148. 排序链表
给你链表的头结点 head ,请将其按 升序 排列并返回 排序后的链表 。
输入:head = [4,2,1,3]
输出:[1,2,3,4]
> 思路1:
采用二路归并排序,分为递归和迭代 两种方法。
递归采用快慢指针,找到链表的中点,断开,然后对两条链表进行二路归并
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head) {
if(!head || !head->next) return head;
ListNode* pre = head, *slow = head, *fast = head;
while(fast && fast->next) {
pre = slow;
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
pre->next = nullptr;
return mergeTwoList(sortList(head), sortList(slow));
}
ListNode* mergeTwoList(ListNode* h1, ListNode* h2) {
if(!h1) return h2;
if(!h2) return h1;
if(h1->val < h2->val) {
h1->next = mergeTwoList(h1->next, h2);
return h1;
}
else {
h2->next = mergeTwoList(h1, h2->next);
return h2;
}
}
};
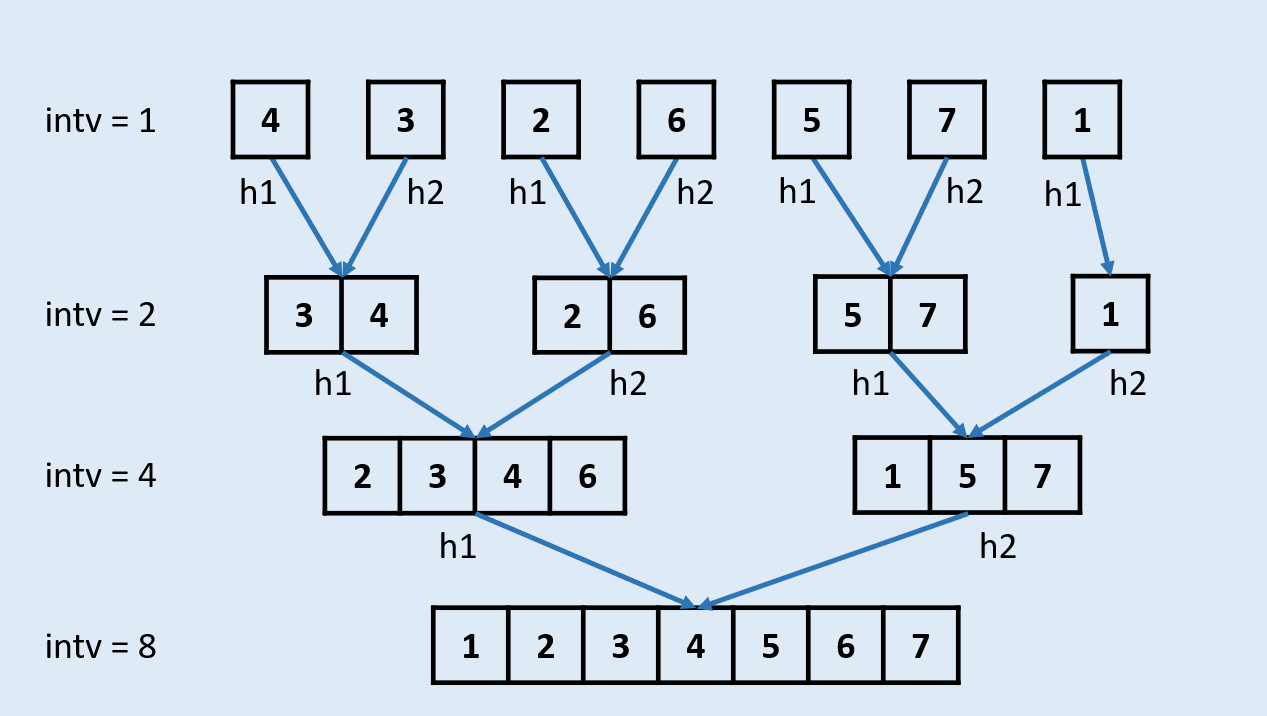
代码中的tail节点用来连接被切断的节点
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode dummyHead(0);
dummyHead.next = head;
auto p = head;
int length = 0;
while (p) {
++length;
p = p->next;
}
for (int size = 1; size < length; size <<= 1) {
auto cur = dummyHead.next;
auto tail = &dummyHead;
while (cur) {
auto left = cur;
auto right = cut(left, size); // left->@->@ right->@->@->@...
cur = cut(right, size); // left->@->@ right->@->@ cur->@->...
tail->next = merge(left, right);
while (tail->next) {
tail = tail->next;
}
}
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
ListNode* cut(ListNode* head, int n) {
auto p = head;
while (--n && p) {
p = p->next;
}
if (!p) return nullptr;
auto next = p->next;
p->next = nullptr;
return next;
}
ListNode* merge(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
ListNode dummyHead(0);
auto p = &dummyHead;
while (l1 && l2) {
if (l1->val < l2->val) {
p->next = l1;
p = l1;
l1 = l1->next;
} else {
p->next = l2;
p = l2;
l2 = l2->next;
}
}
p->next = l1 ? l1 : l2;
return dummyHead.next;
}
};




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理