains: # log_topics: "testa" # - index: "testb-log" # when.contains: # log_topics: "testb" output.elasticsearch: hosts: ["192.168.10.100:9200"] index: "test-other-log" indices: - index: "testa-log" when.contains: log_topics: "testa" - index: "testb-log" when.contains: log_topics: "testb" #----------------------------- Logstash output -------------------------------- #output.logstash: # The Logstash hosts #hosts: ["localhost:5044"] # Optional SSL. By default is off. # List of root certificates for HTTPS server verifications #ssl.certificate_authorities: ["/etc/pki/root/ca.pem"] # Certificate for SSL client authentication #ssl.certificate: "/etc/pki/client/cert.pem" # Client Certificate Key #ssl.key: "/etc/pki/client/cert.key" #================================ Processors ===================================== # Configure processors to enhance or manipulate events generated by the beat. #================================ Logging ===================================== # Sets log level. The default log level is info. # Available log levels are: error, warning, info, debug #logging.level: debug # At debug level, you can selectively enable logging only for some components. # To enable all selectors use ["*"]. Examples of other selectors are "beat", # "publish", "service". #logging.selectors: ["*"] #============================== Xpack Monitoring =============================== # filebeat can export internal metrics to a central Elasticsearch monitoring # cluster. This requires xpack monitoring to be enabled in Elasticsearch. The # reporting is disabled by default. # Set to true to enable the monitoring reporter. #monitoring.enabled: false # Uncomment to send the metrics to Elasticsearch. Most settings from the # Elasticsearch output are accepted here as well. # Note that the settings should point to your Elasticsearch *monitoring* cluster. # Any setting that is not set is automatically inherited from the Elasticsearch # output configuration, so if you have the Elasticsearch output configured such # that it is pointing to your Elasticsearch monitoring cluster, you can simply # uncomment the following line. #monitoring.elasticsearch: #================================= Migration ================================== # This allows to enable 6.7 migration aliases #migration.6_to_7.enabled: true
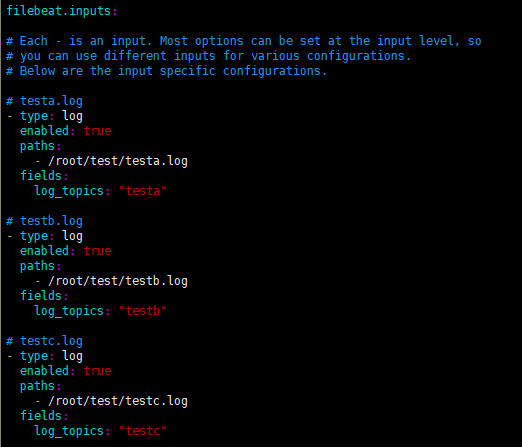
(3.2)输入不存在fields_under_root: true选项
filebeat输入配置如下:
输出配置如下:
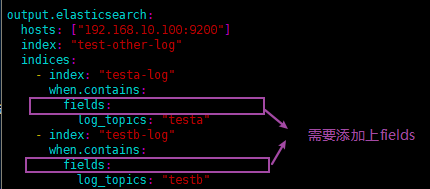
这里附一份完整的filebeat配置文件:

###################### Filebeat Configuration Example ######################### # This file is an example configuration file highlighting only the most common # options. The filebeat.reference.yml file from the same directory contains all the # supported options with more comments. You can use it as a reference. # # You can find the full configuration reference here: # https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/beats/filebeat/index.html # For more available modules and options, please see the filebeat.reference.yml sample # configuration file. #=========================== Filebeat inputs ============================= filebeat.inputs: # Each - is an input. Most options can be set at the input level, so # you can use different inputs for various configurations. # Below are the input specific configurations. # testa.log - type: log enabled: true paths: - /root/test/testa.log fields: log_topics: "testa" # testb.log - type: log enabled: true paths: - /root/test/testb.log fields: log_topics: "testb" # testc.log - type: log enabled: true paths: - /root/test/testc.log fields: log_topics: "testc" # Exclude lines. A list of regular expressions to match. It drops the lines that are # matching any regular expression