线程,有时被称为轻量级进程,是程序执行流的最小单元
线程是程序中一个单一的顺序控制流程。进程内一个相对独立的、可调度的执行单元,是系统独立调度和分派CPU的基本单位指进行中的程序的调度单位。在单个程序中同时运行多个线程完成不同的工作,称为多线程。
python中多个cpu无法同时处理一个进程或其子进程,多个cpu可以同时处理多个线程
1 import time
2 def f1(arg):
3 time.sleep(1)
4 print(arg)
5 import threading
6 t = threading.Thread(target = f1,args = (123,))
7 #t.setDaemon(True)#表示主线程不等子线程
8 t.start()#不代表当前线程会立即被执行
9 t.join(2) #表示主线程到此等待。。。直到子线程执行完成#参数,表示住线程再次最多等待n秒
10
11 print('end')
12 #一秒后显示
13 >>>123
14 >>>end
15
16 import time
17 def f1(arg):
18 time.sleep(1)
19 print(arg)
20 import threading
21 t = threading.Thread(target = f1,args = (123,))
22 t.setDaemon(True)#表示主线程不等子线程
23 t.start()#不代表当前线程会立即被执行
24 #t.join(2) #表示主线程到此等待。。。直到子线程执行完成#参数,表示住线程再次最多等待n秒
25
26 print('end')
27 #立即显示
28 >>>end
#我们可以写个类继承threading模块的Thead类并加入自定义的构造方法,
#用来添加新功能
class MyThread(threading.Thread):
def __init__(self,func,args):
self.func =func
self.args = args
#继承父类的构造方法
super(MyThread,self).__init__()
def run(self):
self.func(self.args)
def f2(arg):
print(arg)
obj = MyThread(f2,123)
obj.start()
>>>123
队列
1 #Python中,队列是线程间最常用的交换数据的形式。Queue模块是提供队列操作的模块,不同的队列应用在不同的场景中
2 #queue.Queue先进先出队列
3 #queue.LifoQueue,后进先出队列
4 #queue.PriorityQueue,优先级队列
5 #queue.deque,双向队列
6
7 import queue
8 q = queue.Queue(3)#参数为队列中最大个数
9 print(q.empty())#判断是否为空
10 >>>True
11 print(q.full())#判断队列是否已满
12 >>>False
13 q.put(11)
14 >>>传入元素
15 q.put(22)
16 >>>传入元素
17 #q.put(33,block=False)#最大值为2传入第三个的时候默认阻塞
18 print(q.qsize())#真实队列剩余个数
19 >>>2
20 print(q.maxsize)#最大个数
21 >>>3
22 print(q.get())#取值当队列中取完之后继续取得时候阻塞
23 >>>11
24 q.task_done()#任务完成
25 print(q.get())#取值
26 >>>22
27 q.task_done()#任务完成,用于释放队列
28 q.join()#不带这个的时候程序完成后释放队列,加上的时候阻塞
1 #先进后出队列
2 q = queue.LifoQueue()
3 q.put(123)
4 q.put(456)
5 print(q.get())
6 #>>>456
7
8 #优先级队列
9 q = queue.PriorityQueue()
10 q.put((1,'alex1'))
11 q.put((1,'alex2'))
12 q.put((3,'alex3'))
13 print(q.get())
14 >>>(1, 'alex1')
15
16
17 #双向队列
18 q= queue.deque()
19 q.append(123)
20 q.append(333)
