Spring 中的接口知识整理
本想每个小知识一篇随笔,但是那样,看起来有些单薄,所以,就放在一片文章里了。而且,以后还会慢慢在最后不断的追加。
目录:
FactoryBean
BeanPostProcessor
1.FactoryBean
FactoryBean接口,它在Spring框架源码内部,被大量使用,如使用AOP创建bean的代理时,使用了ProxyFactoryBean;从JNDI中查找对象时,使用了JndiObjectFactoryBean。
它在框架外,很少使用。但是为了学习,也得研究研究,您说是不?
它怎么使用?首先看看构造。
1 public interface FactoryBean<T> {
// 返回的是这个工厂管理的对象的实例 2 T getObject() throws Exception; 3
// 返回的是工厂创建的对象的类型 4 Class<?> getObjectType(); 5 6 boolean isSingleton(); 7 8 }
上个例子,看具体东西。
1 public class Tool { 2 3 4 private int id; 5 public Tool(int id) { 6 this.id = id; 7 } 8 public int getId() { 9 return id; 10 } 11 12 public void setId(int id) { 13 this.id = id; 14 } 15 }
1 public class ToolFactory implements FactoryBean<Tool> { 2 3 private int factoryId; 4 private int toolId; 5
// 创建的是Tool的对象 6 @Override 7 public Tool getObject() throws Exception { 8 return new Tool(toolId); 9 } 10 11 @Override 12 public Class<?> getObjectType() { 13 return Tool.class; 14 } 15 16 @Override 17 public boolean isSingleton() { 18 return false; 19 } 20 21 public int getFactoryId() { 22 return factoryId; 23 } 24 25 public int getToolId() { 26 return toolId; 27 } 28 29 public void setFactoryId(int factoryId) { 30 this.factoryId = factoryId; 31 } 32 33 public void setToolId(int toolId) { 34 this.toolId = toolId; 35 } 36 37 }
1 public class Test { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 @SuppressWarnings("resource") 5 ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beaFactoryTest.xml"); 6 Tool tool = (Tool) context.getBean("tool");
// 在名字前面加 & 表示要得到工厂类的bean 7 ToolFactory tool2 = (ToolFactory) context.getBean("&tool"); 8 System.out.println("Tool Id is " + tool.getId()); 9 System.out.println("ToolFactory Id is " + tool2.getFactoryId()); 10 11 } 12 }
1 <bean id="tool" class="com.lee.demo.beanfactory.ToolFactory"> 2 <property name="factoryId" value="9090"/> 3 <property name="toolId" value="108"/> 4 </bean>
最后执行结果:
Tool Id is 108
ToolFactory Id is 9090
2.BeanPostProcessor
它叫bean后处理器,也就是处理bean,它针对所有的bean,在初始化前后,对bean进行操作。主要内容我会在例子中描述。
例子:
1 public class HelloWorld { 2 private String message; 3 4 public void setMessage(String message) { 5 this.message = message; 6 } 7 8 public void getMessage() { 9 System.out.println("Your Message : " + message); 10 } 11
// 加上init方法和destory方法,是为了在后面验证他们和postProcessBeforeInitialization postProcessAfterInitialization 执行的先后顺序 12 public void init() { 13 System.out.println("Bean is going through init."); 14 } 15 16 public void destroy() { 17 System.out.println("Bean will destroy now."); 18 } 19 }
1 public class InitHelloWorld implements BeanPostProcessor { 2
// BeanPostProcessor 接口中主要是下面两个方法 初始化前的后处理 初始化后的后处理 3 @Override 4 public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { 5 6 System.out.println("BeforeInitialization : " + beanName); 7 return bean; // you can return any other object as well 8 } 9 10 @Override 11 public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { 12 13 System.out.println("AfterInitialization : " + beanName); 14 return bean; // you can return any other object as well 15 } 16 17 }
Test.java
1 public class Test { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 @SuppressWarnings("resource") 5 AbstractApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beaFactoryTest.xml"); 6 HelloWorld obj = (HelloWorld) context.getBean("helloWorld"); 7 obj.getMessage();
// 注册钩子方法 8 context.registerShutdownHook(); 9 } 10 }
查看源码:
1 @Override
// 在JVM运行期间,注册一个钩子关闭方法,关闭掉这个context。实际的关闭程序的操作,被代理给doClose方法。 2 public void registerShutdownHook() { 3 if (this.shutdownHook == null) { 4 // No shutdown hook registered yet. 5 this.shutdownHook = new Thread() { 6 @Override 7 public void run() { 8 doClose(); 9 } 10 }; 11 Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(this.shutdownHook); 12 } 13 }
xml文件
1 <bean id = "helloWorld" class = "com.lee.demo.beanfactory.HelloWorld" 2 init-method = "init" destroy-method = "destroy"> 3 <property name = "message" value = "Hello World!"/> 4 </bean> 5 6 <bean class = "com.lee.demo.beanfactory.InitHelloWorld" />
执行结果:
1 BeforeInitialization : helloWorld 2 Bean is going through init. 3 AfterInitialization : helloWorld 4 Your Message : Hello World! 5 [org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext] - Closing org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext@6ae40994: startup date [Thu May 17 23:31:53 JST 2018]; root of context hierarchy 6 Bean will destroy now.