from the list. #exclude_lines: ['^DBG'] # Include lines. A list of regular expressions to match. It exports the lines that are # matching any regular expression from the list. #include_lines: ['^ERR', '^WARN'] # Exclude files. A list of regular expressions to match. Filebeat drops the files that # are matching any regular expression from the list. By default, no files are dropped. #exclude_files: ['.gz$'] # Optional additional fields. These fields can be freely picked # to add additional information to the crawled log files for filtering #fields: # level: debug # review: 1 ### Multiline options # Multiline can be used for log messages spanning multiple lines. This is common # for Java Stack Traces or C-Line Continuation # The regexp Pattern that has to be matched. The example pattern matches all lines starting with [ #multiline.pattern: ^\[ # Defines if the pattern set under pattern should be negated or not. Default is false. #multiline.negate: false # Match can be set to "after" or "before". It is used to define if lines should be append to a pattern # that was (not) matched before or after or as long as a pattern is not matched based on negate. # Note: After is the equivalent to previous and before is the equivalent to to next in Logstash #multiline.match: after #============================= Filebeat modules =============================== filebeat.config.modules: # Glob pattern for configuration loading path: ${path.config}/modules.d/*.yml # Set to true to enable config reloading reload.enabled: true # Period on which files under path should be checked for changes #reload.period: 10s #==================== Elasticsearch template setting ========================== setup.template.settings: index.number_of_shards: 1 #index.codec: best_compression #_source.enabled: false setup.template.name: "prod-file*" setup.template.pattern: "prod-file*" setup.ilm.enabled: false #================================ General ===================================== # The name of the shipper that publishes the network data. It can be used to group # all the transactions sent by a single shipper in the web interface. #name: # The tags of the shipper are included in their own field with each # transaction published. #tags: ["service-X", "web-tier"] # Optional fields that you can specify to add additional information to the # output. #fields: # env: staging #============================== Dashboards ===================================== # These settings control loading the sample dashboards to the Kibana index. Loading # the dashboards is disabled by default and can be enabled either by setting the # options here or by using the `setup` command. #setup.dashboards.enabled: false # The URL from where to download the dashboards archive. By default this URL # has a value which is computed based on the Beat name and version. For released # versions, this URL points to the dashboard archive on the artifacts.elastic.co # website. #setup.dashboards.url: #============================== Kibana ===================================== # Starting with Beats version 6.0.0, the dashboards are loaded via the Kibana API. # This requires a Kibana endpoint configuration. setup.kibana: # Kibana Host # Scheme and port can be left out and will be set to the default (http and 5601) # In case you specify and additional path, the scheme is required: http://localhost:5601/path # IPv6 addresses should always be defined as: https://[2001:db8::1]:5601 #host: "localhost:5601" # Kibana Space ID # ID of the Kibana Space into which the dashboards should be loaded. By default, # the Default Space will be used. #space.id: #============================= Elastic Cloud ================================== # These