21 q.appendleft(456)
22 #从左侧插入队列
23 print(q.pop())#从右侧取值
24 print(q.popleft())#从左侧取值
25 >>>333
26 >>>456
生产者消费者模型
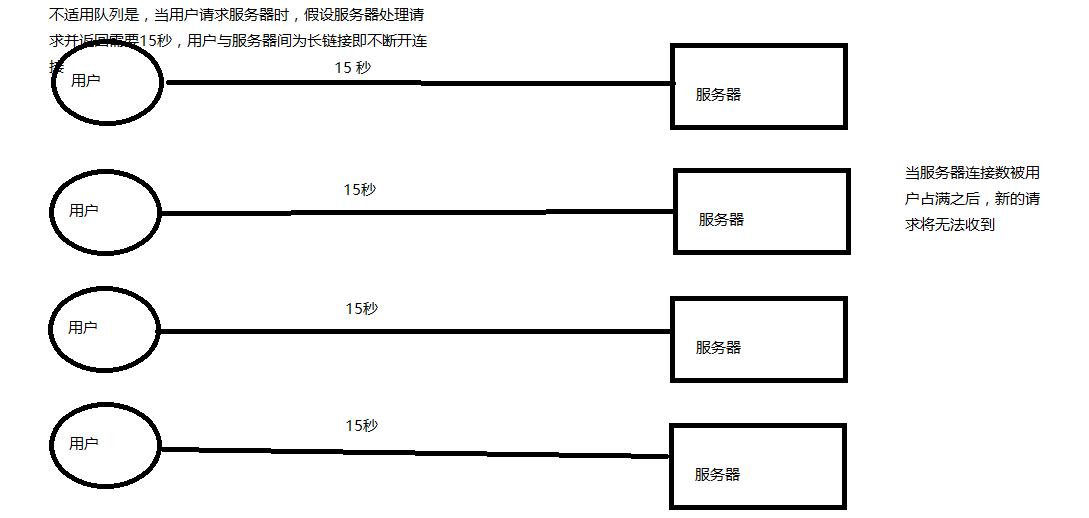
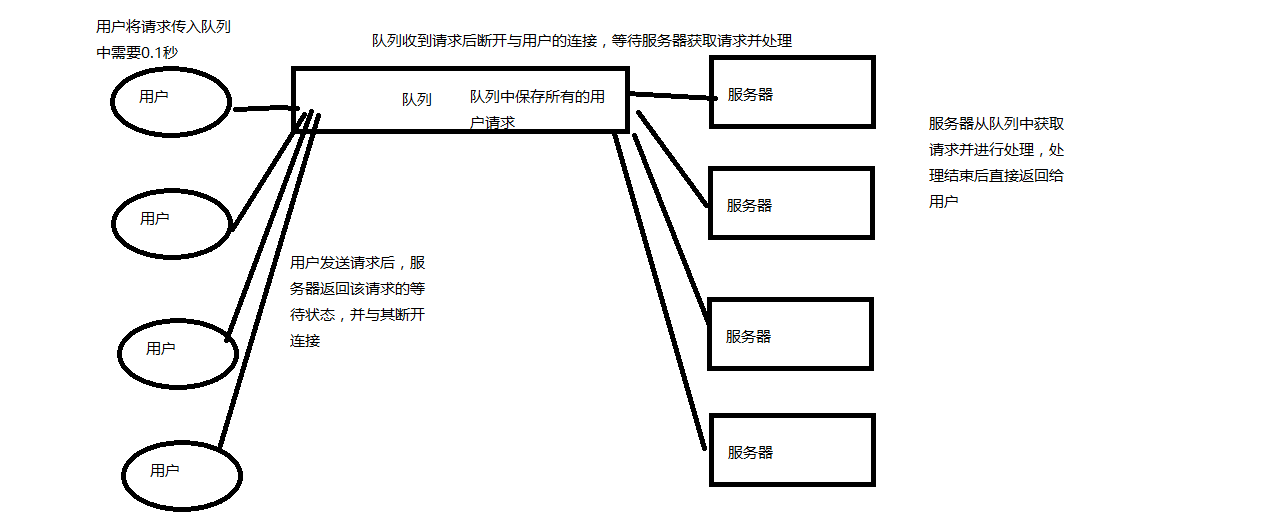
#生产者消费者模型
import queue
import threading
import time
#创建队列
q = queue.Queue(50)
#定义消费者
def productor(arg):
'''
买票
:param arg:
:return:
'''
while True:
q.put(str(arg) + '号产生订单')#提交到队列
#创建300个线程发送请求
for i in range(300):#300个线程同时提交订单相当于300个人同时提交订单
t = threading.Thread(target= productor,args= (i,))
t.start()
#定义生产者
def consumer(arg):
'''
服务器后台
:param arg:
:return:
'''
while True:
print(str(arg) + '处理了'+q.get())#进程从队列中取订单进行处理
#3个线程同时工作
for j in range(3):
t = threading.Thread(target=consumer,args=(j,))
t.start()
线程锁
1 #线程锁
2 import threading
3 import time
4
5 NUM = 10
6 #线程锁线程执行进程通过的接口,用来限制多个线程同时修改一个数据
7 def func(l):
8 global NUM
9 #上锁
10 l.acquire()
11 NUM -=1
12 time.sleep(2)
13 print(NUM)
14 #开锁
15 l.release()
16 #单层锁
17 lock = threading.Lock()
18 #多层锁
19 #lock = threading.RLock()
20
21 for i in range(30):
22 t = threading.Thread(target=func,args = (lock,))
23 t.start()
信号量
1 #设置可通过线程个数
2 import threading
3 import time
4 NUM =10
5 def func(i,l):
6 global NUM
7 #上锁
8 l.acquire()
9 NUM -=1
10 time.sleep(2)
11 print(NUM,i)
12 #开锁
13 l.release()
14
15 #调用信号量设置每次多少个线程处理进程
16 lock = threading.BoundedSemaphore(5)
17
18 for i in range(30):
19 t = threading.Thread(target= func,args=(i,lock,))
20 t.start()
1 #event相当于红绿灯,通过一个标识来批量管理线程
2 import threading
3
4 def func(i,e):
5 print(i)
6 e.wait()#检测时什么灯,如果是红灯,停,绿灯,行
7 print(i+100)
8
9 event = threading.Event()
10
11 for i in range(10):
12 t = threading.Thread(target= func,args = (i,event,))
13 t.start()
14
15 event.clear()#设置成红灯
16 inp = input('>>>')
17 if inp == '1':
18 event.set()#设置成绿灯
1 #根据条件限定线程的执行
2 #!/usr/bin/env python
3 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
4 #设置条件设置线程数第一种方式
5 import threading
6 def func(i,con):
7 print(i)
8 con.acquire()
9 con.wait()
10 print(i+100)
11 con.release()
