(原)FFmpeg.c源码学习笔记1
原出处: https://www.cnblogs.com/lihaiping/p/12771234.html
命令输出格式的解析
当对文件命指定%d.jpg这种形式的时候,ffmpeg.c中是如何处理的?我阅读了ffmpeg.c中open_files()和open_output_file(),以及write_packet()相关函数,均未找到以计数命名相关线索,硬生生读了几遍,找了几遍,都没找到,当时好奇怪。
按道理,如果我们来写这种场景处理的话,可能大家都会以计数形式,打开文件,写完,然后关闭这样的流程走。于是我继续跟代码,看看ffmpeg.c中的open_out_file()函数干了些啥,结果发现ffmpeg是直接将%d.jpg这个输出文件直接传入底层了,我们来看下流程:
err = avformat_alloc_output_context2(&oc, NULL, o->format, filename);
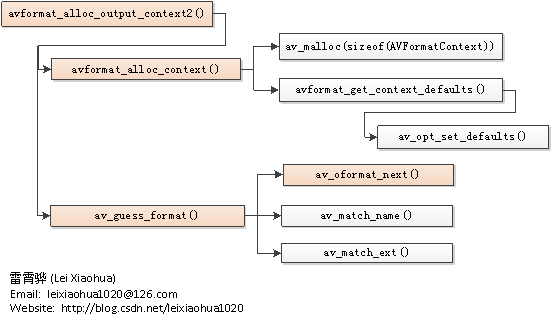
其中在av_guess_format()函数中,有这样一段代码:

AVOutputFormat *av_guess_format(const char *short_name, const char *filename, const char *mime_type) { const AVOutputFormat *fmt = NULL; AVOutputFormat *fmt_found = NULL; void *i = 0; int score_max, score; /* specific test for image sequences */ #if CONFIG_IMAGE2_MUXER //这里是第一步,当我们使用-f image2 %xxd.jpg这种的时候,会进入这种选项 if (!short_name && filename && av_filename_number_test(filename) && ff_guess_image2_codec(filename) != AV_CODEC_ID_NONE) { return av_guess_format("image2", NULL, NULL); } #endif /* Find the proper file type. */ score_max = 0; while ((fmt = av_muxer_iterate(&i))) {//这里会对muxer_list进行遍历 score = 0; if (fmt->name && short_name && av_match_name(short_name, fmt->name)) score += 100; if (fmt->mime_type && mime_type && !strcmp(fmt->mime_type, mime_type)) score += 10; if (filename && fmt->extensions && av_match_ext(filename, fmt->extensions)) { score += 5; } if (score > score_max) { score_max = score; fmt_found = (AVOutputFormat*)fmt; } } return fmt_found; }
经过这个步骤以后,我们就可以找到ff_image2_muxer这个AVOutputFormat了。
然后我再看下这个muxer中的write_packet()的相关内容:

static int write_packet(AVFormatContext *s, AVPacket *pkt) { VideoMuxData *img = s->priv_data; AVIOContext *pb[4]; char filename[1024]; AVCodecParameters *par = s->streams[pkt->stream_index]->codecpar; const AVPixFmtDescriptor *desc = av_pix_fmt_desc_get(par->format); int i; int nb_renames = 0; if (!img->is_pipe) { if (img->update) { av_strlcpy(filename, img->path, sizeof(filename)); } else if (img->use_strftime) { //当我们指定-strftime 1的时候,可以输出以当前时间格式的文件名 time_t now0; struct tm *tm, tmpbuf; time(&now0); tm = localtime_r(&now0, &tmpbuf); if (!strftime(filename, sizeof(filename), img->path, tm)) { av_log(s, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Could not get frame filename with strftime\n"); return AVERROR(EINVAL); } } else if (img->frame_pts) {//可以输出以帧的pts命名的文件 if (av_get_frame_filename2(filename, sizeof(filename), img->path, pkt->pts, AV_FRAME_FILENAME_FLAGS_MULTIPLE) < 0) { av_log(s, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Cannot write filename by pts of the frames."); return AVERROR(EINVAL); } } else if (av_get_frame_filename2(filename, sizeof(filename), img->path, img->img_number, AV_FRAME_FILENAME_FLAGS_MULTIPLE) < 0 && img->img_number > 1) {//这个就是我们以%d这种格式的 av_log(s, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Could not get frame filename number %d from pattern '%s' (either set update or use a pattern like %%03d within the filename pattern)\n", img->img_number, img->path); return AVERROR(EINVAL); } for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) { snprintf(img->tmp[i], sizeof(img->tmp[i]), "%s.tmp", filename); av_strlcpy(img->target[i], filename, sizeof(img->target[i])); if (s->io_open(s, &pb[i], img->use_rename ? img->tmp[i] : filename, AVIO_FLAG_WRITE, NULL) < 0) { av_log(s, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Could not open file : %s\n", img->use_rename ? img->tmp[i] : filename); return AVERROR(EIO); } if (!img->split_planes || i+1 >= desc->nb_components) break; filename[strlen(filename) - 1] = "UVAx"[i]; } if (img->use_rename) nb_renames = i + 1; } else { pb[0] = s->pb; } if (img->split_planes) { int ysize = par->width * par->height; int usize = AV_CEIL_RSHIFT(par->width, desc->log2_chroma_w) * AV_CEIL_RSHIFT(par->height, desc->log2_chroma_h); if (desc->comp[0].depth >= 9) { ysize *= 2; usize *= 2; } avio_write(pb[0], pkt->data , ysize); avio_write(pb[1], pkt->data + ysize , usize); avio_write(pb[2], pkt->data + ysize + usize, usize); ff_format_io_close(s, &pb[1]); ff_format_io_close(s, &pb[2]); if (desc->nb_components > 3) { avio_write(pb[3], pkt->data + ysize + 2*usize, ysize); ff_format_io_close(s, &pb[3]); } } else if (img->muxer) { int ret; AVStream *st; AVPacket pkt2 = {0}; AVFormatContext *fmt = NULL; av_assert0(!img->split_planes); ret = avformat_alloc_output_context2(&fmt, NULL, img->muxer, s->url); if (ret < 0) return ret; st = avformat_new_stream(fmt, NULL); if (!st) { avformat_free_context(fmt); return AVERROR(ENOMEM); } st->id = pkt->stream_index; fmt->pb = pb[0]; if ((ret = av_packet_ref(&pkt2, pkt)) < 0 || (ret = avcodec_parameters_copy(st->codecpar, s->streams[0]->codecpar)) < 0 || (ret = avformat_write_header(fmt, NULL)) < 0 || (ret = av_interleaved_write_frame(fmt, &pkt2)) < 0 || (ret = av_write_trailer(fmt)) < 0) { av_packet_unref(&pkt2); avformat_free_context(fmt); return ret; } av_packet_unref(&pkt2); avformat_free_context(fmt); } else { avio_write(pb[0], pkt->data, pkt->size); } avio_flush(pb[0]); if (!img->is_pipe) { ff_format_io_close(s, &pb[0]);//关闭输出文件 for (i = 0; i < nb_renames; i++) { int ret = ff_rename(img->tmp[i], img->target[i], s);//重命名 if (ret < 0) return ret; } } img->img_number++;//计数 return 0; }