settings simplify using Filebeat with the Elastic Cloud (https://cloud.elastic.co/). # The cloud.id setting overwrites the `output.elasticsearch.hosts` and # `setup.kibana.host` options. # You can find the `cloud.id` in the Elastic Cloud web UI. #cloud.id: # The cloud.auth setting overwrites the `output.elasticsearch.username` and # `output.elasticsearch.password` settings. The format is `<user>:<pass>`. #cloud.auth: #================================ Outputs ===================================== # Configure what output to use when sending the data collected by the beat. #-------------------------- Elasticsearch output ------------------------------ #output.elasticsearch: # hosts: ["192.168.10.30:9200"] # index: "testlog-666" #output.elasticsearch: # hosts: ["192.168.10.30:9200"] # indices: # - index: "testa-log" # when.contains: # log_topics: "testa" # - index: "testb-log" # when.contains: # log_topics: "testb" output.elasticsearch: hosts: ["192.168.10.100:9200"] index: "test-other-log" indices: - index: "testa-log" when.contains: fields: log_topics: "testa" - index: "testb-log" when.contains: fields: log_topics: "testb" #----------------------------- Logstash output -------------------------------- #output.logstash: # The Logstash hosts #hosts: ["localhost:5044"] # Optional SSL. By default is off. # List of root certificates for HTTPS server verifications #ssl.certificate_authorities: ["/etc/pki/root/ca.pem"] # Certificate for SSL client authentication #ssl.certificate: "/etc/pki/client/cert.pem" # Client Certificate Key #ssl.key: "/etc/pki/client/cert.key" #================================ Processors ===================================== # Configure processors to enhance or manipulate events generated by the beat. #================================ Logging ===================================== # Sets log level. The default log level is info. # Available log levels are: error, warning, info, debug #logging.level: debug # At debug level, you can selectively enable logging only for some components. # To enable all selectors use ["*"]. Examples of other selectors are "beat", # "publish", "service". #logging.selectors: ["*"] #============================== Xpack Monitoring =============================== # filebeat can export internal metrics to a central Elasticsearch monitoring # cluster. This requires xpack monitoring to be enabled in Elasticsearch. The # reporting is disabled by default. # Set to true to enable the monitoring reporter. #monitoring.enabled: false # Uncomment to send the metrics to Elasticsearch. Most settings from the # Elasticsearch output are accepted here as well. # Note that the settings should point to your Elasticsearch *monitoring* cluster. # Any setting that is not set is automatically inherited from the Elasticsearch # output configuration, so if you have the Elasticsearch output configured such # that it is pointing to your Elasticsearch monitoring cluster, you can simply # uncomment the following line. #monitoring.elasticsearch: #================================= Migration ================================== # This allows to enable 6.7 migration aliases #migration.6_to_7.enabled: true
其它说明:为什么需要特别注意fields_under_root参数
fields_under_root参数定义如下:
- 如果值为ture,那么fields存储在输出文档的顶级位置,如果与filebeat中字段冲突,自定义字段会覆盖其他字段
- 如果值为false或者未设置,那么fields存储在输出文档的子位置。
如下:
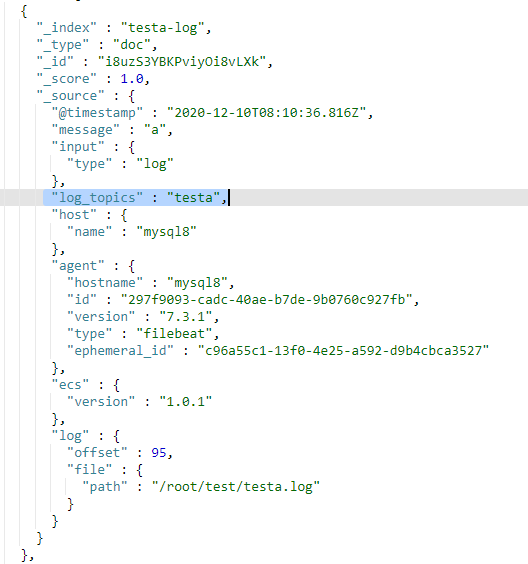
(1)fields_under_root:true
此时在filebeat的input部分定义的字段log_topics是一个顶级字段。
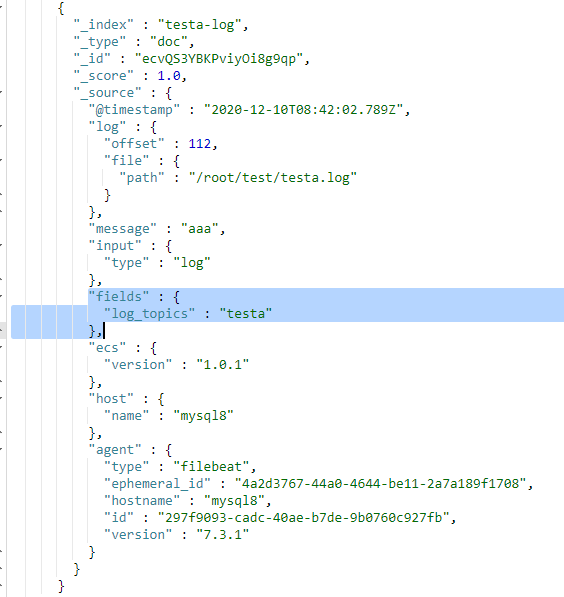
(2)fields_under_root:false或者未设置
此时在filebeat的input部分定义的字段log_topics是fields字段的子字段。
【完】
分类:
--600 ELK Stack





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· 三行代码完成国际化适配,妙~啊~
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?