在这里大致说一下Spring的实例化过程:
实例化Bean对象→设置对象属性→检查Aware相关接口并设置相关依赖→BeanPostProcessor前置处理→检查是否是InitializingBean以决定是否调用afterPropertiesSet方法→
检查是否配置有自定义的init-method方法→BeanPostProcessor后置处理→是否实现DisposableBean接口→是否配置有自定义的destroy方法
3.Aware接口
它是干什么用的呢?作用就是通过上下文(Context)可以获得当前环境。看看它的接口:
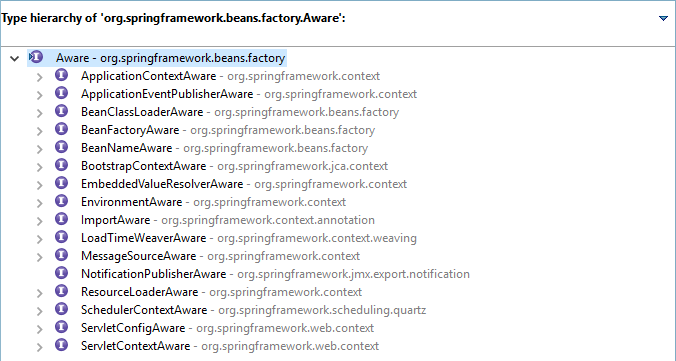
我们拿BeanNameAware来举个例子。
1 public class User implements GetNameAware { 2 3 private String id; 4 private String name; 5 private String address; 6 @Override 7 public void setBeanName(String name) { 8 this.id = name; 9 } 10 public String getId() { 11 return id; 12 } 13 public String getName() { 14 return name; 15 } 16 public String getAddress() { 17 return address; 18 } 19 public void setId(String id) { 20 this.id = id; 21 } 22 public void setName(String name) { 23 this.name = name; 24 } 25 public void setAddress(String address) { 26 this.address = address; 27 } 28 29 }
1 public class User2 { 2 3 private String id; 4 private String name; 5 private String address; 6 public String getId() { 7 return id; 8 } 9 public String getName() { 10 return name; 11 } 12 public String getAddress() { 13 return address; 14 } 15 public void setId(String id) { 16 this.id = id; 17 } 18 public void setName(String name) { 19 this.name = name; 20 } 21 public void setAddress(String address) { 22 this.address = address; 23 } 24 25 }
1 public interface GetNameAware extends BeanNameAware { 2 3 4 }
1 public class Test { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beaFactoryTest.xml"); 4 User user = (User) ctx.getBean("user1"); 5 User2 user2 = (User2) ctx.getBean("user2"); 6 System.out.println("user id " + user.getId() + " user name " + user.getName() + " user address " + user.getAddress()); 7 System.out.println("========================================"); 8 System.out.println("user2 id " + user2.getId() + " user2 name " + user2.getName() + " user2 address " + user2.getAddress()); 9 } 10 }
1 <bean id="user1" class="com.lee.demo.aware.User"> 2 <property name="name" value="lee"/> 3 <property name="address" value="China"/> 4 </bean> 5 6 <bean id="user2" class="com.lee.demo.aware.User2"> 7 <property name="name" value="lin"/> 8 <property name="address" value="Tokyo"/> 9 </bean>
执行结果(user id 因为继承了GetNameAware接口,对BeanName进行了设置):
1 user id user1 user name lee user address China 2 ======================================== 3 user2 id null user2 name lin user2 address Tokyo


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号