12
13 c = threading.Condition()
14 for i in range(10):
15 t = threading.Thread(target=func,args=(i,c))
16 t.start()
17
18 while True:
19 inp = input('>>>')
20 if inp == 'q':
21 break
22 c.acquire()
23 c.notify(int(inp))#根据输入设置通过几个线程数
24 c.release()
25
26 #第二种
27 import threading
28
29 def condition():
30 ret =False
31 r = input('>>>')
32 if r == 'true':
33 ret =True
34 else:
35 ret = False
36 return ret
37
38 def func(i,con):
39 print(i)
40 con.acquire()
41 # 设置condition函数为条件返回true继续运行,条件不成立则不执行此线程
42 con.wait_for(condition)
43 print(i+100)
44 con.release()
45
46 c = threading.Condition()
47 for i in range(10):
48 t = threading.Thread(target=func,args=(i,c))
49 t.start()
Timer
1 #定时器
2 form threading import Time
3
4 def hello():
5 print('hello')
6 t = Timer(1,hello)#一秒后执行
7 t.start()
线程池
1 import queue
2 import threading
3 import time
4
5 class ThreadPool:
6 def __init__(self,maxsize):
7 self.maxsize = maxsize
8 self._q = queue.Queue(maxsize)#创建队列
9 for i in range(maxsize):
10 self._q.put(threading.Thread)#将创建线程的类放入队列
11
12 def get_thread(self):
13 return self._q.get()#获取队列的值
14
15 def add_thread(self):
16 self._q.put(threading.Thread)
17
18 pool = ThreadPool(5)#设置线程池
19 def task(arg,p):
20 print(arg)
21 time.sleep(1)
22 p.add_thread()#添加新的线程
23
24 for i in range(100):
25 t = pool.get_thread()#当获取5次后,阻塞在此
26 obj = t(target = task,args = (i,pool,))#创建线程调用函数task
27 obj.start()
1 #第二种创建线程池方式
2 #!/usr/bin/env python
3 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
4
5
6 import queue
7 import threading
8 import contextlib
9 import time
10
11 StopEvent = object()
12 class Pool:
13 def __init__(self,max_num,max_task_num=None):
14 if max_task_num:
15 self.q=queue.Queue(max_task_num)#创建队列并指定接受任务最大数
16 else:
17 self.q = queue.Queue()#不指定参数
18 self.max_num = max_num#最多有多少个线程
19 self.cancel = False
20 self.terminal = False
21 self.generate_list = []#已创建线程
22 self.free_list = []#空闲线程
23
24 def run(self,func,args,callback = None):#接收参数
25 if self.cancel:
26 return
27 if len(self.free_list) ==0 and len(self.generate_list) < self.max_num:#当没有空闲线程并且,已创建的线程没有达到最大值
28 self.generate_thread() #创建新线程调generte_thread函数
29 w = (func,args,callback,)#将参数传入队列中
30 self.q.put(w)#将参数作为元组传入队列中
31
32 def generate_thread(self):
33 '''
34 创建线程
35 :return:
36 '''
37 t = threading.Thread(target=self.call)#执行call函数
38 t.start()
39 def call(self):
40 '''
41 让线程执行任务
42 :return:
43 '''
44 current_thread = threading.currentThread#获取当前线程数
45 self.generate_list.append(current_thread)#传入已创建线程列表中
46 event =self.q.get()#获取任务
47 while event != StopEvent:#如果任务不为空
48 func,args,callback = event#将传过来的参数赋值给event
49 try:
50 result = func(args)#执行action(i)
51 success = True#任务执行成功
52 except Exception as e:
53 success = False#action任务执行失败
54 if callback is not None:
55 try:
56 callback(success,result)
57 except Exception as c:
58 pass
59 #event.self.q.get()#继续去任务,当存在任务则执行action不存在则删除当前进程
60 with self.worker_state(self.free_list,current_thread):#任务执行完成后设置该线程为空闲
61 if self.terminal:#如果是空闲的
62 event = StopEvent
63 else:
64 event = self.q.get()#如果不是空闲的,则去取任务
65 else:
66 self.generate_list.remove(current_thread)#如果任务为空则删除当前线程
67
68 def close(self):
69 '''
70 执行完所有任务后,所有线程停止
71 :return:
72 '''
73 self.cancel = True
74 full_size = len(self.generate_list)#统计线程个数
75 while full_size:#根据线程个数传入对应个数的False标志
76 self.q.put(StopEvent)
77 full_size -=1
78
79 def terminate(self):
80 """
81 无论是否还有任务,终止线程
82 """
83 self.terminal = True
84
85 while self.generate_list:
86 self.q.put(StopEvent)
87 self.q.empty()
88
89
90 @contextlib.contextmanager
91 def worker_state(self, state_list, worker_thread):
92 """
93 用于记录线程中正在等待的线程数
94 """
95 state_list.append(worker_thread)
96 try:
97 yield
98 finally:
99 state_list.remove(worker_thread)
100 pool = Pool(5)
101
102 def action():
103 pass
104 def callback(i):
105 print(i)
106 for i in range(300):
107 ret = pool.run(action,(i,),callback)#将函数i的值与callback函数传入类中





